PMI PMI-RMP PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP) Exam Exam Practice Test
PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP) Exam Questions and Answers
A project manager for a predictive project just received a scope change request where additional development is required. What should the risk manager do to support the project manager with this scope change request?
During project execution for a software development program, a risk manager notices the results vary from the stated expectations in the planning phase. The project team states that there was unrealistic planning.
What should the risk manager do next to understand the differences between planning and execution?
A project team in a multinational organization is working on a risk management plan for a multimillion-dollar project. This project involves three global regions with a wide range of critical stakeholders with varying degrees of risk appetite.
What should the risk manager advise the project team to do?
The project manager leading a company's digital signature initiative for engineering drawings has identified threats and opportunities using a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) analysis.
What are two potential threats or opportunities under the SWOT analysis? (Choose two.)
A risk manager is confident that they have identified and quantified the risks and opportunities for a project. When presenting their work to management, on what areas should the risk manager focus? (Choose two.)
During the project's lifecycle, project risk managers must monitor any risks and address risk responses. What does this level of monitoring consist of?
A risk manager faces resistance as they try to implement the project's risk strategy. Some members of the project team believe it is a waste of time and money, What should the risk manager do?
A project team identified some risks in a project. Team members became interested in predicting the outcomes of their potential choices following their probability of occurrence.
Which technique should the risk manager use?
A risk manager and project team are managing a software system project, which is expected to be completed within 12 months. The project is currently halfway through, and the team has just delivered the second version of the prototype. During the weekly status meeting, a team member reported that an important stakeholder is facing an issue, which will likely result in a change request that is outside the scope of the current prototype.
What should the risk manager advise the team to do first?
Product testing can be done in multiple ways. A few project team members suggest testing be done in a laboratory environment, whereas others recommend completing the analysis via simu-lation methods. The testing manager has consulted with a peer, who recommends undertaking testing using field trials. The testing manager consults with the risk manager to assess the risk involved in the testing.
Which tool should the risk manager consider for assessing the test risk?
A project manager has requested the risk manager's support in deciding whether to purchase a new component to expedite project execution. The component price is US$100,000 and there is a 30% chance that it might not function as expected resulting in an additional US$50,000 cost However, if the component does work well the project will make a profit of USS500.000. If the component is not purchased, there is an 80% chance of failure with an impact of US$250 000.
What should the risk manager recommend?
The project manager reviews project risks with the risk manager to update, monitor, and close risks in the risk register. The project manager determines one of the risks has a residual risk.
How should the risk manager document the impact of the residual risk?
A risk manager manages risks in a construction project. A stakeholder mentions that if there is less than a 50% chance of rain, construction should continue. Another stakeholder says that if there is less than a 60% chance of rain, construction should continue.
What should the risk manager do next to find out the correct limit?
When selecting strategies as an activity of Plan Risk Response, what is the overall goal?
A project's design has been completed and approved on time. The construction subcontractor should be mobilizing to start construction but does not have the necessary materials in place, causing a delaying in the project. The risk register only contains risks for the design phase of the project.
What should the project manager have done differently?
A risk manager is reviewing documentation for a project following a risk planning workshop with project stakeholders and team members. Several items have been identified on the risk log that would be detrimental to project success, but the associated triggers cannot be managed by the organization and are unlikely to occur.
Which response should the risk manager recommend for these risk items?
A risk manager is conducting a qualitative risk analysis for a renewable energy project that faces tight deadlines. The team identifies risks such as weather unpredictability, material cost fluctuations, and potential regulatory delays. While some members advocate prioritizing high-likelihood risks, others emphasize addressing unlikely but high-impact risks.
What should the risk manager do?
A risk manager is working on the risk management plan for a new digital platform and realizes the project sponsor, who is the IT manager, has not been invited to the project team meetings. The IT manager is concerned that the IT infrastructure is unable to host the new platform the team is creating. The risk manager asks the IT manager to be included in the meetings.
What should the IT manager's role be in the project team meetings?
A project team has just initiated a large project to move an organization's headquarters to another location. The risk manager has scheduled a risk identification session but notices that the project charter, work breakdown structure (WBS). and scope statement are not available.
