- Home
- HRCI
- HRCI Other Certification
- aPHRi
- aPHRi - Associate Professional in Human Resources - International
HRCI aPHRi Associate Professional in Human Resources - International Exam Practice Test
Associate Professional in Human Resources - International Questions and Answers
Which of the following is an organizational structure where the number of employees decreases as responsibility increases?
Options:
Flat
Matrix
Regional
Hierarchical
Answer:
DExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
A hierarchical organizational structure is a pyramid-shaped model where the number of employees decreases as responsibility increases. At the top are a few executives with high responsibility, while the base has many employees with less responsibility.
Option A (Flat): A flat structure has few levels of management, with more employees reporting to each manager.
Option B (Matrix): A matrix structure combines functional and project-based reporting, not necessarily pyramid-shaped.
Option C (Regional): This refers to a structure based on geographic regions, not responsibility levels.
Which of the following should HR do to prepare to interview a candidate?
Options:
Produce a job description
Review the candidate's resume
Share resumes with the hiring manager
Screen applications for relevant experience
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
To prepare for an interview, HR should review the candidate’s resume to understand their background, skills, and experience. This allows HR to ask relevant questions and assess the candidate’s fit for the role.
Option A (Produce a job description): This is done before recruitment begins, not during interview preparation.
Option B (Review the candidate's resume): Correct, as it is a key step in preparing for the interview.
Option C (Share resumes with the hiring manager): This may be part of the process, but it is not HR’s direct preparation for the interview.
The responsibility to provide a safe working environment and promote the health and well-being of the workforce primarily rests with the:
Options:
Employer
Employee
Labor union
Government
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
The employer has the primary responsibility to provide a safe working environment and promote employee health and well-being, as mandated by occupational health and safety laws (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., or the Health and Safety at Work Act in the UK). This includes implementing safety policies, providing training, and addressing hazards.
Option A (Employer): Correct, as employers are legally and ethically responsible for workplace safety.
Option B (Employee): Employees must follow safety protocols, but the primary responsibility lies with the employer.
Option C (Labor union): Unions advocate for safety but do not bear primary responsibility.
Match the best recruitment method to the type telnet the organization is trying to hire.

Options:
Answer:
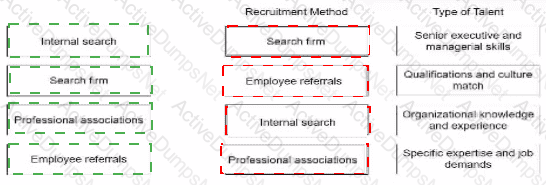
Explanation:
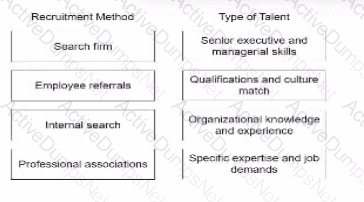
Matched Recruitment Method to the Talent Type:
Internal Search → Organizational Knowledge and Experience
Explanation:Internal searches involve identifying talent within the existing workforce. Employees already familiar with the organization's culture, policies, and operations are best suited for roles requiring organizational knowledge and experience. Internal promotions or lateral movements also enhance employee retention and morale.
Which of the following elements should be included in an employee handbook?
Options:
Job specification
Employment contract
Equal employment practices
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Answer:
CExplanation:
Key Elements in an Employee Handbook:
An employee handbook provides essential policies, procedures, and expectations, including equal employment practices to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards.
Why Equal Employment Practices are Correct:
Including equal employment policies ensures transparency, fairness, and compliance with anti-discrimination laws.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Job specification: This is part of job descriptions, not employee handbooks.
B. Employment contract: Typically a separate legal document, not part of the handbook.
D. Key performance indicators (KPIs): Related to performance management, not policy handbooks.
International HR References:
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act (U.S.): Requires equal opportunity practices in the workplace.
ILO Discrimination (Employment and Occupation) Convention: Promotes equal treatment and non-discrimination.
Match each HR function with the type of document associated with it.
