PRMIA 8006 Exam I: Finance Theory Financial Instruments Financial Markets - 2015 Edition Exam Practice Test
Exam I: Finance Theory Financial Instruments Financial Markets - 2015 Edition Questions and Answers
Which of the following statements are true:
A and B are two stocks with normally distributed returns. The returns for stock A have a mean of 5% and a standard deviation of 20%. Stock B has a mean of 3% and standard deviation of 5%. Their correlation is -0.6. What is the mean and volatility of a portfolio which holds stocks A and B in the ratio 6:4?
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
Which of the following best describes a writer extendible option
A futures clearing house:
The theta of a delta neutral options position is large and positive. What can we say about the gamma of the position?
A borrower pays a floating rate on a loan and wishes to convert it to a position where a fixed rate is paid. Which of the following can be used to accomplish this objective?
I. A short position in a fixed rate bond and a long position in an FRN
II. An long position in an interest rate collar and long an FRN
III. A short position in a fixed rate bond and a short position in an FRN
IV. An interest rate swap where the investor pays the fixed rate
A stock has a spot price of $102. It is expected that it will pay a dividend of $2.20 per share in 6 months. What is the price of the stock 9 months forward? Assume zero coupon interest rates for 6 months to be 6%, for 9 months to be 7%, and 12 months to be 8% - all continuously compounded.
The rule that optimal portfolios will maximize the Sharpe ratio only applies when which of the following conditions is satisfied:
I. It is possible to borrow or lend any amounts at the risk free rate
II. Investors' risk preferences are fully described by expected returns and standard deviation
III. Investors are risk neutral
Using a single step binomial model, calculate the delta of a call option where future stock prices can take the values $102 and $98, and the call option payoff is $1 if the price goes up, and zero if the price goes down. Ignore interest.
Which of the following indicate a long position on the TED (treasury-Eurodollar) spread?
For a portfolio of equally weighted uncorrelated assets, which of the following is FALSE:
In the context of futures contracts traded on an exchange, the term 'open interest' refers to:
The price of a bond will approach its par as it approaches maturity. This is called:
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Protective puts are a form of insurance against a fall in prices
II. The maximum loss for an investor holding a protective put is equal to the decline in the value of the underlying
III. The premium paid on the put options held as a protective put is a loss if the value of the underlying goes up
IV. Protective puts can be a useful strategy for an investor holding a long position but with a negative short term view of the markets
Buying an option on a futures contract requires:
Using covered interest parity, calculate the 3 month CAD/USD forward rate if the spot CAD/USD rate is 1.1239 and the three month interest rates on CAD and USD are 0.75% and 0.4% annually respectively.
What is the running yield on a 6% coupon bond selling at a clean price of $96?
Which of the following expressions represents the Treynor ratio, where μ is the expected return, σ is the standard deviation of returns, rm is the return of the market portfolio and rf is the risk free rate:
A)
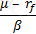
B)
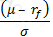
C)
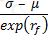
D)
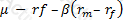
What would be the expected return on a stock with a beta of 1.2, when the risk free rate is 3% and the broad market index is expected to earn 8%?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. The convexity of a zero coupon bond maturing in 10 years is more than that of a 4% coupon bond with a modified duration of 10 years
II. The convexity of a bond increases in a linear fashion as its duration is increased
III. Convexity is always positive for long bond positions
IV. The convexity of a zero coupon bond maturing in 10 years is less than that of a 4% coupon bond maturing in 10 years
A)
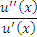
B)
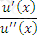
C)
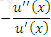
D)
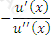
A currency with a lower interest rate will trade:
Which of the following is NOT an assumption underlying the Black Scholes Merton option valuation formula:
The quote for which of the following methods of physical delivery of a futures contract would be the cheapest?
For a stock that does not pay dividends, which of the following represents the delta of a futures contract?
Repos are used for:
I. Short term borrowings
II. Managing credit risk exposures
III. Money market operations by central banks
IV. Facilitating short positions
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Rebalancing frequency is a consideration for a risk manager when assessing the adequacy of delta hedging procedures on an options portfolio
II. Stock options granted to employees that are exercisable 5 years in the future will lead to a decline in the share price 5 years hence only if the options are exercised.
III. In a delta neutral portfolio, theta is often used as a proxy for gamma by traders.
IV. Vega is highest when the option price is close to the strike price
The vast majority of exchange traded futures contracts are:
A company has a long term loan from a bank at a fixed rate of interest. It expects interest rates to go down. Which of the following instruments can the company use to convert its fixed rate liability to a floating rate liability?
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
What is the current conversion premium for a convertible bond where $100 in market value of the bond is convertible into two shares and the current share price is $50?
It is October. A grower of crops is concerned that January temperatures might be too low and destroy his crop. A heating-degree-days futures contract (HDD futures contract) is available for his city. What would be the best course of action for the grower?
For a forward contract on a commodity, an increase in carrying costs (all other factors remaining constant) has the effect of:
A 15 year bond is trading at par. Its modified duration is 11 years and convexity is 80. Determine the price of the bond following a 10 basis point increase in interest rates
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Forward prices for a stock will fall if dividend expectations increase for the period the contract is alive
II. Three month forward prices will decline if the 10 year rate goes up, and short term rates stay unchanged
III. Futures exchanges require buyers but not sellers to deposit initial margins
IV. Variation margin is to be deposited when a futures contract is entered into
V. Futures exchanges requires hedgers and speculators to deposit identical margins
VI. Interest rate futures contracts carry duration but no convexity due to the daily cash settlements
The LIBOR square swap offers the square of the interest rate change between contract inception and settlement date. If LIBOR at inception is y, and upon settlement is x, the contract pays (x - y)2 for x > y; and -(x - y)2 for x < y.
What of the following cannot be a value of the gamma of this contract?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Cash markets tend to be more liquid than derivative markets
II. A higher credit risk is associated with lower liquidity in times of crises
III. A higher bid-ask spread indicates greater liquidity when compared to a lower bid-ask spread
IV. A higher normal market size indicates greater liquidity than a lower market size
If ∆, γ and Θ represent the delta, gamma and theta of any derivative whose value is V; r be the risk free rate; σ be the volatility and S the spot price of the underlying, which of the following equations will hold true? (Note that ∂ is the notation used for partial derivatives)
I. 202.21.q1
II. 202.21.q2
III. 202.21.q3
IV. 202.21.q4
Which of the following statements is true:
I. The OTC market for foreign exchange is much larger than the exchange traded futures market for foreign currencies
II. DVP arrangements help avoid the risk of counterparty defaults on settlements
III. Exchanges offer the advantage of lower trading costs than ECNs
IV. ISDA master agreements form the basis of a large number of OTC derivative trades
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT according to CAPM:
A normal yield curve is generally:
If the implied volatility is known for a call option, what can be said about the implied volatility for a put option with the same strike and maturity?
When considering an appropriate mix of debt and equity, Chief Financial Officers generally consider:
I. Tax advantage of debt
II. Financial distress costs
III. Agency costs of equity
IV. Retaining financial flexibility
The most risky tranche of a structured credit derivative is called:

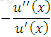 https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/102.07.a.png is the coefficient of risk aversion at x. Its inverse, ie
https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/102.07.a.png is the coefficient of risk aversion at x. Its inverse, ie 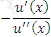 https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/102.07.b.png , is called the coefficient of risk tolerance.
https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/102.07.b.png , is called the coefficient of risk tolerance.