Linux Foundation CKS Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS) Exam Practice Test
Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS) Questions and Answers
Context
A default-deny NetworkPolicy avoids to accidentally expose a Pod in a namespace that doesn't have any other NetworkPolicy defined.
Task
Create a new default-deny NetworkPolicy named defaultdeny in the namespace testing for all traffic of type Egress.
The new NetworkPolicy must deny all Egress traffic in the namespace testing.
Apply the newly created default-deny NetworkPolicy to all Pods running in namespace testing.

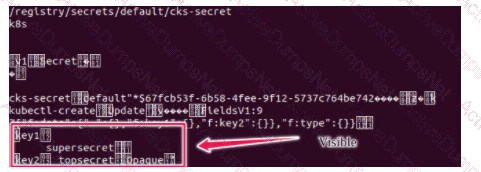
Secrets stored in the etcd is not secure at rest, you can use the etcdctl command utility to find the secret value
for e.g:-
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl get /registry/secrets/default/cks-secret --cacert="ca.crt" --cert="server.crt" --key="server.key"
Output
Using the Encryption Configuration, Create the manifest, which secures the resource secrets using the provider AES-CBC and identity, to encrypt the secret-data at rest and ensure all secrets are encrypted with the new configuration.
Context
You must implement auditing for the kubeadm provisioned cluster.
Task
First, reconfigure the cluster 's API server, so that:
. the basic audit policy located at
/etc/kubernetes/logpolicy/audit-policy.yaml is used,
. logs are stored at /var/log/kubernetes/audit-logs.txt,
. and a maximum of 2 logs are retained for 10 days.
The cluster uses the Docker Engine as its container runtime . If needed, use the docker command to troubleshoot running containers.
The basic policy only specifies what not to log.
Next, edit and extend the basic policy to log:
. namespaces interactions at RequestResponse level
. the request body of deployments interactions in the namespace webapps
. ConfigMap and Secret interactions in all namespaces at the Metadata level
. all other requests at the Metadata level
Make sure the API server uses the extended policy.
Failure to do so may result in a reduced score.
You must complete this task on the following cluster/nodes: Cluster: immutable-cluster
Master node: master1
Worker node: worker1
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context immutable-cluster
Context: It is best practice to design containers to be stateless and immutable.
Task:
Inspect Pods running in namespace prod and delete any Pod that is either not stateless or not immutable.
Use the following strict interpretation of stateless and immutable:
1. Pods being able to store data inside containers must be treated as not stateless.
Note: You don't have to worry whether data is actually stored inside containers or not already.
2. Pods being configured to be privileged in any way must be treated as potentially not stateless or not immutable.
You must complete this task on the following cluster/nodes:
Cluster: trace
Master node: master
Worker node: worker1
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context trace
Given: You may use Sysdig or Falco documentation.
Task:
Use detection tools to detect anomalies like processes spawning and executing something weird frequently in the single container belonging to Pod tomcat.
Two tools are available to use:
1. falco
2. sysdig
Tools are pre-installed on the worker1 node only.
Analyse the container’s behaviour for at least 40 seconds, using filters that detect newly spawning and executing processes.
Store an incident file at /home/cert_masters/report, in the following format:
[timestamp],[uid],[processName]
Note: Make sure to store incident file on the cluster's worker node, don't move it to master node.
Create a new ServiceAccount named backend-sa in the existing namespace default, which has the capability to list the pods inside the namespace default.
Create a new Pod named backend-pod in the namespace default, mount the newly created sa backend-sa to the pod, and Verify that the pod is able to list pods.
Ensure that the Pod is running.
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context test-account
Task: Enable audit logs in the cluster.
To do so, enable the log backend, and ensure that:
1. logs are stored at /var/log/Kubernetes/logs.txt
2. log files are retained for 5 days
3. at maximum, a number of 10 old audit log files are retained
A basic policy is provided at /etc/Kubernetes/logpolicy/audit-policy.yaml. It only specifies what not to log.
Note: The base policy is located on the cluster's master node.
Edit and extend the basic policy to log:
1. Nodes changes at RequestResponse level
2. The request body of persistentvolumes changes in the namespace frontend
3. ConfigMap and Secret changes in all namespaces at the Metadata level
Also, add a catch-all rule to log all other requests at the Metadata level
Note: Don't forget to apply the modified policy.

Context
You must resolve issues that a CIS Benchmark tool found for the kubeadm provisioned cluster.