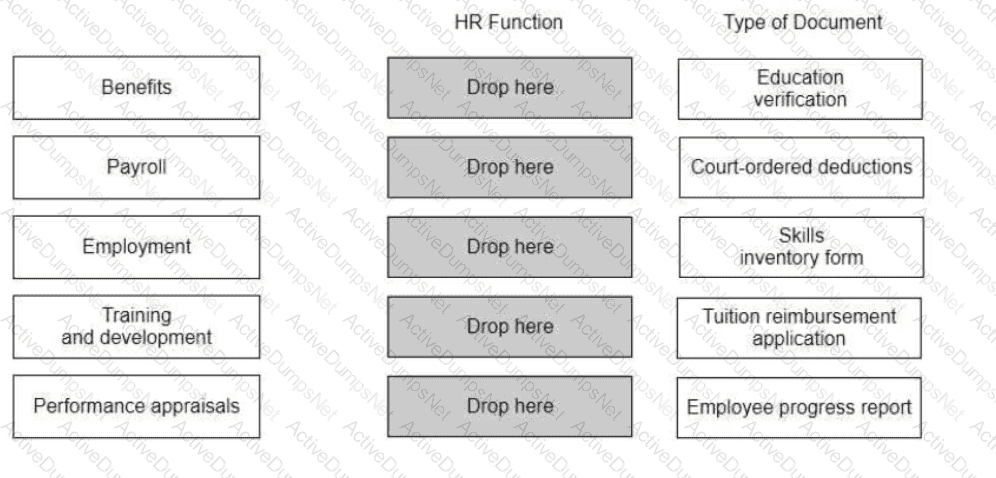
Options:
Answer:
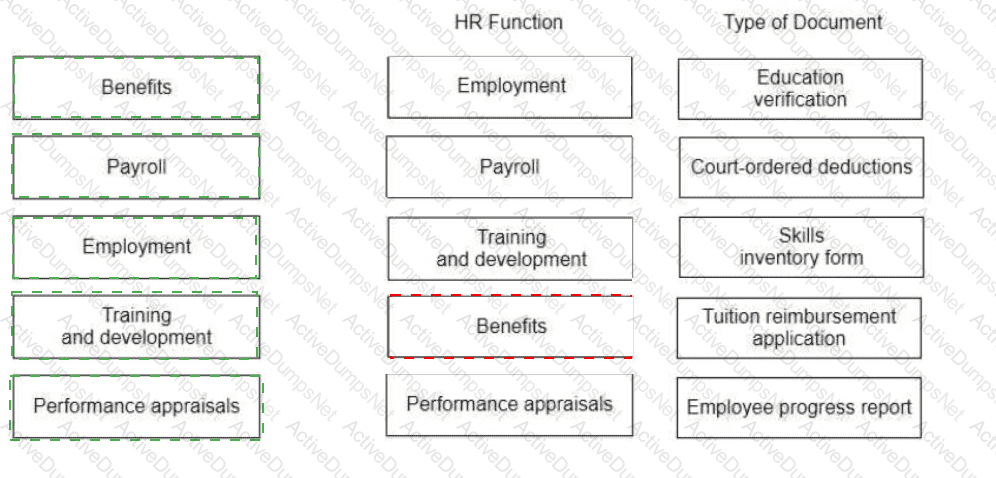
Explanation:
Here is the correct matching for each HR function with the associated type of document:
Benefits → Tuition reimbursement application
Payroll → Court-ordered deductions
Employment → Education verification
Training and development → Skills inventory form
Performance appraisals → Employee progress report
Step-by-Step Explanation
Benefits: Documents related to benefits often include applications and forms for various employee perks, such as tuition reimbursement. The tuition reimbursement application is associated with the Benefits function as it falls under employee benefits management.
Payroll: Payroll documentation includes information regarding deductions, taxes, and other financial records. Court-ordered deductions (such as garnishments) are processed through payroll, making it a key document in this area.
Employment: Employment-related documents verify an employee’s qualifications and credentials. Education verification is a standard document used in the hiring process to confirm an applicant’s educational background.
Training and Development: This HR function involves tracking and managing employee skills, training programs, and development plans. A skills inventory form is used to document the skills of employees, making it relevant to training and development.
Performance Appraisals: Performance appraisals involve assessing and documenting an employee’s work performance. An employee progress report is part of this function, as it provides feedback on performance and areas for improvement.
In a given year, there were 10 injuries recorded in a population of 200 employees. The incident rate in this organization is ______%.
Options:
(Not provided in original)
(Not provided in original)
(Not provided in original)
(Not provided in original)
Answer:
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
The incident rate (or injury rate) is calculated as the number of incidents (injuries) per 100 employees. The formula is:
Incident rate = (Number of injuries ÷ Total employees) × 100.
Given: Number of injuries = 10, Total employees = 200.
Incident rate = (10 ÷ 200) × 100 = 0.05 × 100 = 5%.
Thus, the incident rate is 5%. This metric is commonly used in HR to assess workplace safety and compliance with occupational health standards.
Which of the following refers to the act of an interview evaluating all job candidate in comparison to a single candidate?
Options:
Halo effect
Contrast error
Recency effect
First impression
Answer:
BExplanation:
Definition of Contrast Error:
Contrast error occurs when an interviewer evaluates all candidates in comparison to one standout candidate (either positively or negatively), rather than assessing each candidate against the job criteria.
Why Contrast Error is Correct:
This bias leads to inconsistent evaluations, as the comparison skews perceptions instead of focusing on individual qualifications relative to the job requirements.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Halo effect: Occurs when one positive attribute overshadows all other characteristics.
C. Recency effect: Refers to giving undue weight to recent events or interactions.
D. First impression: Refers to basing judgment on initial encounters rather than comprehensive evaluations.
International HR References:
SHRM Hiring Bias Resources: Highlights contrast error as a common interview bias.
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC): Encourages structured interviews to minimize bias.
An organization with deeply held values that are widely shared has a strong:
Options:
Corporate image
Employee value proposition
Organizational culture
Workforce diversity program
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Organizational culture refers to the shared values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors that define how people interact within an organization. A strong organizational culture exists when these values are deeply held and widely shared across the workforce, creating a cohesive and unified work environment.
Option A (Corporate image): This refers to the external perception of the organization, not internal values.
Option B (Employee value proposition): This is the set of benefits and rewards offered to employees in exchange for their work, not about shared values.
Option C (Organizational culture): Correct, as deeply held and widely shared values are the hallmark of a strong organizational culture.
Which of the following is a mandatory employment requirement?
Options:
Providing benefits
Giving work breaks
Administering orientation
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
A mandatory employment requirement refers to a practice that employers are legally obligated to follow under labor laws. While the mandatory nature of these options depends on the jurisdiction, giving work breaks is often a legal requirement in many regions to ensure employee health and safety.
Option A (Providing benefits): Providing benefits like health insurance or paid leave is not universally mandatory. For example, in the U.S., the FLSA does not require benefits, though some countries (e.g., the UK) mandate certain benefits like paid vacation.