What should the risk manager consider?
A risk manager and relevant stakeholders have completed a risk response plan for a project. They have identified and planned responses to the known risks; however, a risk owner has identified and reported some residual risks not previously addressed.
What should the risk manager do first?
An organization with a portfolio of unique business functions kicks-off a performance improvement project across the entire organization. There are a large number of stakeholders the project team will need to consider during risk identification.
What three actions should the risk manager ensure the project team performs during risk identification? (Choose 3)
The risk manager conducted an updated Monte Carlo simul-ation for the project at the end of a phase. The simul-ation reveals a key activity is now on the critical path.
What recommendation should the risk manager make to the project manager?
A new company initiates a project to incorporate a cybersecurity team. Which three documents should the risk manager analyze first? (Choose 3)
During a meeting to develop the risk management plan, the risk manager recognizes that risks may be identified that could also impact other projects that the company is pursuing. What should the risk manager do?
During a virtual workshop presenting a product to potential clients, a facilitator emails the product brochure and asks attendees to check their spam folder if the email does not appear in their inbox. What kind of threat strategy is the facilitator applying?
A risk manager is managing risks of a mission critical application. A subject matter expert (SME) asks the risk manager to treat every single risk identified as an extremely high priority.
What should the risk manager do?
A project team is leading a software development project. During the project kickoff meeting, the risk manager discovers that a vendor has not finalized the timeline for delivering an essential component. This creates uncertainty in the overall project schedule.
What should the risk manager do to address the risk?
A risk manager for a hospital extension project is leading a project team in developing a risk management plan. One team member is responsible for conducting risk identification. The team member just joined the team and is struggling to ensure the coverage of all risks that might arise in this complex project.
How should the risk manager address this concern?
A project manager has just been assigned to a new project. The project manager has been tasked by the project sponsor to ensure the project risks are closely managed. The project manager starts with developing the risk management plan.
What is the expected outcome of developing the risk management plan?
During a meeting with a project team, a project manager asks a risk manager to determine the risk events that could potentially have the most impact on a 2-year project with a budget of US$800 000. Which approach should the risk manager suggest the project manager take?
A risk manager has been assigned to replace a risk manager on sick leave. The new risk manager notices that the risk register is missing data that are key to the risk management process.
Which data will the risk manager require first?
A risk manager wants to determine what risk has the biggest impact on project cost. The risk manager identified three risks, which could occur in different phases of the project.
What should the risk manager do first to understand the impact on project cost?
An organization performs an annual strategies and initiatives workshop during which a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) analysis is being conducted. As part of this process the functional managers identify the opportunities and threats.
What should the risk manager do next?
A risk management team has completed a quantitative analysis, and the individual score in terms of schedule and cost has been identified. The team is consolidating inputs for contingency planning and notices that the available time and funds are not sufficient for all the risks.
What should the risk manager advise the project team?
An organization faces immense competition in the market and decides to accelerate a key project. What is the first action for the project risk manager to take?
During a risk reassessment workshop with the project team and some external stakeholders, two key external stakeholders are overemphasizing the impact of a few project risks. This has led to a conflict.
How should the risk manager handle this situation?
A company manages confidential customer information, and a data breach exposing sensitive information was discovered. What should the risk manager do?
The project manager asks the risk manager to determine the initial risk assessment for a six month initiative that is about to kick-off. Which two artifacts will help the risk manager conduct the related analysis? (Choose two.)
The risk manager loaded the risk register, built the risks into the simul-ation software, and ran the Monte Carlo analysis. The P80 and P90 end dates are the same as the deterministic date.
What should be the risk manager's next step?
As part of standard procedure to monitor and control a project, a risk manager should constantly update the risk register. The risk register updates should include information on risk reassessment, risk audits, and periodic risk reviews.
What additional information should the risk manager prioritize in the risk register updates?
While performing risk identification exercises, the risk manager often encounters biases from the project team. How can the risk manager accurately identify what will trigger a risk?
A financial service firm adheres to heavily regulated compliance legislation. During the firm's latest project, the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) and the Chief Information Officer (CIO) endorsed a risk-based approach. This approach ensured compliance with the legislative requirements for properly storing confidential employee salary information. The risk manager recorded this information in the project's risk management plan.