Task
Fix all issues via configuration and restart the affected components to ensure the new settings take effect.
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the kubelet:
The cluster uses the Docker Engine os its container runtime, If needed, use the
docker command to troubleshaot running containers.
Ensure that the anonymous-auth argument is set to false FAIL
Ensure that the -authorization-mode argument is not set to FAIL
AlwaysAllow
Use Webhook authentication /authorization where possible.
Fix all of the following violations that were found against ettd :
Ensure that the -client cert auth argument is set to true FAIL
a. Retrieve the content of the existing secret named default-token-xxxxx in the testing namespace.
Store the value of the token in the token.txt
b. Create a new secret named test-db-secret in the DB namespace with the following content:
username: mysql
password: password@123
Create the Pod name test-db-pod of image nginx in the namespace db that can access test-db-secret via a volume at path /etc/mysql-credentials
Create a Pod name Nginx-pod inside the namespace testing, Create a service for the Nginx-pod named nginx-svc, using the ingress of your choice, run the ingress on tls, secure port.

Context
Your organization’s security policy includes:
ServiceAccounts must not automount API credentials
ServiceAccount names must end in "-sa"
The Pod specified in the manifest file /home/candidate/KSCH00301 /pod-m
nifest.yaml fails to schedule because of an incorrectly specified ServiceAccount.
Complete the following tasks:
Task
1. Create a new ServiceAccount named frontend-sa in the existing namespace qa. Ensure the ServiceAccount does not automount API credentials.
2. Using the manifest file at /home/candidate/KSCH00301 /pod-manifest.yaml, create the Pod.
3. Finally, clean up any unused ServiceAccounts in namespace qa.
use the Trivy to scan the following images,
1. amazonlinux:1
2. k8s.gcr.io/kube-controller-manager:v1.18.6
Look for images with HIGH or CRITICAL severity vulnerabilities and store the output of the same in /opt/trivy-vulnerable.txt
Analyze and edit the given Dockerfile
FROM ubuntu:latest
RUN apt-get update -y
RUN apt-install nginx -y
COPY entrypoint.sh /
ENTRYPOINT ["/entrypoint.sh"]
USER ROOT
Fixing two instructions present in the file being prominent security best practice issues
Analyze and edit the deployment manifest file
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: security-context-demo-2
spec:
securityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
containers:
- name: sec-ctx-demo-2
image: gcr.io/google-samples/node-hello:1.0
securityContext:
runAsUser: 0
privileged: True
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
Fixing two fields present in the file being prominent security best practice issues
Don't add or remove configuration settings; only modify the existing configuration settings
Whenever you need an unprivileged user for any of the tasks, use user test-user with the user id 5487
Service is running on port 389 inside the system, find the process-id of the process, and stores the names of all the open-files inside the /candidate/KH77539/files.txt, and also delete the binary.
On the Cluster worker node, enforce the prepared AppArmor profile
#include
profile nginx-deny flags=(attach_disconnected) {
#include
file,
# Deny all file writes.
deny /** w,
}
EOF'
Edit the prepared manifest file to include the AppArmor profile.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: apparmor-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: apparmor-pod
image: nginx
Finally, apply the manifests files and create the Pod specified on it.
Verify: Try to make a file inside the directory which is restricted.
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context dev
Context:
A CIS Benchmark tool was run against the kubeadm created cluster and found multiple issues that must be addressed.
Task:
Fix all issues via configuration and restart the affected components to ensure the new settings take effect.