Option B (Giving work breaks): Correct, as many jurisdictions require employers to provide breaks. For instance, the EU Working Time Directive mandates a 20-minute break for shifts over 6 hours, and some U.S. states (e.g., California) require meal and rest breaks. This makes it the most likely mandatory requirement among the options.
Which of the following parties is responsible for scheduling health and safety training in an organization?
Options:
Employer
Regulatory body
Safety consultant
Independent auditor
Answer:
AExplanation:
Employer Responsibility in Health and Safety Training:Employers have a legal and ethical duty to ensure the health and safety of their employees. This includes scheduling, organizing, and funding health and safety training programs as part of their obligations under various workplace safety laws and regulations globally.
Global Legal Frameworks and Obligations:
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) - United States:The employer is required to provide health and safety training under OSHA's General Duty Clause (Section 5(a)(1)). This mandates employers to furnish a workplace free from recognized hazards and to provide adequate training on safety procedures.
Health and Safety at Work Act (1974) - United Kingdom:Employers must ensure that their employees receive training and supervision to perform their work safely (Section 2). This explicitly puts the responsibility for scheduling and managing training on employers.
International Labour Organization (ILO) Standards:The ILO's Occupational Safety and Health Convention, 1981 (No. 155) emphasizes that employers are responsible for organizing ongoing training to ensure a safe working environment.
Role of Other Parties:
B. Regulatory Body:Regulatory bodies (e.g., OSHA, HSE) provide guidelines, compliance standards, and sometimes offer resources or inspections, but they do not schedule training for organizations. Their role is supervisory and advisory.
C. Safety Consultant:Safety consultants may assist in designing or delivering training programs, but they act as external advisors. The responsibility for scheduling rests with the employer.
D. Independent Auditor:Independent auditors evaluate compliance with safety standards and may recommend training. However, they are not involved in planning or scheduling training programs.
Best Practices for Employers:Employers must:
Conduct a needs analysis to identify specific training requirements based on industry risks.
Develop a training calendar and ensure sessions are scheduled for all employees, including new hires and those requiring refresher training.
Keep documentation of training provided to comply with legal requirements and audits.
The primary purpose of a needs assessment is to:
Options:
Align compensation
Motivate employees
Identify training gaps
Evaluate performance
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
A needs assessment is a systematic process used in HR to identify gaps between current and desired performance or skills within an organization. Its primary purpose is to determine training and development needs by assessing what skills, knowledge, or behaviors employees lack to meet organizational goals. This ensures that training programs are targeted and effective.
Option A (Align compensation): Compensation alignment involves adjusting pay structures, not assessing training needs.
Option B (Motivate employees): While training can motivate employees, motivation is not the primary purpose of a needs assessment.
Option C (Identify training gaps): Correct, as a needs assessment focuses on identifying deficiencies in skills or knowledge that training can address.
An employee's current experience and abilities are determined by using a(n):
Options:
Skills inventory
Succession plan
Performance management system
Applicant tracking system
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
A skills inventory is a tool used to catalog an employee’s current experience, skills, qualifications, and abilities. It helps HR understand the workforce’s capabilities for purposes like training, development, or workforce planning.
Option A (Skills inventory): Correct, as it directly assesses an employee’s current experience and abilities.
Option B (Succession plan): This identifies employees for future leadership roles, not their current skills.
Option C (Performance management system): This evaluates performance, not a comprehensive skills assessment.
Which of the following best defines the process of promoting an organization as desirable in the labor market?
Options:
Social influencing
Strategic planning
Marketing initiatives
Employment branding
Answer:
DExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Employment branding is the process of promoting an organization as a desirable place to work in the labor market. It involves creating a positive employer image through messaging, culture, and benefits to attract top talent.
Option A (Social influencing): This is not a standard HR term and is unrelated to employer branding.
Option B (Strategic planning): This is a broader business process, not specific to promoting the organization as an employer.
Option C (Marketing initiatives): This refers to product or service marketing, not employer branding.
A form of employee recognition that rewards top performance is:
Options:
Long service incentive.
Short-term incentive
Guaranteed annual bonus.
Pension contributions
Answer:
BExplanation:
Definition of Short-Term Incentive:
Short-term incentives are rewards given for outstanding performance within a specific period, such as bonuses, commissions, or other financial rewards.
Why Short-Term Incentive is Correct:
It directly acknowledges and rewards top performance, motivating employees to maintain high standards.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Long service incentive: Recognizes tenure, not performance.
C. Guaranteed annual bonus: Is not tied to performance but often contractual.
D. Pension contributions: Are long-term benefits unrelated to performance recognition.
International HR References:
SHRM Compensation Guidelines: Discusses short-term incentives for rewarding exceptional performance.
Which of the following is found in a candidate database?
Options:
Disciplinary actions
Job skills
Benefit expectations
Performance appraisals
Answer:
BExplanation:
A candidate database is designed to store information pertinent to recruitment and selection. It includes:
Job Skills: Key competencies and qualifications relevant to job roles, helping recruiters match candidates to positions.
Explanation of Other Options:
A. Disciplinary actions: These are internal records maintained post-hiring, not typically part of a candidate database.
C. Benefit expectations: These are discussed during negotiations and not stored in a pre-hiring database.
D. Performance appraisals: These are post-hiring evaluations, irrelevant to candidate databases.
Which of the following refers to an organizational action to help with community and environment issues?
