NCC EFM Certified - Electronic Fetal Monitoring Exam Practice Test
Certified - Electronic Fetal Monitoring Questions and Answers
A fetus displays a baseline heart rate of 125 beats per minute with moderate variability. During a contraction, the baseline rate drops abruptly to 80 beats per minute with gradual return to baseline over 90 seconds. This is classified as:
Upon admission, the clinician discusses indications, risks, and benefits of electronic fetal monitoring. This reflects which ethical concept?
A key differentiating factor when determining if a deceleration is early or late is the
A woman who is one week past a confirmed due date has serial ultrasounds to determine:
When fetal arterial blood pressure increases, the baroreceptors send impulses to the vagus nerve resulting in:
A fetal heart rate pattern characteristic of fetal neurological injury and impending intrapartum fetal demise is:
Maternal-fetal oxygen transfer takes place in the:
Amnioinfusion can cause what changes in the fetal heart rate tracing?
This fetal heart rate tracing represents:

Maternal–fetal exchange during labor is diminished by:
The ratio of oxyhemoglobin to the total amount of hemoglobin available is called oxygen
A woman at 38-weeks gestation is admitted to labor and delivery following a fall down the stairs three hours ago. She started feeling contractions in the ambulance. The fetal heart rate tracing shown is on initial evaluation and represents 25 minutes. This tracing is most consistent with a

During amnioinfusion, the infusion should be stopped periodically to assess changes in:
A 30-minute tracing with moderate variability, accelerations, and one variable deceleration would be classified as:
The main reason intrauterine pressure catheters are placed is to:
The presence of fetal breathing movements on a biophysical profile reflects adequate:
An internal electronic fetal monitor tracing continues to record artifact despite equipment troubleshooting and replacement of the spiral electrode. The next action is to:
A woman is admitted to labor and delivery with vaginal bleeding. This tracing is obtained. This is most consistent with:

When accelerations precede a variable deceleration pattern, this is caused by
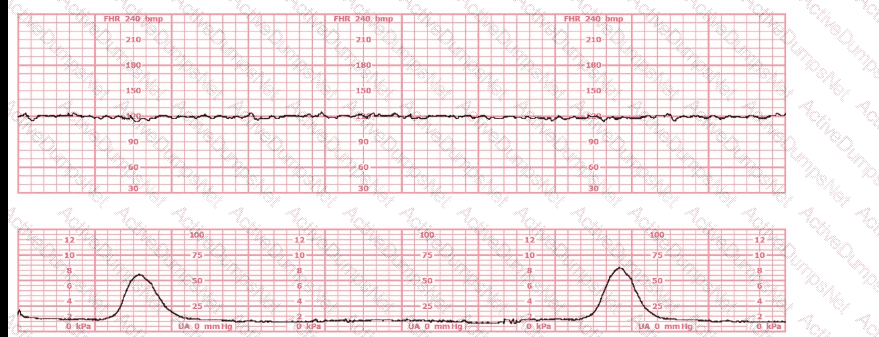
This tracing reflects:
The most highly oxygenated blood in the fetal circulation is found in the
Patient safety is enhanced when alarms:
A sentinel or reportable event as defined by the Joint Commission or other regulatory bodies/agencies is one that
The duration of a contraction is best represented by which colored arrow?

Maternal conditions of autoimmunity can result in fetal heart block due to antibodies that target:
This is a tracing of a multiparous woman in the second stage of labor. The vertex is at +3 station. This pattern has continued for the last 20 minutes. She has been pushing for 2½ hours, and oxytocin is infusing at 12 milliunits/minute. Management should include

When monitoring monochorionic-monoamniotic twins, which of the following fetal heart rate patterns would be anticipated?
A characteristic of early decelerations is that they
The factor that differentiates a prolonged deceleration from bradycardia is:
(Full question statement)
Interobserver reliability in interpretation of fetal heart rate tracings is greatest when the tracing is:
(Full question statement)
A dysrhythmia is noted. The pregnancy and labor course has been normal with no complications. The next step in management is to
Maternal fever can cause fetal tachycardia because the increased maternal temperature:
The tracing shown is from a woman at 28-weeks gestation in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) after an appendectomy. She is alert and awake. Based on this fetal heart rate pattern, the most appropriate intervention is:

An electronic fetal monitoring factor that best correlates with fetal well-being is:
In the event of recurrent variable decelerations with thick meconium, amnioinfusion is recommended to:
(Full question statement)
Recurrent decelerations are defined as occurring with 50% or more of contractions in any window of how many minutes?
A woman reports 12 fetal movements over one hour. The best recommendation is to:
