IAM IAM-Certificate The Institute of Asset Management Certificate Exam Practice Test
The Institute of Asset Management Certificate Questions and Answers
In what year did the term "asset management" start to be used?
Which of the following statements isnota management asset?
The objectives that the organization wants to achieve from its asset management activities, are ....
A definition of asset management is:
Assurance is the combination of monitoring and control (of processes and outcomes) to confirm the assets, systems and processes are operating as intended.
What is the purpose of whole-life cost analysis?
Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements best describes the difference between an Asset Management Policy and an Asset Management Strategy?
To successfully establish, operate and improve asset management within an organisation, it is essential that leadership, and commitment, is demonstrated by all levels of management – from senior executives to supervisors.
What are the main cost elements of a whole-life cost approach?
What is NOT usually considered in the decision to decommission and dispose of assets?
There are many factors that can drive the decommissioning of assets,except:
A policy is best defined as...
External stakeholders can influence asset management activities within an organisation by:
A change of maintenance contractor for an operational system is being proposed. Which of the following processes should be applied?
This covers everything that goes into planning, designing, and procuring an asset.
Which of the following requirements would you expect to find included within an Asset Management Strategy?
The benefits of an asset management system are...
A public transportation company has a fleet of 150 trams. Type A (25 years old), Type B (19 years), Type C (2 years). Expected lifetime is 30 years. Type A and B perform sufficiently but suffer obsolescence and spare parts issues.
What would be a feasible action now?
Ignoring the time-based value of money, in Whole Life Cost Modelling, annualised costs are:
Risk is best described as:
Vou ate presenting an 'Introduction lo good Asset Management' workshop. A member of the audience asks you to draw a simple diagram that best describes the three main parameters Involved in good practice Risk Management. Which of the following diagrams are you most likely to draw?
A)
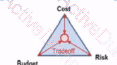
B)
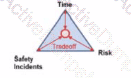
C)

D)
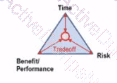
E)
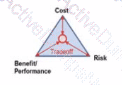
Which of the following is NOT normally an input to an asset management plan?
The term optimizing describes:
The following things are taken into consideration in developing an asset management strategy,except:
How is risk best quantified within an ISO 55001 compliant Asset Management System?
Asset Management is explicitly focused on helping organisations to achieve their defined objectives and to determine the optimal blend of activities based on these objectives.