Options:
Environment responsibility
Corporate social responsibility
Environment scanning
Corporate outreach
Answer:
BExplanation:
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) refers to organizational actions that address social, community, and environmental issues as part of its ethical obligations.
Examples: Sustainability initiatives, charitable contributions, and community outreach programs.
Explanation of Other Options:
A. Environmental responsibility: A subset of CSR focusing specifically on environmental issues.
C. Environment scanning: Refers to analyzing external business environments for trends and risks.
D. Corporate outreach: Describes community engagement efforts but does not encompass broader CSR activities.
Compensation surveys are used to:
Options:
Benchmark pay practices against competitors.
Identity hiring trends within the industry.
Calculate an organization’s return on investment (ROI).
Review an organization’s benefits program.
Answer:
AExplanation:
Compensation surveys are designed to:
Collect data on salaries, benefits, and other compensation components across similar organizations or industries.
Help organizations compare and align their pay structures with competitors to remain competitive in attracting and retaining talent.
Explanation of Other Options:
B. Identify hiring trends: Typically analyzed through labor market studies, not compensation surveys.
C. Calculate ROI: Involves financial performance metrics, unrelated to compensation surveys.
D. Review benefits programs: May be included in surveys but is not the primary purpose.
A job evaluation that compares salary to external factors is known as:
Options:
Ranking
Pay grade
Market-based
Content-based
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Job evaluation is the process of determining the relative worth of jobs within an organization to establish fair pay structures. A market-based job evaluation compares the salary of a position to external market data (e.g., industry benchmarks) to ensure competitiveness.
Option A (Ranking): The ranking method involves ordering jobs from highest to lowest value within the organization, not comparing to external factors.
Option B (Pay grade): Pay grades are salary ranges assigned to jobs, not a method of evaluation.
Option C (Market-based): Correct, as this method directly compares salaries to external market rates to determine job value.
Which of the following is the best way to ensure compliance with employment laws?
Options:
Performance intervention
HR survey
Performance evaluation
HR audit
Answer:
DExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
An HR audit is a comprehensive review of an organization’s HR policies, practices, and procedures to ensure compliance with employment laws and regulations. It identifies gaps, ensures adherence to legal standards (e.g., wage laws, anti-discrimination laws), and mitigates risks.
Option A (Performance intervention): This addresses individual performance issues, not legal compliance.
Option B (HR survey): Surveys collect employee feedback, not directly ensure legal compliance.
Option C (Performance evaluation): This assesses employee performance, not compliance with laws.
When disciplining an employee, the role of human resources is to:
Options:
Administer the disciplinary action to protect the supervisor and employee relationship
Train employees to avoid further disciplinary action
Serve in an advisory role and guide the supervisor in the process
Promote well-trained employees to supervisory roles to avoid similar issues
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
In the disciplinary process, HR’s role is to act as a neutral advisor, ensuring that the process is fair, consistent, and compliant with organizational policies and legal standards. HR guides the supervisor on how to handle the situation, including following proper procedures, documenting the issue, and ensuring the employee’s rights are protected. This helps maintain fairness and reduces the risk of legal issues.
Option A (Administer the disciplinary action to protect the supervisor and employee relationship): While HR may help maintain relationships, their primary role is not to administer the action but to advise. Supervisors typically administer discipline.
Option B (Train employees to avoid further disciplinary action): Training may follow discipline, but it is not HR’s primary role during the disciplinary process.
Option C (Serve in an advisory role and guide the supervisor in the process): Correct, as HR ensures the process is handled appropriately and legally.
Which of the following is most likely to be included in a new employee orientation handbook?
Options:
Top performers of the organization
Change management process
Budget statements
Organizational chart
Answer:
DExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
A new employee orientation handbook is designed to help new hires understand the organization, its structure, policies, and expectations. It typically includes information that helps employees integrate into the workplace, such as the company’s mission, values, policies, benefits, and structure. An organizational chart is a common inclusion because it visually represents the company’s hierarchy, helping new employees understand reporting lines and departmental structures.
Option A (Top performers of the organization): This is not typically included in an orientation handbook, as it is not directly relevant to a new employee’s onboarding process and may change frequently.
Option B (Change management process): While important for organizational development, change management processes are too complex and situational to be a standard part of an orientation handbook.
Option C (Budget statements): Budget statements are financial documents meant for management or stakeholders, not new employees, and are not relevant to orientation.
An organization of 360 employees reported a turnover rate of 5%, or ______ separation(s) in a given year.
Options:
(Not provided in original)
(Not provided in original)
(Not provided in original)
(Not provided in original)
Answer:
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Turnover rate is calculated as the percentage of employees who leave an organization over a specific period. To find the number of separations, we use the formula:
Number of separations = Total employees × (Turnover rate ÷ 100).
Given: Total employees = 360, Turnover rate = 5%.
Number of separations = 360 × (5 ÷ 100) = 360 × 0.05 = 18.
Thus, a 5% turnover rate for 360 employees results in 18 separations in the year. This calculation aligns with HR metrics commonly covered in aPHRi, which emphasizes understanding turnover and its impact on workforce planning.
Which of the following describes the act of placing employees into suitable positions?
Options:
Job design
Job matching
Workforce planning
Succession planning
Answer:
BExplanation:
Job matching refers to the process of placing employees into positions that align with their skills, experience, and qualifications. This ensures that individuals are in roles where they can perform effectively and contribute to organizational goals.
