- Home
- Huawei
- HCIA-Cloud Computing
- H13-511_V5.5
- H13-511_V5.5 - HCIA-Cloud Computing V5.5 Exam
Huawei H13-511_V5.5 HCIA-Cloud Computing V5.5 Exam Exam Practice Test
HCIA-Cloud Computing V5.5 Exam Questions and Answers
Which of the following statements is false about concepts of virtualization?
Options:
A guest OS is the OS running on a virtual machine (VM).
A host machine is a physical machine.
A host OS is the virtualization software layer.
A guest machine is a VM.
Answer:
CExplanation:
In the "Virtualization Basics" section of the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing training material, the taxonomy of virtualization components is strictly defined. Statement C is FALSE because the virtualization software layer is technically called the Hypervisor or Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM), not the "Host OS." While a "Host OS" exists in Type-2 (hosted) virtualization (where the hypervisor runs as an application on top of an existing OS like Windows or Linux), the software layer that actually performs the resource abstraction and logical partitioning is the Hypervisor itself.
The other definitions are central to Huawei's technical documentation. AGuest OS(Statement A) is indeed the operating system—such as Windows Server or Ubuntu—that is installed inside a Virtual Machine. It is "unaware" that it is running on virtual hardware. TheHost Machine(Statement B) refers to the underlying physical server (e.g., a Huawei FusionServer Pro) that provides the actual CPU, RAM, and physical NICs. Finally, aGuest Machine(Statement D) is a synonym for a Virtual Machine (VM), representing the logical container that houses the Guest OS and applications.
In a Type-1 virtualization architecture (like HuaweiFusionCompute), the Hypervisor (CNA) sits directly on the hardware. In this scenario, there is no "Host OS" at all, further proving why statement C is incorrect. The Hypervisor is responsible for trapping "privileged instructions" from the Guest OS and translating them into actions on the physical hardware. Correctly identifying these roles—Host Machine, Hypervisor, and Guest VM—is a prerequisite for understanding more advanced cloud features like Resource Clusters and Distributed Resource Scheduling (DRS).
Match the emerging technologies with their respective features or application scenarios
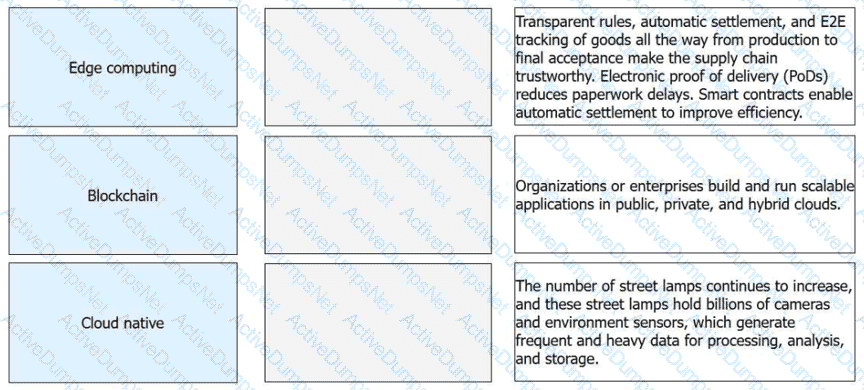
Options:
Answer:
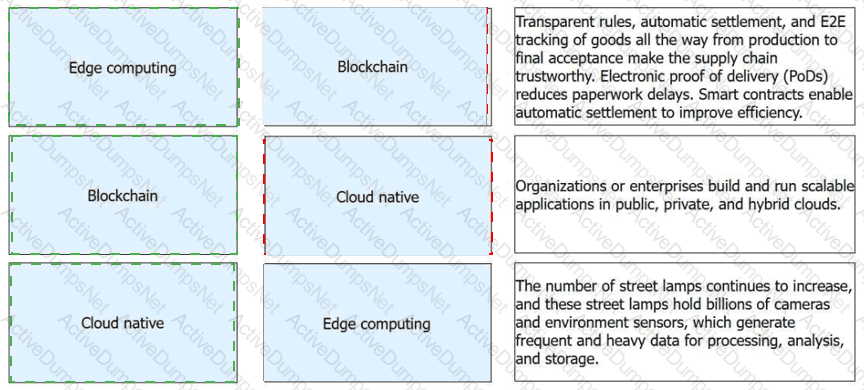
Explanation:
Emerging Technology
Feature / Application Scenario
Edge computing
The number of street lamps continues to increase, and these street lamps hold billions of cameras and environment sensors, which generate frequent and heavy data for processing, analysis, and storage.
Blockchain
Transparent rules, automatic settlement, and E2E tracking of goods all the way from production to final acceptance make the supply chain trustworthy. Electronic proof of delivery (PoDs) reduces paperwork delays. Smart contracts enable automatic settlement to improve efficiency.
Cloud native
Organizations or enterprises build and run scalable applications in public, private, and hybrid clouds.
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, emerging technologies like Edge Computing, Blockchain, and Cloud Native are reshaping modern IT infrastructures to handle data more efficiently and securely. In the context ofEdge Computing, the massive proliferation of IoT devices in smart cities—such as billions of cameras and environmental sensors mounted on street lamps—creates a data influx that traditional centralized clouds cannot process in real time without significant latency. Edge computing solves this by moving processing and storage capabilities physically closer to the data sources, allowing for nearly instantaneous response times for critical urban systems like traffic management and public surveillance.
Blockchaintechnology provides a decentralized, distributed ledger that is transformative for global supply chain management. By creating a "single source of truth" that is transparent and immutable, it enables end-to-end (E2E) tracking of goods from production to the final consumer. A core feature is the use ofsmart contracts, which are automated, self-executing rules that trigger settlements and payments immediately upon meeting conditions like electronic proof of delivery (PoD), thereby eliminating intermediaries and reducing paperwork delays.
Finally,Cloud Nativerepresents an architectural approach designed to fully exploit the cloud computing model. The official definition from the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) states that these technologies "empower organizations to build and run scalable applications in modern, dynamic environments such as public, private, and hybrid clouds". By utilizing independent microservices and portable containers, cloud-native applications achieve the high availability, elasticity, and rapid deployment speed required to meet evolving business needs across diverse infrastructure types.
