National Payroll Institute PF1 Payroll Fundamentals 1Exam Exam Practice Test
Payroll Fundamentals 1Exam Questions and Answers
Anne Massy works for Liberty Promotions in Nunavut and is provided with a company-leased automobile. The automobile was in Anne’s possession for 365 days. Of the 34,134 kilometres driven, 15,805 kilometres were for business purposes. The monthly lease cost of the vehicle was $198.60, excluding GST calculated at 5%. Anne requested in writing that Liberty Promotions use the optional operating cost method if all conditions apply. She did not reimburse the company for any of the expenses associated with the automobile. Calculate Anne’s annual automobile taxable benefit.
(PF1 Exam – Net Pay Calculation Template Worksheet: Quebec)
Question ID: pf1-exam-npc-q-f
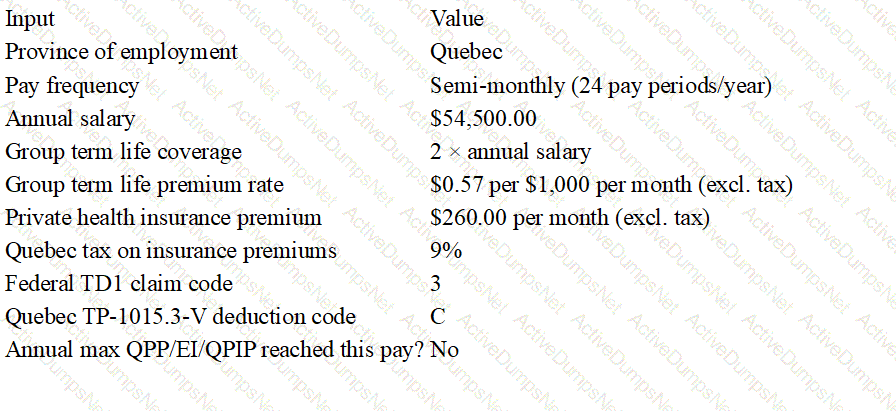
Mara Poirier works for Affordable Transport in Quebec and earns an annual salary of $54,500.00, paid on a semi-monthly basis.
In addition to her regular salary, Mara’s employer provides the following benefits:
Group term life insurance coverage through a third party of two times her annual salary.
Monthly group term life insurance premiums are $0.57 per $1,000.00 of coverage, excluding taxes.
Private health insurance benefits with a monthly premium of $260.00, excluding taxes.
The tax on insurance premiums in Quebec is 9%.
Mara’s federal TD1 claim code is 3 and her provincial TP-1015.3-V deduction code is C.
Mara will not reach the annual maximums for QPP, EI, or QPIP in this pay period.
Required: Calculate Mara’s net pay, following the order of the steps in the net pay template.
EXHIBIT A — Net Pay Template (Fill in all blanks)
Earnings / Income Bases


Step 1 — Calculate Mara’s gross earnings for this pay period (GTE).
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Step 2 — Calculate the pensionable earnings (PE).
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Step 3 — Calculate the insurable earnings (IE).
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Step 4 — Calculate the net taxable income (CRA) (NTI).
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Step 5 — Calculate the net taxable income (RQ) (NTI).
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Step 6 — Calculate Mara’s Quebec Pension Plan (QPP) contribution.
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Step 7 — Calculate Mara’s Employment Insurance (EI) premium.
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Step 8 — Calculate Mara’s Quebec Parental Insurance Plan (QPIP) premium.
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Step 9 — Determine Mara’s federal income tax.
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Step 10 — Determine Mara’s Quebec provincial income tax.
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Step 11 — Calculate Mara’s total deductions.
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Step 12 — Calculate Mara’s net pay.
[ ____________________________________________ ]
Helen is reimbursed for the cost of the protective clothing that is legally required for her job. The clothing she bought isnot supported by receiptsand is a reasonable reimbursement amount. This is considered:
Paula is granted a pay increase. The paperwork informing the payroll department of the pay increase is two pay periods late. What method would be used to calculate income taxes on the separate retroactive payment?
Dollar values attributed to something the employer has either provided to an employee or paid for on an employee’s behalf are:
Which of the following types of earnings are not considered income from employment?
Ursula is 17 years old, works in Quebec and earns $750.00 weekly. Ursula pays weekly union dues of $18.00 along with a special weekly union assessment of $10.00 for construction of a new union hall for its members. Ursula also has registered pension plan (RPP) contributions of $20.00 deducted from each pay. Calculate Ursula’s net federal taxable income.
A paper Record of Employment must be issued:
An interruption of earnings occurs when there is a period of how many days with no insurable earnings?
The formula for calculating net pay is:
When is the government-prescribed rate of interest set?
The authorization for hiring form should contain a checklist to ensure the organization obtains all required information. What is an example of an item that could be on that checklist?
Which of the following types of payments made by a private organization would not be subject to all statutory deductions?
A premium payment for overtime hours worked or a rate per piece of goods produced is an example of:
By the authority of which Act can the Canada Revenue Agency garnish the wages of an employee who has failed to pay Employment Insurance premiums, Canada Pension Plan contributions, or income tax deductions?
Jasmine works for a Saskatchewan employer and earns $500.00 weekly. Calculate her Employment Insurance (EI) premium.
The amount of notice the employer must give an employee depends on:
A Third Party Demand is issued by the Canada Revenue Agency for:
A death benefit is a:
A 900-series Social Insurance Number is issued to:
Feraz Dalia is due $12,523.00 in legislated wages in lieu of notice that will be added to his last weekly pay of $1,080.00. Calculate Feraz’s Employment Insurance (EI) premium, if his employer is situated in Saskatchewan and the yearly maximum contribution will not be exceeded.