Explanation of Other Options:
A. Job design: Refers to structuring or restructuring job roles, not placement.
C. Workforce planning: Focuses on long-term staffing needs, not immediate placement.
D. Succession planning: Prepares employees for future leadership roles, not general job placement.
Which of the following tests measures the capacity for learning?
Options:
Aptitude
Attainment
Intelligence
Personality
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Aptitude tests are designed to measure an individual’s potential or capacity to learn and perform specific tasks or skills in the future. They assess inherent abilities, such as problem-solving, reasoning, or numerical skills, which indicate how well someone can acquire new knowledge or skills. In the context of HR, aptitude tests are often used during recruitment to predict a candidate’s ability to succeed in a role.
Option A (Aptitude): Correct, as aptitude tests measure the capacity for learning and future performance.
Option B (Attainment): Attainment tests measure what someone has already learned or achieved (e.g., a certification exam), not their capacity to learn.
Option C (Intelligence): Intelligence tests (e.g., IQ tests) measure cognitive abilities like reasoning and memory, which are related to learning capacity, but they are broader and not specifically focused on learning potential for a job.
The interaction between an organization and its employees is best known as:
Options:
Strategic planning
Union negotiations
Employee relations
Employee engagement
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Employee relations refers to the overall interaction between an organization and its employees, encompassing communication, conflict resolution, policy enforcement, and maintaining a positive work environment. It focuses on fostering a productive relationship.
Option A (Strategic planning): This is a broader business process, not specific to employee interactions.
Option B (Union negotiations): This is a subset of employee relations, specific to unionized environments.
Option C (Employee relations): Correct, as it broadly describes the organization-employee relationship.
Which factor is most likely to have a positive impact on employee retention?
Options:
Competitive pay
Casual dress code
Preferential treatment
Comfortable workspace
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Competitive pay is a critical factor in employee retention because it ensures employees feel fairly compensated for their work, reducing the likelihood of them seeking better-paying opportunities elsewhere. Pay is a primary driver of job satisfaction and loyalty.
Option A (Competitive pay): Correct, as it directly addresses a key reason employees stay or leave.
Option B (Casual dress code): While appreciated, a dress code has a smaller impact on retention compared to pay.
Option C (Preferential treatment): This can lead to unfairness and actually decrease retention by causing resentment.
Stalking text messages and threatening emails are examples of:
Options:
Power abuse
Cyberbullying
Interpersonal conflict
Sexual harassment
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Stalking text messages and threatening emails constitute cyberbullying, which involves using digital communication to harass, threaten, or intimidate someone. In the workplace, this behavior violates anti-harassment policies and can create a hostile work environment.
Option A (Power abuse): This involves misuse of authority, not necessarily through digital means.
Option B (Cyberbullying): Correct, as it directly describes harassment via digital communication.
Option C (Interpersonal conflict): This is a broader term for disagreements, not specific to digital harassment.
The total number of days jobs are open, divided by the total number of jobs available, is the formula used to calculate:
Options:
Turnover
Time-to-fill
Yield ratio
Vacancy costs
Answer:
BExplanation:
Definition of Time-to-Fill:
Time-to-fill measures the number of calendar days it takes to fill a job vacancy, starting from the date the job is posted to the date a candidate accepts the offer.
Formula: Time-to-Fill=Total Number of Days Jobs Are OpenTotal Number of Jobs Available\text{Time-to-Fill} = \frac{\text{Total Number of Days Jobs Are Open}}{\text{Total Number of Jobs Available}}Time-to-Fill=Total Number of Jobs AvailableTotal Number of Days Jobs Are Open
Why Time-to-Fill is Correct:
It is a key recruitment metric used to evaluate the efficiency of the hiring process.
Lower time-to-fill indicates a streamlined recruitment process, while higher values may suggest bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Turnover: Refers to the rate at which employees leave the organization and is unrelated to job openings.
C. Yield ratio: Measures the efficiency of recruiting efforts (e.g., percentage of candidates moving from one stage to the next).
D. Vacancy costs: Refers to financial losses due to unfilled positions, not the time metric.
International HR References:
SHRM Metrics Toolkit: Highlights the importance of time-to-fill for evaluating recruitment efficiency.
ISO 30414: Guidelines for human capital reporting, including recruitment metrics like time-to-fill.
When confirming a candidate’s personal and professional records, an organization may conduct a(n):
Options:
Resume screening
Background check
Behavioral interview
Employment investigation
Answer:
BExplanation:
Purpose of a Background Check:
Background checks verify a candidate’s personal and professional records, ensuring their qualifications, employment history, and criminal records (if applicable) meet organizational standards.
Why Background Check is Correct:
This process confirms the accuracy of the information provided by the candidate and minimizes risks to the organization.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Resume screening: Involves reviewing resumes to shortlist candidates but does not confirm records.
C. Behavioral interview: Evaluates behavioral traits, not factual records.
D. Employment investigation: This term is less commonly used and may imply a deeper, often internal, investigation.
International HR References:
FCRA (U.S.): Provides guidelines on conducting lawful background checks.
The main goal of a training program is:
Options:
An increase an employee effectiveness
Adherence to statutory requirements.
A decrease in an organization’s attrition rate.
Answer:
AExplanation:
The main goal of any training program is to enhance employee skills, knowledge, and capabilities to perform their roles more effectively, which directly contributes to organizational success.
Explanation of Other Options:
B. Adherence to statutory requirements: Compliance training is one aspect but not the overarching goal of all training programs.
C. A decrease in attrition: Training indirectly impacts attrition by improving job satisfaction but is not the primary objective.