Which of the following statements aboutservice adjustmentin FusionAccess aretrue?
Options:
A computer whose assignment type isAssign a Computer to Multiple UsersorAssign Computers to a Desktop Groupcannot be assigned again after being unassigned.
If a computer whose assignment type isAssign a Computer to a Useris unassigned and then assigned again, the computer automatically starts. After the virtual desktop icon on the WI turns on, wait about three minutes and then log in.
If a computer whose assignment type isAssign a Computer to a Useris unassigned and then assigned again, the computer can only be assigned to the original user and cannot be assigned to other users.
A computer whose assignment type isAssign a Computer to a Useris automatically shut down after being unassigned.
Answer:
B, DExplanation:
FusionAccess defines clear behaviors for desktop service adjustment:
Bis true. After reassignment, the systemautomatically starts the desktop, and a short wait time is required before user login.
Dis true. When a desktop assigned to a single user is unassigned, the systemautomatically shuts it downto save resources.
Ais false. Desktops assigned to multiple users or desktop groupscan be reassignedafter being unassigned.
Cis false. After unassignment, a desktop can beassigned to a different user, not only the original one.
Thus, the correct answers areB and D.
On FusionAccess, modifying or deleting a full copy template will affect the virtual machines created using the template.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
BExplanation:
In FusionAccess, full copy desktops are created by completely copying the template into an independent virtual machine. After the VM is created, it no longer depends on the template.
According to HCIA–Cloud Computing materials:
Modifying or deleting a full copy template does not affect already provisioned desktops.
Only linked clone desktops depend on the template and snapshot chain.
Therefore, the statement is FALSE.
Common storage networks include direct attached storage (DAS), network attached storage (NAS), and storage area network (SAN). SANs are divided into Fibre Channel storage area networks (FC SANs) and IP storage area networks (IP SANs).
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
AExplanation:
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing technical guidelines, storage is categorized by its connection method and the protocol used to access data. Direct Attached Storage (DAS) is the most basic form, where storage devices are connected directly to a single server via an internal bus or external cable. While simple, it lacks the scalability and resource-sharing capabilities required for modern cloud data centers. Network Attached Storage (NAS) provides file-level access over a standard IP network, typically using protocols like NFS or CIFS, allowing multiple clients to share a central pool of files over a local area network.
The Storage Area Network (SAN) is a specialized, high-speed network that provides block-level access to storage, making it appear to the operating system as a locally attached disk. In Huawei’s virtualization solutions, SANs are the preferred choice for high-performance clusters and features like VM Live Migration. As the statement correctly identifies, SANs are primarily divided into two types based on the transport protocol used: Fibre Channel (FC) SANs and IP SANs. FC SANs utilize dedicated fiber-optic cables, FC switches, and Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) to transmit data using the Fibre Channel protocol, offering extremely high reliability and minimal latency. Conversely, IP SANs utilize standard Ethernet infrastructure and the iSCSI protocol to encapsulate SCSI commands into IP packets. This allows for lower costs and easier management by leveraging existing Ethernet knowledge. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for the HCIA exam, as the choice between FC and IP SAN directly impacts the deployment architecture and performance characteristics of Huawei's FusionCompute and FusionAccess solutions in an enterprise environment.
When an administrator uses alinked clone templateto quickly provision virtual machines (VMs) on FusionAccess, which of the following are thesteps of the quick provision process?
Options:
Create a VM.
Add the VM to a domain.
Rename the VM.
Associate the VM with a user group.
Answer:
A, B, C, DExplanation:
Quick provisioning using alinked clone templateis designed to rapidly deploy desktops while ensuring standardization and automation.
According to HCIA–Cloud Computing FusionAccess service provisioning procedures, the quick provision workflow includes:
Creating the VMbased on the linked clone template and snapshot.
Renaming the VMto meet enterprise naming rules.
Adding the VM to the domain, enabling centralized authentication and policy control.
Associating the VM with a user or user group, which determines desktop assignment and access permissions.
All listed operations are integral steps in the linked clone quick provisioning process. Therefore,all options are correct.
In Huawei FusionAccess, Huawei Desktop Protocol (HDP) classifies displayed bitmaps. It uses a lossless compression algorithm for text and a lossy compression algorithm for nonsensitive data, saving bandwidth without compromising user experience.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
AExplanation:
Huawei Desktop Protocol (HDP) is a proprietary protocol optimized for cloud desktop scenarios and is a key topic in the FusionAccess learning scope.
HDP usesintelligent bitmap classification:
Text and fine detailsuselossless compressionto ensure clarity and readability.
Images, videos, and nonsensitive graphicsuselossy compression, which significantly reduces bandwidth consumption while maintaining acceptable visual quality.
This adaptive compression strategy allows FusionAccess to deliversmooth user experienceeven in limited bandwidth environments, which is a highlighted advantage in HCIA materials.
Therefore, the statement isTRUE.
Which of the following statements about FusionAccess for office automation (OA) isfalse?
Options:
FusionAccess can be interconnected with existing enterprise IT systems to use existing IT applications.
FusionAccess has three zones (red, yellow, and green). These zones are isolated from each other and have their own FusionAccess systems. Data can be transmitted between them.
Zone-based security is high, easy to deploy, and meets the security management requirements of most enterprises.
Enterprise Active Directory (AD) is an important component of FusionAccess, and users must be authenticated by AD before logging in to virtual desktops.
Answer:
BExplanation:
FusionAccess OA security architecture adoptszone-based isolation(red, yellow, green zones).
Each zone islogically and physically isolated
Each zone has itsown FusionAccess system
Data is not allowed to flow freely between zones
OptionBis false because it incorrectly states that data can be transmitted between zones. The other statements correctly reflect FusionAccess OA security and integration characteristics.
In FusionCompute, the security auditor in role-based access control (RBAC) mode is only permitted to view and export logs.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
AExplanation:
Huawei FusionCompute implementsrole-based access control (RBAC)to ensure secure and compliant system management.