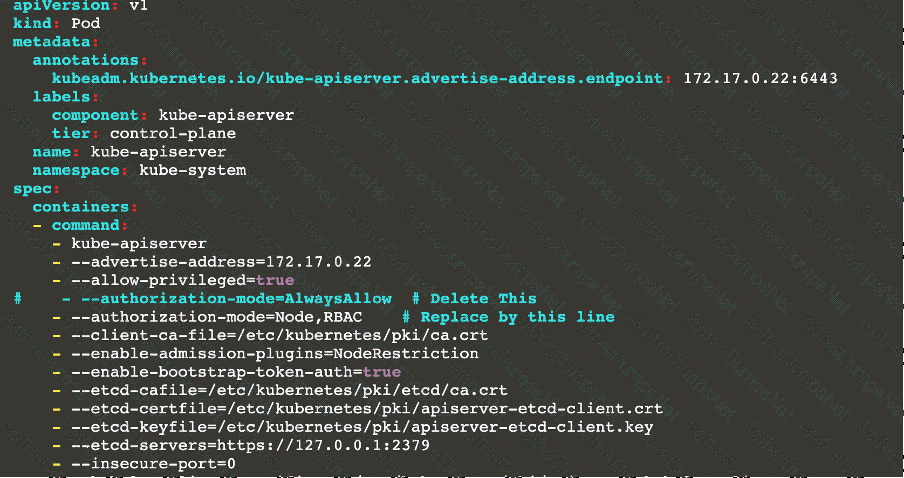
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the API server:
1.2.7 authorization-mode argument is not set to AlwaysAllow FAIL
1.2.8 authorization-mode argument includes Node FAIL
1.2.7 authorization-mode argument includes RBAC FAIL
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the Kubelet:
4.2.1 Ensure that the anonymous-auth argument is set to false FAIL
4.2.2 authorization-mode argument is not set to AlwaysAllow FAIL (Use Webhook autumn/authz where possible)
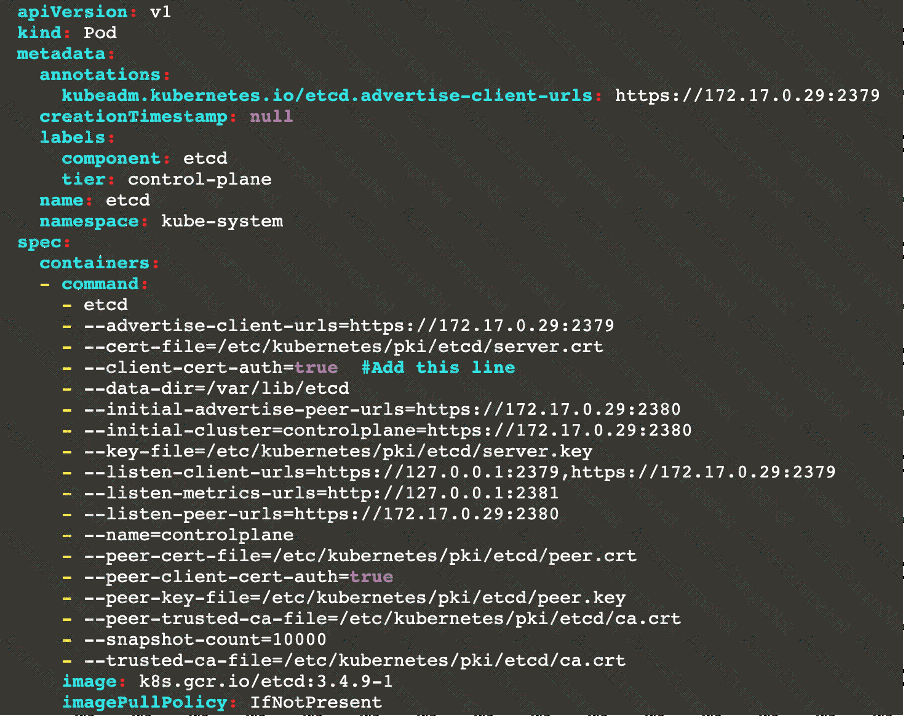
Fix all of the following violations that were found against etcd:
2.2 Ensure that the client-cert-auth argument is set to true
Documentation dockerd
You must connect to the correct host . Failure to do so may result in a zero score.
[candidate@base] $ ssh cks000037
Task
Perform the following tasks to secure the cluster node cks000037 :
Remove user developer from the docker group.
Do not remove the user from any other group.
Reconfigure and restart the Docker daemon to ensure that the socket
file located at /var/run/docker.sock is owned by the group root.
Re-configure and restart the Docker daemon to ensure it does not listen on any TCP port.
After completing your work, ensure the Kubernetes cluster is healthy.
Create a User named john, create the CSR Request, fetch the certificate of the user after approving it.
Create a Role name john-role to list secrets, pods in namespace john
Finally, Create a RoleBinding named john-role-binding to attach the newly created role john-role to the user john in the namespace john.
To Verify: Use the kubectl auth CLI command to verify the permissions.
Given an existing Pod named nginx-pod running in the namespace test-system, fetch the service-account-name used and put the content in /candidate/KSC00124.txt
Create a new Role named dev-test-role in the namespace test-system, which can perform update operations, on resources of type namespaces.
Create a new RoleBinding named dev-test-role-binding, which binds the newly created Role to the Pod's ServiceAccount ( found in the Nginx pod running in namespace test-system).