A foundation fo A contingent search occurs when an organization pays a staffing agency only after successfully filling a position. This type of search is often used for single job placements or specific hiring needs.
Explanation of Other Options:
B. Online search: Refers to job postings or online recruitment efforts.
C. Retained search: Involves an upfront fee for exclusive recruitment services, not tied to filling a single position.
D. Reference search: Focuses on verifying candidate credentials, unrelated to agency hiring.
r designing and administering pay system is the:
Options:
Corporate budget strategy
Accounting policy
Compensation philosophy
Sales incentive strategy
Answer:
CExplanation:
A compensation philosophy serves as the foundation for designing and administering a pay system. It defines the organization's stance on pay competitiveness, equity, and structure relative to the market.
Explanation of Other Options:
A. Corporate budget strategy: Guides overall financial planning, not specific to pay systems.
B. Accounting policy: Focuses on financial reporting and compliance, unrelated to pay system design.
D. Sales incentive strategy: Targets specific performance bonuses, not the entire pay system.
Which of the following is the primary owner of the onboarding process?
Options:
HR manager
Line manager
Administration manager
Answer:
BExplanation:
Primary Role in Onboarding:
The line manager is directly responsible for integrating new employees into their roles, teams, and workflows. They provide role-specific guidance, set expectations, and ensure the new hire has the tools and support needed to succeed.
Why Line Manager is Correct:
Onboarding is most effective when the line manager takes ownership, as they have direct insights into the job responsibilities and team dynamics.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. HR manager: Facilitates the onboarding framework but is not primarily responsible for day-to-day integration.
C. Administration manager: Typically handles logistical aspects, not employee integration or engagement.
International HR References:
SHRM Onboarding Essentials: Emphasizes the role of line managers in onboarding.
ISO 30414: Highlights onboarding as a collaborative process with line managers playing a key role.
Which of the following are the main purposes of a total compensation system? (Select TWO options.)
Options:
To eliminate turnover for employees
To have a tool for disciplinary action
To lead the market in pay and benefits
To retain strong performing employees
To align employees' pay with organizational goals
Answer:
D, EExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
A total compensation system includes all forms of pay and benefits (e.g., salary, bonuses, health insurance) provided to employees. Its main purposes are to attract, motivate, and retain talent while ensuring alignment with organizational objectives.
Option A (To eliminate turnover for employees): While compensation can reduce turnover, “eliminating” it is unrealistic, as turnover can occur for many reasons.
Option B (To have a tool for disciplinary action): Compensation is not a disciplinary tool; discipline involves other processes.
Option C (To lead the market in pay and benefits): Leading the market may be a strategy, but it is not a main purpose of a compensation system.
Option D (To retain strong performing employees): Correct, as a key purpose is to retain talent by offering competitive rewards.
Which of the following is considered an environmental factor an organization should evaluate when seeking to have a healthy workspace?
Options:
Weather conditions
Personal hygiene
Employee morale
Air ventilation
Answer:
DExplanation:
Air ventilation is an environmental factor crucial for a healthy workspace. Proper ventilation ensures air quality, reduces the risk of respiratory issues, and enhances overall employee well-being.
Why Air Ventilation (D) is Correct:
Air ventilation is an environmental factor critical to maintaining a healthy workspace. Proper ventilation ensures adequate air circulation, reduces the concentration of airborne contaminants, and helps prevent respiratory issues and the spread of illnesses. Good air quality directly impacts employee health, productivity, and overall well-being.
An organizational structure where departments are defined by the services they provide to the organization is called a:
Options:
Hybrid structure
Functional structure
Product structure
Matrix structure
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
A functional structure organizes departments based on the services or functions they provide (e.g., HR, finance, marketing). Each department specializes in a specific area, supporting the organization’s operations.
Option A (Hybrid structure): This combines elements of different structures, not specifically service-based.
Option B (Functional structure): Correct, as it defines departments by their functional services.
Option C (Product structure): This organizes departments by product lines, not services.
Which of the following assessments is conducted to evaluate a candidate's general intelligence?
Options:
Aptitude
Cognitive
Polygraph
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
A cognitive assessment evaluates a candidate’s general intelligence, including abilities like reasoning, problem-solving, memory, and verbal or numerical skills. These tests (e.g., IQ tests) are often used in recruitment to predict job performance.
Option A (Aptitude): Aptitude tests measure specific abilities or potential to learn, not general intelligence.
Option B (Cognitive): Correct, as cognitive assessments focus on general intelligence.
A key benefit of an employee recognition program is to:
Options:
increase job performance
promote company visibility
support employee advancement
improve employee accountability
Answer:
AExplanation:
Employee recognition programs are designed to acknowledge and reward positive behavior, which in turn encourages high job performance. HRCI notes that recognizing employees for their contributions motivates them to maintain or improve performance, benefiting both the individual and the organization.
The most common way to source passive job candidates is to use:
Options:
Professional associations.
A jon fair
An internal posting
Radio advertisement
Answer:
AExplanation:
Professional associations are one of the most common ways to source passive job candidates, as they often house directories, forums, and networking opportunities for experienced professionals who are not actively seeking jobs but are open to discussions.
Why Professional Associations (A) is Correct:
Professional associations are one of the most effective ways to source passive candidates, as they are typically composed of individuals who are already employed and engaged in their respective industries or professions. These associations provide networking opportunities, industry events, and specialized job boards where recruiters can identify and connect with high-caliber talent who may not be actively looking for new roles.