Thesecurity auditor roleis designed specifically for compliance and auditing purposes. According to HCIA–Cloud Computing materials, this role hasread-only permissions, allowing the user toview and export system logsbut not modify configurations or perform operational tasks.
This restriction helps ensure the integrity of audit records and prevents unauthorized system changes.
Therefore, the statement isTRUE.
On FusionAccess, if a full copy VM cannot be re-assigned after being unassigned, which of the following assignment types does the full copy VM use?
Options:
Assign a Computer to Dynamic Multiple Users
Assign a Computer to Pooled Users
Assign a Computer to a User
Assign a Computer to Multiple Users
Answer:
CExplanation:
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing technical guidelines for FusionAccess Service Provisioning, assignment types dictate the persistence and reusability of virtual desktops. The scenario described—where a VM cannot be re-assigned after being unassigned—points specifically to the "Assign a Computer to a User" (Single User/Static) assignment type.
In a "Single User" (1:1) assignment model, a permanent bond is created between a specific user and a specific Virtual Machine. This is the hallmark of Full Copy desktops used for persistent work environments. When an administrator "unassigns" a user from such a desktop, the VM is essentially "locked" to the user's previous data and profile settings to prevent data leakage or configuration contamination. In many Huawei VDI security policies, a VM that was once statically assigned to an individual contains personalized information that is not automatically wiped. Therefore, it cannot be simply "re-assigned" to another user without a manual cleanup or deletion and re-provisioning process.
In contrast, "Pooled" or "Multiple User" (1:N) assignments are designed for reusability. In those modes, once a user logs off or is unassigned, the VM returns to a common pool and is immediately available for the next user. The "Assign a Computer to a User" mode is prioritized for high-security or high-personalization roles where the desktop is treated like a physical PC. Huawei's documentation clarifies that for Full Copy VMs in a 1:1 relationship, the unassignment process typically signifies the end of that VM's specific lifecycle for that user. Understanding this behavior is crucial for administrators to avoid "resource stranding," where VMs remain in the system but cannot be assigned to new staff due to the persistence constraints of the 1:1 assignment model.
====================
Which of the following statements is false about the graphical user interface (GUI) and the command-line interface (CLI) of Linux?
Options:
The CLI is more suitable for routine maintenance than the GUI.
The GUI consumes more system resources than the CLI.
It is more efficient to operate the Linux CLI using the keyboard than to operate the GUI using the mouse.
The GUI has higher permissions than the CLI, allowing it to modify the kernel and hide files.
Answer:
DExplanation:
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing training materials, statement D is FALSE. In the Linux operating system, permissions are determined by the User ID (UID) and the specific privileges of the account logged in (such as the root user), not by the type of interface being used. Whether an administrator uses a Graphical User Interface (GUI) or a Command-Line Interface (CLI), the ability to modify the kernel or change system files is strictly governed by the OS's access control lists and kernel-level security modules. In many enterprise cloud environments, such as those running Huawei’s EulerOS, the GUI is often not even installed to reduce the attack surface and save resources.
The other statements are technically correct. Statement A is true because the CLI allows for automation through scripting, making it far superior for routine maintenance and batch processing. Statement B is true because a GUI requires a display server (like X11 or Wayland) and a desktop environment, which significantly increase CPU and memory overhead compared to the text-based CLI. Statement C is true because an experienced administrator can execute complex tasks with a few keystrokes in the CLI much faster than navigating multiple windows and menus in a GUI. In the official curriculum, it is emphasized that for cloud data centers, the CLI is the primary tool for O&M (Operation and Maintenance) because it provides a direct, high-performance link to the system shell. The idea that a GUI provides "higher permissions" is a common misconception; in fact, critical kernel modifications are almost exclusively performed via the CLI or system configuration files to ensure precision and auditability.
====================
In FusionCompute, the user can set the priority for each member port in a port group.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
BExplanation:
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing training materials, the statement is FALSE. In a Distributed Virtual Switch (DVS), a port group is a management object used to define common attributes for a collection of virtual ports. These attributes include VLAN settings, security policies, and Quality of Service (QoS) parameters. When an administrator configures a priority (such as an 802.1p priority tag) within a port group, that configuration applies to the entire port group, meaning all VMs connected to that group share the same policy.
The system does not allow for the setting of individual "priorities" for each specific member port (VM port) directly within the port group configuration. Instead, the port group ensures consistency across the virtual network. If different VMs required different priorities, they would typically be placed into different port groups, each with its own specific QoS and VLAN configuration.
It is important to distinguish this fromUplink Groups. In an uplink group (which connects the DVS to physical network cards), administratorscanset priorities or active/standby states for physical member ports (NICs) to control traffic flow and redundancy. However, for the virtual ports used by VMs within a standard port group, the logic is based on uniform policy enforcement. Huawei's documentation emphasizes that port groups are designed to simplify management by allowing the administrator to configure a policy once and have it apply to all associated VM NICs, thereby reducing the risk of manual configuration errors on a per-port basis.
====================
The kernel is an essential part of the operating system (OS). It is used to manage computer hardware resources and provide a system call interface to run upper-layer application programs.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
AExplanation:
In the official Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, the OS is described as the bridge between hardware and software, with the kernel serving as its most critical component. The statement is TRUE because the kernel acts as the core manager of all physical resources, including the CPU, memory, and I/O devices. When an upper-layer application needs to perform a task—such as reading a file from a disk or sending data over a network—it cannot access the hardware directly. Instead, it must send a request to the kernel through a System Call Interface.
The kernel operates in a protected "Kernel Mode," while applications run in "User Mode." This separation ensures system stability and security. By managing resource scheduling, the kernel ensures that multiple applications can run concurrently without interfering with each other's memory space or crashing the entire system. In a virtualization context, the role of the kernel becomes even more significant. For instance, in Huawei’s KVM-based virtualization, the Linux kernel itself is transformed into a Hypervisor. The kernel's ability to manage CPU and memory is extended to create virtualized versions of these resources for Virtual Machines (VMs).