What is the organization's risk maturity level?
A risk manager is assigned to a new system deployment project with a strict contractually agreed-on schedule. One of the key risks identified is the availability of experts because many are shared on other strategic projects in the organization.
What should the risk manager do to address this situation?
During a brainstorming session, a stakeholder identifies a risk that, if realized, could greatly impact their team. The stakeholder insists that this particular risk should be
mitigated to the greatest extent possible, however, the majority of other stakeholders feel that different risks have higher probabilities of occurring.
Which action should the risk manager take to address this risk?
Stakeholder deliverable reviews will start soon and additional work is expected to resolve any issues or required adjustments. Budget overruns during execution have put serious constraints on the remainder of the project's budget.
What should the project manager do next?
What should the risk owner use as an effective information-gathering technique during the planning session?
The risk manager of a major project needs to ensure the organizational process assets (OPAsj are updated as a result of risk management activities. How will the risk manager accomplish this?
Project stakeholders can often be risk averse with little to no knowledge of the risk process. How should a risk manager increase stakeholder risk appetite?
A risk management professional is currently facilitating the risk planning process with the project team. To increase the breadth of considered risks, the team wants to include high-level and strategic project risks.
What should the risk management professional do next?
A project team is concerned about a risk which, if occurs, might add additional complexity to their work. The team will need help from an external vendor, but the contracting process is long.
What should the risk manager do in this case?
In the middle of a construction project, the primary construction materials provider canceled the contract and moved to a competitor offering a higher price. The risk manager considers
this a low-impact issue because many construction materials providers can fulfill the project demands. However, after informing the stakeholders of this issue, the major investor is about
to drop their intention to continue executing the project. The risk manager does not understand their decision.
What should the risk manager do next to understand the major stakeholder's decision regarding the project?
A project manager is working on a construction project. Based on past experience, the project manager identifies a risk that a supplier of a critical material may not deliver on time. The project manager has already accounted for this risk in the risk management plan. If this risk materializes, the project manager plans to procure the material from a different supplier. A potential risk in this plan is that there may be differences in the material provided by the first and second supplier.
What type of risk is this?
A project manager managing a high-risk rating project was just informed that one of the key project resources has decided to leave the organization. The project manager asks the risk manager for their recommendations. The risk manager previously identified this as a risk and had created a transition plan to enable another resource to carry out the same duties. The risk manager was informed that by transitioning the responsibilities to the new resource, new risks to the completion dates of other project-related tasks appear.
What should the risk manager advise the project manager?
In a highly dynamic project environment, the project manager is known to have project risks as a permanent agenda item in their periodic project progress meetings. How will this help improve the project's risk management activities? (Choose 3)
A newly assigned risk manager realizes that a project has unrealistic funding and low resources. Which document should the risk manager review?
An experienced and the only developer on a software implementation project will be on leave for several weeks. The risk of this critical resource's availability was added to the risk register. Contingencies were made for a support developer to job shadow this resource, depending on how things go prior to their leave. The project team was pleased with the backup plan and the new resource was able to shadow for a few weeks.
What should the risk manager do next?
A project manager wants to introduce a new technology to improve a project's performance. However, there are some costs associated that are beyond the current budget, and the proposed technology has not been applied to any previous company projects.
What should the project manager do in this situation?
The project sponsor asks the project manager about the accuracy of the project data. The project manager realizes that some risks have not been updated recently.
What should the project manager do regarding those risks?
In a project to promote public health and mitigate health risks, the national health authorities intend to take actions to limit the risks of harmful insects by using pesticides; however, it is expected that some residents will have negative health effects due to the use of the pesticides but according to the assessment completed by the health authorities, not moving forward with this plan will have much more serious consequences on public health rather than following through with the original plan.
How should the project manager address this concern with the health authorities?
A project to deploy a new technology in field offices across the country has just been initiated. Some stakeholders are not supportive of this project because their teams will potentially be impacted by staff reductions once the technology is implemented.
How should the risk manager address this concern?