Medical records are usually kept separate from employee general data for:
Options:
Emergency use
Privacy protection
Background checks
Ease of accessibility
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Medical records are sensitive and contain personal health information that must be protected under privacy laws (e.g., HIPAA in the U.S., GDPR in the EU). Keeping them separate from general employee data ensures privacy protection, limiting access to authorized personnel only and reducing the risk of unauthorized disclosure.
Option A (Emergency use): While medical records may be used in emergencies, this is not the primary reason for separation.
Option B (Privacy protection): Correct, as it ensures compliance with privacy laws.
Option C (Background checks): Medical records are not typically part of background checks.
An employee who has come to a time where there is little or no possibility of promotion has reached a(n):
Options:
Dual career ladder
Career plateau
Employment conflict
Vesting cliff
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
A career plateau occurs when an employee reaches a point in their career where there is little or no opportunity for further promotion or advancement, often due to organizational structure, lack of openings, or the employee’s current skill level. This can impact motivation and requires HR to provide alternative development opportunities.
Option A (Dual career ladder): This is a system allowing employees to advance in technical or managerial tracks, not a lack of promotion.
Option B (Career plateau): Correct, as it describes the situation where promotion opportunities are limited.
Option C (Employment conflict): This refers to disputes or issues in the workplace, not a lack of promotion.
Which of the following best describes a primary aspect of a grievance procedure?
Options:
Leads to a positive resolution for the employee
Initiated by the employer
Protection of the employer
Protection of the employee
Answer:
DExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
A grievance procedure is a formal process for employees to raise concerns or complaints about workplace issues, such as unfair treatment, policy violations, or working conditions. The primary aspect of a grievance procedure is to protect the employee by providing a structured, fair mechanism to address their concerns, ensuring they are heard and treated equitably, often with legal protections against retaliation. This aligns with the aPHRi focus on employee relations, which emphasizes maintaining a fair and transparent workplace.
Option A (Leads to a positive resolution for the employee): While the goal of a grievance procedure is to resolve issues, a positive outcome for the employee is not guaranteed. The resolution may favor the employer or be neutral, depending on the facts.
Option B (Initiated by the employer): Grievance procedures are typically initiated by the employee, not the employer, as they are designed to address employee concerns.
Option C (Protection of the employer): While a grievance procedure may indirectly protect the employer by resolving issues before they escalate (e.g., into lawsuits), its primary purpose is to safeguard the employee’s rights.
Which of the following advantages do performance appraisals offer an employee?
Options:
Direct feedback
Training objectives
Financial incentives
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Performance appraisals provide employees with direct feedback on their work, highlighting strengths, areas for improvement, and progress toward goals. This feedback helps employees understand expectations and grow professionally.
Option A (Direct feedback): Correct, as appraisals offer clear, personalized feedback.
Option B (Training objectives): While appraisals may identify training needs, this is an outcome, not a direct advantage.
An employment has strong interpersonal traits but below average technical skills. If the employee’s manager gives an overall performance rating of ‘excellent’ based on the employee’s personally.
Options:
The halo effect
A contrast error
A strictness error
The recency effect
Answer:
AExplanation:
The halo effect occurs when a manager gives an employee an overall performance rating based on one positive trait (e.g., interpersonal skills) while ignoring other areas (e.g., technical skills). This cognitive bias skews the evaluation toward one aspect of the employee's performance.
Explanation of Other Options:
B. A contrast error: Happens when an employee is compared to others rather than an objective standard.
C. A strictness error: Refers to consistently rating employees lower than deserved.
Managers write descriptions about an employee's performance using the:
Options:
Rating method
Narrative method
Comparison method
Critical incident method
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
The narrative method of performance appraisal involves managers writing detailed, descriptive accounts of an employee’s performance, often in essay or paragraph form. This method focuses on providing qualitative feedback about the employee’s strengths, weaknesses, and overall contributions.
Option A (Rating method): This involves assigning numerical or categorical ratings (e.g., 1-5) to performance criteria, not writing descriptions.
Option B (Narrative method): Correct, as this method specifically involves writing descriptive accounts of performance.
Option C (Comparison method): This involves ranking employees against each other (e.g., forced ranking), not writing descriptions.
To help protect the internal network, an organization should:
Options:
Warm employees by sharing suspicious emails.
Prevent the installation of unlicensed software.
Reveal passwords only to supervisors and managers.
Give all employees access to the organization’s firewall.
Answer:
BExplanation:
Protecting Internal Networks:
Unlicensed software can pose significant risks, including malware, data breaches, and legal liabilities. Preventing its installation ensures a secure network environment.
Why Preventing Unlicensed Software is Correct:
This practice reduces vulnerabilities and ensures compliance with software licensing laws, safeguarding the network.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Warn employees by sharing suspicious emails: While useful, it’s a reactive measure and less effective as a preventive strategy.
C. Reveal passwords only to supervisors and managers: Passwords should never be shared, regardless of rank.
D. Give all employees access to the organization’s firewall: This would compromise the firewall’s effectiveness.
International HR References:
ISO/IEC 27001: Recommends software compliance and cybersecurity measures.
Which of the following is a key benefit of HR policies and procedures?
Options:
Giving employees a complete list of all rules
Helping managers to reduce absenteeism
Making it easier for HR to punish wrongdoers
Helping managers resolve employee relations issues
Answer:
DExplanation:
Purpose of HR Policies and Procedures:
HR policies and procedures provide a structured framework for managing workplace expectations, addressing issues, and ensuring compliance with employment laws.