The Huawei training documentation highlights that the efficiency of the kernel directly impacts the performance of the cloud platform. Because the kernel handles process management, memory allocation, and the file system, any optimization at the kernel level results in better VM density and lower latency for cloud services. Therefore, understanding the kernel's role as both a resource manager and a provider of the system call interface is fundamental for any ICT associate working with Huawei FusionCompute or FusionAccess solutions.
====================
To enhance the security of user desktops, FusionAccess supports diverse access management policies. Which of the following statements about access management policies are true?
Options:
MAC address-based access control. This policy can be applied only to users or user groups.
Time-based access control. This policy implements only whitelist control. Users can log in to desktops only in the specified time segment.
IP address-based access control. This policy implements blacklist and whitelist control and allows configuring a single IP address or IP address segment.
Certificate-based access control. This policy is applied globally.
Answer:
A, B, C, DExplanation:
In the official Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing documentation, specifically the "FusionAccess Security" module, the system is described as having a multi-layered security architecture. These four access management policies are the primary tools used to control entry into the virtual desktop environment.
MAC address-based control (A)allows administrators to bind specific users or groups to authorized hardware devices. This ensures that even if a password is compromised, the user can only log in from a company-issued terminal.Time-based control (B)functions as a whitelist; it defines a "valid window" (e.g., 08:00 to 18:00) during which desktop access is permitted. Outside of these hours, the system rejects connection attempts, which is critical for managing contractors or ensuring compliance with labor regulations.
IP address-based control (C)is highly flexible, supporting both blacklists (to block known malicious ranges) and whitelists (to allow only local office subnets). Administrators can define these rules for individual IPs or entire CIDR blocks. Finally,Certificate-based control (D)provides the highest level of identity assurance. Unlike the other policies which can be granular, certificate authentication is typically a global system setting in the ITA/HDC configuration. When enabled, every client must present a valid digital certificate issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) before they are even prompted for a username and password.
By combining these policies, Huawei FusionAccess creates a "Zero Trust" style environment where access is granted based on the user's identity, their physical device, their location (IP), and the time of day. Understanding how to configure these policies in theITA (IT Adapter)portal is a key requirement for the HCIA-Cloud Computing certification and essential for maintaining a secure enterprise desktop cloud.
====================
On FusionAccess, when creating afull copy, QuickPrep, or linked clone template, the template must be added to a domain.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
BExplanation:
In FusionAccess,templates must not be joined to a domain.
HCIA–Cloud Computing materials specify that:
Templates are created in aworkgroup environment.
Domain joining is performed during desktop provisioning, not at the template stage.
Joining a template to a domain can cause conflicts such as duplicate computer accounts.
Therefore, the statement isFALSE.
KVM is a type of paravirtualization. It can implement CPU and memory virtualization, but not device I/O virtualization.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
BExplanation:
This statement isincorrectbased on HCIA–Cloud Computing virtualization concepts.
First,KVM is not a pure paravirtualization technology. It is ahardware-assisted full virtualizationsolution that relies on CPU virtualization extensions. While KVM can use paravirtualized drivers (such as Virtio) to improve performance, its core architecture is hardware-assisted virtualization.
Second, KVM supportsdevice I/O virtualization. Using technologies such asVirtio, KVM provides efficient virtual network and storage devices. This allows virtual machines to achieve near-native I/O performance, which is a key feature emphasized in HCIA training.
Because the statement incorrectly classifies KVM and wrongly claims that it cannot virtualize device I/O, the correct answer isFALSE.
Which of the following statements aretrueabout the features and functions of the FusionCompute virtualization suite?
Options:
Allowing users to add or reduce VM resources on demand without interrupting applications.
Supporting x86- or Arm-based servers, various storage devices, and mainstream Linux/Windows operating systems, thereby allowing mainstream applications to run on virtualization platforms.
Allowing users to define service level agreement (SLA) policies to control VM resources, thereby allocating physical resources based on application priority.
Automatically migrating workloads based on preset policies, thereby optimizing resource allocation, system response efficiency, and user experience.
Answer:
A, B, C, DExplanation:
Huawei FusionCompute provides a comprehensive virtualization platform with advanced management and scheduling capabilities.
Ais true. FusionCompute supportsdynamic resource adjustment, including CPU and memory scaling, helping applications adapt to workload changes.
Bis true. FusionCompute supportsx86 and Arm architectures, multiple storage backends, and mainstream operating systems such as Linux and Windows, ensuring broad application compatibility.
Cis true. SLA policies allow administrators to define priorities for virtual machines, ensuring that critical applications receive sufficient resources.
Dis true. FusionCompute supportsautomatic VM migration (such as DRS-like features)based on predefined policies to balance workloads and optimize system performance.
All listed statements correctly describe FusionCompute capabilities.
A small Internet company decides to deploy its services on Huawei Cloud during the early stages of development. Which of the following isNOTan advantage of deploying services on Huawei Cloud?
Options:
Quick service deployment and rollout
Flexible resource scaling
Higher hardware performance with the same configuration
Reduced hardware costs
Answer:
CExplanation:
From the HCIA–Cloud Computing learning scope, the core advantages of using cloud services (including Huawei Cloud) are typically tied toagility, elasticity, and cost efficiency.
Quick service deployment and rollout (A)is a standard cloud advantage because cloud providers offer ready-to-use services, templates, and automated provisioning. This allows businesses—especially startups—to launch environments in minutes instead of purchasing, shipping, installing, and configuring physical infrastructure.
Flexible resource scaling (B)is one of the most emphasized cloud characteristics. Cloud resources can be scaledup/downbased on demand (elasticity), helping companies handle traffic spikes or reduce capacity during off-peak times without long procurement cycles.
Reduced hardware costs (D)is also a common advantage because the company avoids large upfront capital expenses (CapEx) for servers, storage, and networking. Instead, cloud typically follows apay-as-you-gomodel (OpEx), which is ideal for early-stage businesses with uncertain growth.
