Nokia 4A0-116 Nokia Segment Routing Exam Exam Practice Test
Nokia Segment Routing Exam Questions and Answers
Which of the following statements about enabling and using traffic engineering for Segment Routing is FALSE?
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of using a PCE for the computation of TE-constrained LSP paths, as compared to using CSPF locally on the PE router?
Which of the following statements about segment routing fast re-route is FALSE?
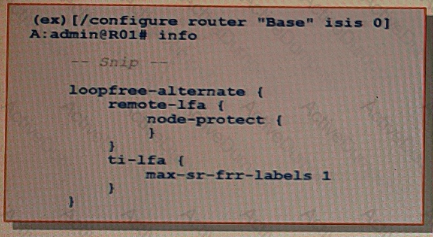
The exhibit shows the fast re-route configuration on router R1, in which both R-LFA and TI-LFA have been enabled. Assume that there are multiple potential backup paths for a given prefix. Which of the following options will router R1 use?
Which of the following statements about Segment Routing tunnels is FALSE?
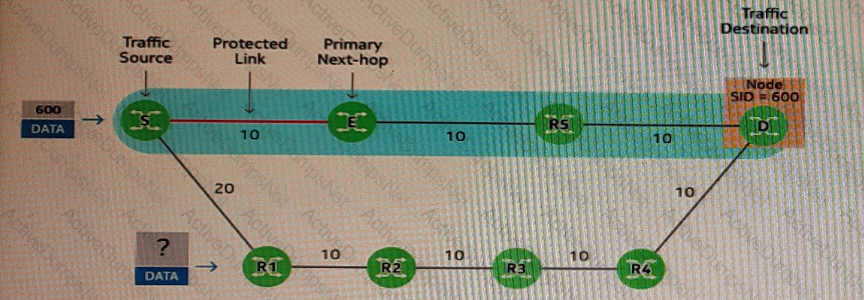
The exhibit highlights in blue the primary path of a segment going from router S to router D. The exhibit also shows a backup path. The protected link fails and fast re-route is triggered on router S. If the backup path has been calculated using standard LFA, how many SIDs are included in the label stack of the data packet forwarded to router R1?