Why Resolving Employee Relations Issues is Key:
Policies and procedures offer clear guidance on conflict resolution, grievance handling, and workplace conduct, empowering managers to address employee concerns effectively and fairly.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Giving employees a complete list of all rules: Policies focus on critical guidelines, not exhaustive rules.
B. Helping managers to reduce absenteeism: While policies may influence attendance, this is not their primary benefit.
C. Making it easier for HR to punish wrongdoers: Policies aim to promote fairness, not punitive measures.
International HR References:
SHRM Essentials of Human Resources: Highlights the role of policies in maintaining positive employee relations.
ISO 30414: Encourages transparent HR policies for conflict resolution.
Compensation surveys are used to:
Options:
Benchmark pay practices against competitors
Identify hiring trends within the industry
Calculate an organization's return on investment (ROI)
Review an organization's benefits program
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Compensation surveys collect data on pay and benefits from other organizations, typically within the same industry or region, to help employers benchmark their pay practices against competitors. This ensures their compensation is competitive to attract and retain talent.
Option A (Benchmark pay practices against competitors): Correct, as this is the primary use of compensation surveys.
Option B (Identify hiring trends within the industry): While surveys may provide some hiring insights, their main focus is on pay data.
Option C (Calculate an organization's return on investment (ROI)): ROI is a financial metric, not directly related to compensation surveys.
Which of the following is a reason why HT should monitor internal social platforms?
Options:
To encourage self-management
To encourage social behaviors
To gauge employee absenyteeism
To gauge the employee morale
Answer:
DExplanation:
Monitoring Internal Social Platforms:
Internal social platforms provide insights into employee interactions, concerns, and overall sentiment, offering a pulse on workplace morale.
Why Gauging Employee Morale is Correct:
Monitoring these platforms helps HR identify issues, improve engagement, and address challenges affecting employee satisfaction and productivity.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. To encourage self-management: Internal platforms are not focused on self-management practices.
B. To encourage social behaviors: Encouraging behavior is secondary to understanding morale.
C. To gauge employee absenteeism: Absenteeism is tracked through attendance systems, not social platforms.
International HR References:
Gallup Employee Engagement Reports: Highlights monitoring tools for assessing morale.
What department is responsible for producing a product from available resources?
Options:
Legal
Operations
Marketing
Sales
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
The operations department is responsible for managing the production process, which includes transforming available resources (e.g., raw materials, labor) into finished products or services. Operations ensures efficiency and quality in production, a key function in manufacturing or service-oriented organizations.
Option A (Legal): The legal department handles compliance and legal issues, not production.
Option B (Operations): Correct, as operations oversees the production process.
Option C (Marketing): Marketing focuses on promoting products, not producing them.
Which of the following are the best reasons to develop a membership program? (Select TWO options.)
Options:
Performance appraisals
Succession planning
Reward and discipline
Career development
Reduce absenteeism
Answer:
B, DExplanation:
Comprehensive Detailed Explanation:
Succession planning: Developing a membership program supports identifying and nurturing talent for future leadership roles.
Career development: Membership programs often provide resources and opportunities to enhance employees’ skills and advance their careers.
Explanation of Other Options:
A. Performance appraisals: Focuses on evaluation, not membership programs.
C. Reward and discipline: Membership programs are not related to managing behavior.
E. Reduce absenteeism: Indirectly impacted but not the primary goal.
Which of the following terms is used to describe working outside of the regular work location on a regular basis?
Options:
Compressed schedule
Telecommuting
Job sharing
Flex-time
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed in Depth Explanation:
Telecommuting refers to a work arrangement where employees perform their job duties from a location outside the traditional office, such as from home, on a regular basis, often using technology to communicate with the workplace. This is a common practice in modern HR to support work-life balance and flexibility.
Option A (Compressed schedule): This involves working the same number of hours in fewer days (e.g., a 40-hour week in 4 days), typically at the regular workplace, not outside it.
Option B (Telecommuting): Correct, as it directly describes working outside the regular work location regularly.
Option C (Job sharing): This is when two or more employees share the responsibilities of one full-time position, not necessarily related to location.
A typical performance management cycle includes:
Options:
Screening, selection, interview, and hiring
Planning, execution, assessment, and review
Welcome, develop, communicate, and encourage.
Orientate, acquaint, present information, and inspire
Answer:
BExplanation:
Performance Management Cycle Overview:
A performance management cycle involves a continuous process of setting objectives (planning), executing work, assessing outcomes, and reviewing performance to ensure alignment with organizational goals.
Why Planning, Execution, Assessment, and Review is Correct:
This cycle reflects the stages of performance management: setting expectations, monitoring progress, evaluating results, and providing feedback.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Screening, selection, interview, and hiring: Refers to recruitment, not performance management.
C. Welcome, develop, communicate, and encourage: Focuses on onboarding, not performance management.
D. Orientate, acquaint, present information, and inspire: Refers to employee orientation.
International HR References:
SHRM Performance Management Guidelines: Emphasizes a cyclical approach to managing performance.
==================
Unlock aPHRi Features
- aPHRi All Real Exam Questions
- aPHRi Exam easy to use and print PDF format
- Download Free aPHRi Demo (Try before Buy)
- Free Frequent Updates
- 100% Passing Guarantee by Activedumpsnet
Questions & Answers PDF Demo
- aPHRi All Real Exam Questions
- aPHRi Exam easy to use and print PDF format
- Download Free aPHRi Demo (Try before Buy)
- Free Frequent Updates
- 100% Passing Guarantee by Activedumpsnet