A project team is discussing which risk requires more attention and resources for response planning. The team evaluated the schedule to determine which activity had the greatest impact on the project's total duration.
After analyzing the quantitative analysis results, which activity should the team pay more attention to?
Use the chart for the analysis.
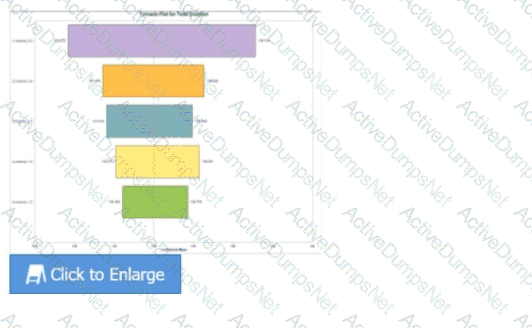
A key project is delayed and all contingency reserves have been used even though the project team has implemented all planned risk responses. What should the risk manager do next?
The risk manager is facilitating risk planning activities with the team. The team is documenting all the check points along the way that might indicate delays on critical deliverables.
What is this an example of?
A project team does not understand why a very low probability risk occurred during project execution. The team was especially vigilant about planning for this type of risk during the risk planning phase. The project has been delayed by 2 months, and the stakeholders are considering canceling the project. The risk manager needs to demonstrate that the project can be concluded.
Which analysis should the risk manager perform to demonstrate this to the stakeholders'?
The sponsor of a construction project is upset about the results of the risk management team. The sponsor believes the team did not properly identify the risks that could affect the project. The team did manage the risks; however, some of the risk response strategies created secondary risks.
What should the risk management team have done to manage this situation?
Several key stakeholders approach the project manager with concerns. The stakeholders have received feedback from local businesses that have reported a reduction in customers because of construction activities at the worksite, and they plan to submit a claim to the municipality to fine the project manager's company.
How should the project manager address this concern?
Upon reviewing the risk analysis results, the project manager notices several risks that occur more frequently than others. What should the project manager do?
An organization is executing two projects — Project A and Project B — simultaneously. A previously identified risk will impact the schedule for Project A. While executing the mitigation plan, a number of residual risks are identified that could provide cost savings for Project B.
Which action should the risk manager for Project A take?
The risk manager also serves as a facilitator for a project and realizes the project team members have biases impacting how they perceive risks. What analysis is currently being used?
A new risk manager has been hired on a project and meets with the project director. The project director supplies the project's risk register and asks the risk manager for an analysis of its effectiveness.
What two actions should the risk manager do next? (Choose two.)
At an oil and gas company, a major unified management information system is to be implemented. The project manager noted that risks gathered from the organization's business functions are not properly identified and categorized, making it difficult to develop an effective risk response.
How should the project manager handle this situation?
During the construction of a housing development, a project team realizes they exceeded their materials budget during the first of three execution stages. The risk manager observed that the team did not notice that the cost of the materials increased due to continuous inflation in the steel market.
What could have been done during project planning to avoid overspending?
An organization is embarking on a multi-million-dollar project with numerous identified risks. What should the project risk team do to navigate the risks on this project?
A project manager has finished the project charter for a project and has now moved into the planning phase. In the first planning meeting, the project manager is trying to determine the risk tolerance and risk attitudes of the project's key stakeholders.
What is the first resource the project manager should reference?
During the monthly executive review meeting, the project sponsor would like to understand how the project team has planned to manage risks that were identified in the last meeting. What should the project manager do?
A risk manager has been assigned to prepare a risk management plan for a new project. Which factor should the risk manager prioritize when tailoring the risk management processes for the new project?
A highly complex project is about to start Considering that many changes and new information will arise as the work moves forward, key stakeholders are anxious about not addressing risks on time
What should the risk manager do in this situation?
A risk manager for a financial organization is assigned to support a project team in developing a custom software solution to manage loans. Which document should the risk manager request first from the project sponsor to identify major risks?
The risk manager for a large-scale software development project with a tight deadline and multiple stakeholders highlights concerns about potential delays, communication gaps, and vendor reliability. During the early stages of the project, the project sponsor requests that the risk manager identify and address any potential risks that could disrupt project delivery.
What should the risk manager do?