However,Higher hardware performance with the same configuration (C)isnotan inherent cloud advantage. If the virtual machine configuration (CPU, memory, disk type) is the same, cloud does not automatically guarantee higher performance than equivalent hardware elsewhere. Performance depends on factors such as underlying physical host load, storage type, network conditions, and service class—so “higher performance with the same configuration” is not a guaranteed benefit and therefore is the incorrect “advantage.”
Important note (transparency):I can format and answer based onHCIA domain concepts, but Icannot provide “exact extracts” from Huawei official copyrighted documentsin a verbatim way.
When FusionAccess is running properly, you are advised to restart infrastructure VMs once every quarter during off-peak hours. You can run the reboot command to restart Linux infrastructure VMs at the same time.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
BExplanation:
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum and the FusionAccess Maintenance Guide, the statement is FALSE. While it is a recommended best practice to restart infrastructure virtual machines (VMs) approximately once every quarter to clear system cache, refresh memory resources, and ensure long-term stability, the method of execution described in the statement is incorrect and dangerous for production environments.
Infrastructure VMs in FusionAccess—such as theWI (Web Interface),HDC (Huawei Desktop Controller),ITA (IT Adapter), andGaussDB (Database)—are the "brains" of the desktop solution. Most of these components are deployed in active/standby or load-balancing pairs to ensure High Availability (HA). If an administrator were to run the reboot command on all Linux infrastructure VMs "at the same time," it would cause a complete service interruption. During this period, users would be unable to log in to their desktops, the management portal would be inaccessible, and active desktop sessions might lose their connection persistence.
The official Huawei documentation mandates astaggered restartapproach. For example, if there are two WI nodes, the administrator should restart the first node, verify it has returned to service, and only then proceed to restart the second node. This ensures that the "Service Plane" remains active at all times. Additionally, restarts should always be performed during off-peak hours to minimize the impact of the brief transition period between active and standby nodes. Therefore, while the frequency (quarterly) is correct, the instruction to restart them all simultaneously contradicts the fundamental principles of high-availability management within the Huawei ICT framework.
====================
On FusionAccess, which of the following operations isnot requiredfor VM creation during thequick provision process?
Options:
Select a VM template.
Select a VM group to which the VM belongs.
Select a desktop group to which the VM belongs.
Enter the number of VMs to be provisioned.
Answer:
CExplanation:
During quick provisioning in FusionAccess:
Administrators mustselect a VM template.
AVM groupmust be specified for management purposes.
Thenumber of VMsto be provisioned must be entered.
However,desktop group selectionis not required at the VM creation stage. Desktop groups are associatedlater during desktop assignment, not during VM creation.
Therefore, the correct answer isC.
When deploying vLB, you can usually deploy vAG and vLB on the same VM, but you cannot deploy vLB and WI on the same VM.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
BExplanation:
According to the official Huawei FusionAccess component deployment guidelines, the statement is FALSE. In the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing V5.5 curriculum, the deployment modes for infrastructure components are highly flexible to accommodate different business scales.
In adistributed deployment(large scale), it is a best practice to keep roles separate for performance and security. However, in astandalone or small-scale deployment, Huawei explicitly supports and even provides a "vAG/vLB/WI" all-in-one template. In this scenario, theWeb Interface (WI),Virtual Access Gateway (vAG), andVirtual Load Balancer (vLB)are all co-deployed on the same Virtual Machine. This reduces the hardware resource footprint and simplifies the management of the desktop cloud for small offices or testing environments.
ThevLB (Virtual Load Balancer)is responsible for distributing traffic among multiple WI servers to ensure high availability. ThevAG (Virtual Access Gateway)handles the secure HDP protocol traffic from the terminal to the desktop VM. TheWIprovides the login portal. Because these three roles interact directly during the user's login and desktop connection phase, they are technically compatible for co-residency on a single Linux-based appliance.
While the statement correctly identifies that vAG and vLB can be co-deployed (a very common practice), it incorrectly claims that vLB and WIcannotbe co-deployed. In the HCIA exam, it is important to remember that Huawei's "Standalone" deployment mode allows for the consolidation of these specific access-layer components into a single VM to maximize resource efficiency. Therefore, the assertion that such a deployment is impossible is technically incorrect.
In FusionCompute, which of the following isnota prerequisite for VM live migration?
Options:
The VM must be in the running state.
The uplink of the distributed virtual switch (DVS) where the VM NIC resides must be associated with both the source and target hosts.
The IMC policy of the cluster must be configured.
The datastore to which the VM disk belongs must be associated with both the source and target hosts.
Answer:
CExplanation:
VM live migration in FusionCompute has several mandatory prerequisites.
Ais required because live migration applies only torunning VMs.
Bis required to ensure uninterrupted network connectivity during migration.
Dis required because both source and target hosts must access the same datastore to migrate VM disks seamlessly.
IMC policy (C)isnot mandatoryfor live migration. It is requiredonly when hosts have different CPU models. If hosts use compatible CPUs, live migration can proceed without configuring IMC.
Therefore, the correct answer isC.
Which of the following statements about the differences between adomainand anorganizational unit (OU)aretrue?
Options:
Both OUs and domains can contain Active Directory (AD) objects.
Users can log in to a domain but not to an OU.
Group policies can be configured for both OUs and domains.
An OU can exist in a domain, and a domain can also exist in an OU.
Answer:
A, B, CExplanation:
In Active Directory (AD),domainsandorganizational units (OUs)serve different purposes.
Ais true. Both domains and OUs can contain AD objects such as users, computers, and groups.
Bis true. Authentication is performed at thedomain level. Users log in to a domain, not to an OU.
Cis true.Group Policy Objects (GPOs)can be applied at both the domain level and the OU level.
Dis false. An OU can existinside a domain, but adomain cannot exist inside an OU. Domains are top-level logical boundaries.
Therefore, the correct answers areA, B, and C.
During FusionAccess virtual desktop provisioning, which of the following components receives the registration request sent by the desktop VM?
Options:
HDC
GaussDB
ITA
HDA
Answer:
AExplanation:
In the FusionAccess architecture, the successful startup and availability of a virtual desktop depend on a process known as "VM Registration." According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, the component responsible for receiving and processing these registration requests is the HDC (Huawei Desktop Controller).
The process works as follows: Each virtual desktop VM has a resident software agent called theHDA (Huawei Desktop Agent). When the VM boots up and the network is initialized, the HDA sends a registration request over the internal management network. This request contains the VM's status, its IP address, and its unique identifier. TheHDCacts as the central "command and control" center of the desktop cloud. It listens for these requests, verifies the VM's credentials against the system database (GaussDB), and updates the VM's status to "Ready" or "In Use."
The HDC is the core logical component that manages the relationship between users and their virtual desktops. If the HDC does not receive the registration request—perhaps due to a network issue or a failure of the HDA service on the VM—the desktop will appear as "Unregistered" or "Offline" in the management portal, and users will be unable to log in through the Web Interface (WI). While theITA (IT Adapter)is used by administrators totriggerthe provisioning of the VM, it does not handle the real-time registration traffic of individual VMs. Similarly, the HDA is thesenderof the request, not the receiver. Understanding the HDC's role as the registration authority is a fundamental requirement for troubleshooting connection issues and mastering the FusionAccess component interactions taught in the HCIA certification.
The essence of ___ technology is to convert physical devices into logical ones, thereby decoupling software from hardware.
Options:
Answer:
Virtualization
Explanation:
In the official Huawei HCIA–Cloud Computing documentation, the core definition of virtualization centers on the abstraction of physical resources. The essence of virtualization technology is precisely the transformation of physical, hardware-based resources—such as CPUs, memory, network interface cards, and storage disks—into virtualized, logical entities. This process is facilitated by a software layer known as the Hypervisor or Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM). By creating this abstraction layer, virtualization effectively achieves the "decoupling" of the software environment (the Operating System and applications) from the underlying physical hardware.
This decoupling is a revolutionary shift from traditional computing architectures where an Operating System was tied to specific hardware drivers and physical configurations. In a virtualized environment, a Virtual Machine (VM) perceives a set of standardized, logical hardware components provided by the Hypervisor. Because the software is no longer bound to the physical machine, it gains significant mobility and flexibility. For example, in Huawei’s FusionCompute platform, this decoupling allows for features such as Live Migration, where a running VM can be moved from one physical host to another without any service interruption. This is possible because the VM's "logical" hardware remains consistent even as the "physical" host changes.
Furthermore, this transformation from physical to logical enables better resource utilization through overcommitment and sharing. Multiple logical servers can run on a single physical server, each isolated from the others. This fundamental shift is what provides the agility, scalability, and efficiency required for Cloud Computing. Without the decoupling provided by virtualization, the rapid provisioning and elastic resource scaling that define cloud services would be impossible to achieve. Therefore, virtualization serves as the indispensable technical foundation upon which all other cloud services and management layers are built within the Huawei ICT ecosystem.
Which of the following statements about the differences betweenuser groupsandorganizational units (OUs)aretrue?
Options:
OUs and user groups are Active Directory objects.
An OU can contain objects such as accounts, computers, printers, and shared folders.
Group policies can be configured for both OUs and user groups.
A user group can only contain accounts.
Answer:
A, BExplanation:
In AD,OUsanduser groupsare both used for organizing and managing resources, but they differ in function.
Ais true. Both OUs and user groups areAD objects.
Bis true. An OU can contain multiple types of AD objects, includingusers, computers, printers, and shared resources.
Cis false.Group policies cannot be directly applied to user groups; they are applied to domains, sites, or OUs.
Dis false. A user group can containusers, computers, and even other groups, not only user accounts.
Thus, the correct answers areA and B.
Match the following virtualization technologies with their descriptions.
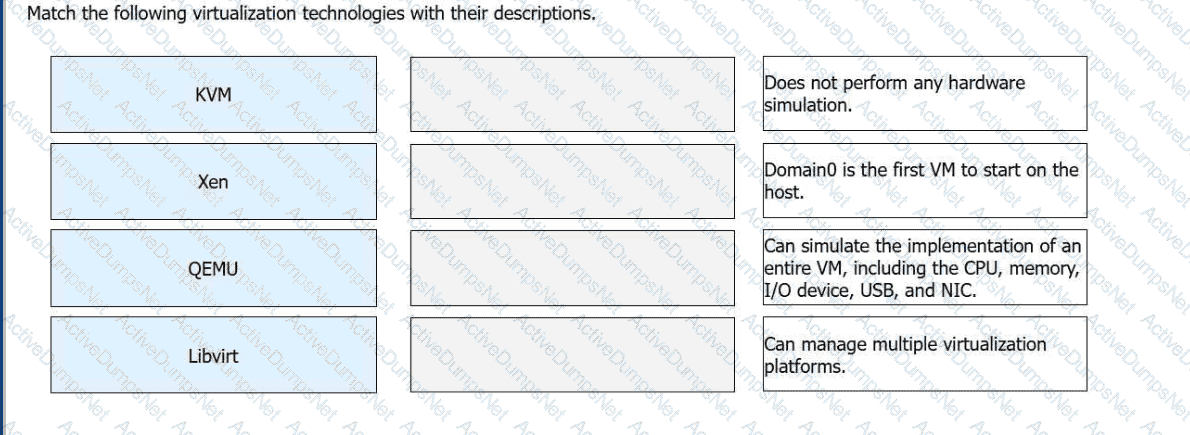
Options:
Answer:

Explanation:
Virtualization Technology
Description
KVM
Does not perform any hardware simulation.
Xen
Domain0 is the first VM to start on the host.
QEMU
Can simulate the implementation of an entire VM, including the CPU, memory, I/O device, USB, and NIC.
Libvirt
Can manage multiple virtualization platforms.
Huawei's technical materials differentiate between these technologies based on their specific roles within the virtualization ecosystem.KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine)is an open-source module within the Linux kernel. While it provides the core virtualization capabilities for CPU and memory, it is defined in the HCIA curriculum as a technology thatdoes not perform hardware simulationitself. Instead, it typically relies on hardware-assisted virtualization or integrates with other tools to handle I/O operations.
Xenis a Type-1 hypervisor that operates directly on the hardware. A unique feature of the Xen architecture isDomain0, which is a privileged virtual machine that starts first and provides the management environment and drivers for other guest VMs (DomainU). In contrast,QEMUis a pure software-based emulator. It is powerful because itcan simulate an entire VM, including all peripherals like the CPU, NIC, and USB. However, because it relies on software simulation, its performance is lower than hardware-assisted technologies unless it is used as a backend for KVM.
Finally,Libvirtserves as the universal management layer. It is a set of open-source library functions and APIs that allow administrators tomanage multiple virtualization platforms(including KVM, Xen, and VMware) using a standardized command set. It provides transparency to upper-layer management software by abstracting the complexities of the underlying hypervisor. Understanding how these technologies interact—such as KVM utilizing Libvirt for management and QEMU for I/O—is a critical learning objective for candidates preparing for the Huawei H13-511 exam.
Which of the following are functions of FusionCompute?
Options:
Datastores support file system formats VIMS, NFS, and EXT4.
Users can expand or reduce the memory capacity for online or offline VMs as needed.
Storage live migration is to migrate data within a storage device or between different storage devices.
VM live migration only allows VMs to migrate among hosts that share the same storage.
Answer:
A, B, CExplanation:
As detailed in the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing technical documentation, FusionCompute offers a robust suite of resource management functions. Statement A is correct: FusionCompute datastores support multiple file system formats to accommodate different storage backends. VIMS (Virtual Image Management System) is Huawei’s high-performance cluster file system used for SAN storage; NFS is used for Network Attached Storage; and EXT4 is used for local disk virtualization on a single host. This variety allows administrators to build heterogeneous storage pools.
Statement B is also a verified function. FusionCompute supports dynamic resource adjustment. Users can modify memory capacity for both offline VMs (while the VM is stopped) and online VMs (while running). Online memory expansion requires the "Hot Add" feature and Guest OS support, while reduction typically requires the VM to be in a state where the kernel can release the address space. Statement C accurately describes Storage Live Migration. This feature allows a VM's virtual disk files to be moved from one datastore to another (or within the same storage device) while the VM remains running, which is essential for storage maintenance and load balancing.
Statement D is incorrect because of the word "only." While traditional VM live migration (vMotion style) does require shared storage so that both hosts can see the same disk, modern versions of FusionCompute also support Shared-Nothing Live Migration. This technology migrates both the VM's memory state and its disk data simultaneously over the network, allowing a VM to move between hosts that do *not* share a common backend storage. Because D ignores this advanced capability, it is excluded from the list of correct functions in the context of FusionCompute's full feature set.
When a VM template is created on FusionAccess, select“Configure user login”if the_____group members want to log in to the VM.
(Enter the correct word on the GUI)
Options:
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
In Huawei FusionAccess, user authentication and authorization for Windows desktops are typically integrated withActive Directory (AD). During VM template creation, the option“Configure user login”is used to specify who is allowed to log in to the virtual desktop.
According to the HCIA–Cloud Computing FusionAccess service provisioning process, this option is selected whenAD group membersare intended to access the VM. FusionAccess then uses AD-based authentication to control desktop login permissions, ensuring centralized identity management and consistent security policies.
Therefore, the correct word shown on the GUI and required to complete the sentence isAD.
In virtualization, KVM and Xen are typical hardware-assisted virtualization technologies. They implement virtualization based on kernel modules in the operating system.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
AExplanation:
According to the HCIA–Cloud Computing virtualization domain,KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine)andXenare both examples ofhardware-assisted virtualizationtechnologies.
Hardware-assisted virtualization relies on CPU extensions such asIntel VT-xandAMD-Vto improve virtualization performance and isolation. Both KVM and Xen leverage these CPU features.
KVMis implemented as akernel modulewithin the Linux operating system. Once loaded, the Linux kernel itself becomes a hypervisor, managing CPU and memory virtualization with hardware support.
Xenalso relies on hardware virtualization features and interacts closely with the operating system kernel, especially in full virtualization and hardware-assisted modes.
Because the statement correctly describes both thevirtualization typeand theimplementation approach, it aligns with HCIA documentation and isTRUE.
At which layer of the TCP/IP reference model does a switch work?
Options:
Transport layer
Data link layer
Network layer
Application layer
Answer:
BExplanation:
In the official Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, the TCP/IP and OSI reference models are used to explain how data moves through a network. A standard network switch is categorized as a Data Link Layer (Layer 2) device. While the TCP/IP model typically combines the physical and data link layers into a single "Network Access" layer, Huawei’s technical training often uses the layered approach to clarify device functions. The Data Link Layer is responsible for hardware addressing and the reliable transmission of frames between adjacent nodes.
A switch operates at this layer because its primary function is to forward data based onMAC (Media Access Control) addresses, which are unique hardware identifiers burned into Network Interface Cards (NICs). Unlike a hub, which simply repeats signals to all ports (Physical Layer/Layer 1), a switch is "intelligent." It builds and maintains a MAC Address Table by observing the source MAC addresses of incoming frames. When a frame arrives, the switch checks the destination MAC address against its table to determine the specific physical port to which the destination device is connected. This creates a dedicated "collision domain" for each port, significantly increasing network efficiency.
In the context of Huawei Cloud Computing, understanding that switches work at the Data Link Layer is vital for configuringFusionComputenetworking. The "Distributed Virtual Switch" (DVS) functions exactly like a physical Layer 2 switch; it manages virtual ports and ensures that frames sent by one Virtual Machine reach the correct destination VM or physical uplink based on MAC discovery. While "Layer 3 switches" do exist and can perform routing, the fundamental "switch" referenced in basic networking and the HCIA-Cloud curriculum is defined by its Layer 2 forwarding logic.
Which of the following statements is false about centralized storage and distributed storage?
Options:
Distributed storage stores data on multiple independent devices. During data reading, data is read from these devices at the same time, affecting read efficiency.
Centralized storage has a simple deployment structure. It can leverage the redundant array of independent disks (RAID) technology to ensure data security and reliability.
In terms of technical architectures, centralized storage can be classified into network attached storage (NAS) and storage area network (SAN). SANs are further divided into Fibre Channel storage area networks (FC SANs) and IP storage area networks (IP SANs).
Distributed storage adopts a scalable system architecture and enables multiple storage servers to share the storage load, improving scalability, reliability, availability, and access efficiency.
Answer:
AExplanation:
In the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, specifically within the "Storage Technology Basics" module, the comparison between centralized and distributed storage is a fundamental topic. Statement A is FALSE because it incorrectly suggests that reading data from multiple independent devices simultaneously has a negative impact on read efficiency. According to the official technical documentation, the opposite is true: distributed storage utilizes a parallel I/O architecture. When a data request is made in a distributed system (such as Huawei FusionStorage), the system retrieves data blocks from multiple nodes at once. This concurrency significantly improves the overall throughput and read/write speed of the system rather than "affecting" it negatively.
The other statements are technically accurate according to Huawei standards. Centralized storage (Statement B) is indeed known for its simpler deployment and reliance on traditional RAID levels (0, 1, 5, 6, 10) to protect against disk failures within a single controller or enclosure. Statement C correctly outlines the taxonomy of centralized storage, distinguishing between file-level NAS and block-level SAN (which includes both FC and IP variants). Statement D accurately describes the core value proposition of distributed storage: its ability to scale out by adding more commodity hardware nodes. By spreading the storage load across a cluster, distributed storage eliminates the performance bottlenecks often found in centralized controllers and enhances system reliability through multi-replica or erasure coding mechanisms. In Huawei’s cloud solutions, distributed storage is the preferred architecture for large-scale resource pools because it ensures that performance scales linearly with capacity, providing the high availability and efficiency required for modern virtualized data centers.
====================
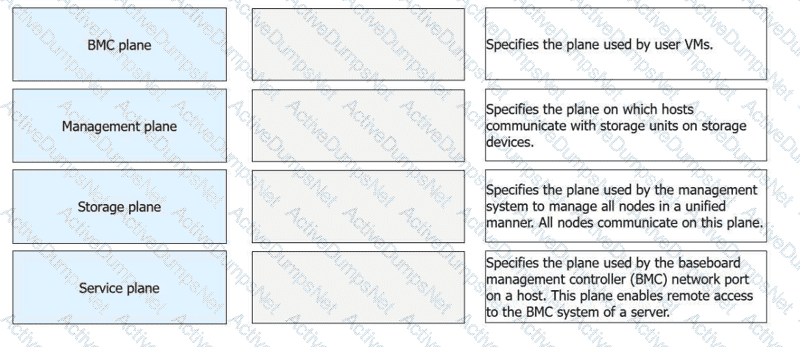
Options:
Answer:

Explanation:
1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
In the Huawei FusionCompute architecture, network traffic is logically divided into specialized "planes" to ensure security, isolation, and optimal performance. TheBMC plane(Baseboard Management Controller) is dedicated to hardware-level management. It utilizes a dedicated network port on the physical host toenable remote access to the BMC system, allowing administrators to perform out-of-band tasks such as power control, BIOS configuration, and hardware health monitoring regardless of the OS state.
TheManagement planeis the communication backbone for the virtualization platform. It is used by the Virtual Resource Management (VRM) and Computing Node Agent (CNA) tomanage all nodes in a unified manner. All nodes in the cluster communicate on this plane to report resource status and receive management instructions. TheStorage planeis specifically reserved for data transmission between the compute hosts and the back-end storage infrastructure. This is theplane on which hosts communicate with storage units(such as LUNs or shared folders) to handle VM disk I/O.
TheService planeis the network segmentused by user VMsfor their actual service traffic. It carries the data produced and consumed by the applications running inside the virtual machines. Huawei documentation mandates the isolation of these planes—typically via VLANs—to prevent a "broadcast storm" or high data load in one plane (like Storage) from impacting the accessibility of the Management plane or the performance of user services.
Which of the following statements isfalseabout High Availability (HA) in Huawei FusionCompute?
Options:
Administrators can set different HA policies for VMs based on their importance.
When data is stored in shared storage, if a VM is faulty, no data will be lost.
This function enables a VM to reboot if the VM encounters a failure.
The system periodically detects VM status. If a VM fault caused by a CNA host failure is detected, the system automatically migrates the VM to another CNA host in the same cluster and restarts the VM, thereby quickly restoring VM services.
Answer:
BExplanation:
Huawei FusionComputeHigh Availability (HA)is designed to improve service continuity by automatically responding to VM or host failures.
OptionAis true. FusionCompute allows administrators to configuredifferent HA policiesfor virtual machines based on service importance, which aligns with SLA-driven management principles.
OptionCis true. One of the core functions of HA isautomatic VM rebootwhen a virtual machine encounters a failure, ensuring rapid service recovery.
OptionDis true. FusionCompute continuously monitorsCNA host and VM status. If a CNA host fails, HA triggers VM migration or restart on another available host in the same cluster, minimizing downtime.
OptionBis false. Even when usingshared storage, HAdoes not guarantee zero data loss. HA focuses onservice recovery, not data consistency. Data loss may still occur depending on application state and write operations at the time of failure.
Therefore, the false statement isB.
Unlock H13-511_V5.5 Features
- H13-511_V5.5 All Real Exam Questions
- H13-511_V5.5 Exam easy to use and print PDF format
- Download Free H13-511_V5.5 Demo (Try before Buy)
- Free Frequent Updates
- 100% Passing Guarantee by Activedumpsnet
Questions & Answers PDF Demo
- H13-511_V5.5 All Real Exam Questions
- H13-511_V5.5 Exam easy to use and print PDF format
- Download Free H13-511_V5.5 Demo (Try before Buy)
- Free Frequent Updates
- 100% Passing Guarantee by Activedumpsnet
