- Home
- HP
- Aruba-ACNSA
- HPE6-A78
- HPE6-A78 - Aruba Certified Network Security Associate Exam
HP HPE6-A78 Aruba Certified Network Security Associate Exam Exam Practice Test
Aruba Certified Network Security Associate Exam Questions and Answers
A company has AOS-CX switches deployed in a two-tier topology that uses OSPF routing at the core.
You need to prevent ARP poisoning attacks. To meet this need, what is one technology that you could apply to user VLANs on access layer switches? (Select two.)
Options:
ARP inspection
OSPF passive interface
BPDU guard (protection)
DHCPv4 snooping
BPDU filtering
Answer:
A, DExplanation:
The scenario involves AOS-CX switches in a two-tier topology (access and core layers) using OSPF routing at the core. The goal is to prevent ARP poisoning attacks on user VLANs at the access layer switches, where end-user devices connect. ARP poisoning (also known as ARP spoofing) is an attack where a malicious device sends fake ARP messages to associate its MAC address with the IP address of another device (e.g., the default gateway), allowing the attacker to intercept traffic.
ARP Inspection (Dynamic ARP Inspection, DAI): This feature prevents ARP poisoning by validating ARP packets against a trusted database of IP-to-MAC bindings. On AOS-CX switches, ARP inspection uses the DHCP snooping binding table to verify that ARP messages come from legitimate devices. If an ARP packet does not match the binding table, it is dropped.
DHCPv4 Snooping: This feature protects against rogue DHCP servers and builds a binding table of legitimate IP-to-MAC mappings by snooping DHCP traffic. The binding table is used by ARP inspection to validate ARP packets. DHCP snooping must be enabled before ARP inspection can function effectively, as it provides the trusted data for validation.
Option A, "ARP inspection," is correct. ARP inspection (DAI) directly prevents ARP poisoning by ensuring that ARP packets are legitimate, making it a key technology for this purpose.
Option B, "OSPF passive interface," is incorrect. OSPF passive interface is used to prevent OSPF from sending routing updates on specific interfaces, typically to reduce routing protocol traffic on user-facing interfaces. It does not prevent ARP poisoning, which is a Layer 2 attack.
Option C, "BPDU guard (protection)," is incorrect. BPDU guard protects against spanning tree protocol (STP) attacks by disabling a port if it receives BPDUs (e.g., from an unauthorized switch). It does not address ARP poisoning, which is unrelated to STP.
Option D, "DHCPv4 snooping," is correct. DHCP snooping is a prerequisite for ARP inspection, as it builds the binding table used to validate ARP packets. It also protects against rogue DHCP servers, which can indirectly contribute to ARP poisoning by assigning incorrect IP addresses.
Option E, "BPDU filtering," is incorrect. BPDU filtering prevents a port from sending or receiving BPDUs, which can be used to protect against STP attacks, but it does not prevent ARP poisoning.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-CX 10.12 Security Guide states:
"To prevent ARP poisoning attacks on user VLANs, enable Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) on access layer switches. DAI validates ARP packets against the DHCP snooping binding table to ensure they come from legitimate devices. Use the command ip arp inspection vlan
Additionally, the guide notes:
"DHCP snooping and ARP inspection work together to protect against Layer 2 attacks like ARP poisoning. DHCP snooping builds a trusted database of IP-to-MAC bindings, which ARP inspection uses to filter out malicious ARP packets." (Page 146, Best Practices Section)
What is one benefit of enabling Enhanced Secure mode on an ArubaOS-Switch?
Options:
Control Plane policing rate limits edge ports to mitigate DoS attacks on network servers.
A self-signed certificate is automatically added to the switch trusted platform module (TPM).
Insecure algorithms for protocol such as SSH are automatically disabled.
All interfaces have 802.1X authentication enabled on them by default.
Answer:
CExplanation:
In the context of ArubaOS-Switches, enabling Enhanced Secure mode has several benefits, one of which includes disabling insecure algorithms for protocols such as SSH. This is in line with security best practices, as older, less secure algorithms are known to be vulnerable to various types of cryptographic attacks. When Enhanced Secure mode is enabled, the switch automatically restricts the use of such algorithms, thereby enhancing the security of management access.
What is one method for HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) to use DHCP to classify an endpoint?
Options:
It can determine information such as the endpoint OS from the order of options listed in Option 55 of a DHCP Discover packet.
It can respond to a client’s DHCP Discover with different DHCP Offers and then analyze the responses to identify the client OS.
It can snoop DHCP traffic to register the clients’ IP addresses. It then knows where to direct its HTTP requests to actively probe for information about the client.
It can alter the DHCP Offer to insert itself as a proxy gateway. It will then be inline in the traffic flow and can apply traffic analytics to classify clients.
Answer:
AExplanation:
HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) uses device profiling to classify endpoints, and one of its passive profiling methods involves analyzing DHCP traffic. DHCP fingerprinting is a technique where ClearPass examines the DHCP packets sent by a client, particularly the DHCP Discover packet, to identify the device’s operating system or type based on specific attributes.
Option A, "It can determine information such as the endpoint OS from the order of options listed in Option 55 of a DHCP Discover packet," is correct. DHCP Option 55 (Parameter Request List) is a field in the DHCP Discover packet where the client specifies the list of DHCP options it requests from the server. The order and combination of these options are often unique to specific operating systems or device types (e.g., Windows, Linux, macOS, or IoT devices). ClearPass maintains a database of DHCP fingerprints and matches the Option 55 data against this database to classify the endpoint.
Option B, "It can respond to a client’s DHCP Discover with different DHCP Offers and then analyze the responses," is incorrect because ClearPass does not act as a DHCP server or send DHCP Offers. It passively snoops DHCP traffic rather than actively responding to DHCP requests.
Option C, "It can snoop DHCP traffic to register the clients’ IP addresses," is partially correct in that ClearPass does snoop DHCP traffic, but the purpose is not just to register IP addresses for HTTP probing. While ClearPass can use IP addresses for active probing (e.g., HTTP or SNMP), the question specifically asks about using DHCP to classify, which is done via fingerprinting, not IP registration.
Option D, "It can alter the DHCP Offer to insert itself as a proxy gateway," is incorrect because ClearPass does not modify DHCP packets or act as a proxy gateway. This is not a function of ClearPass in the context of DHCP-based profiling.
The HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager 6.11 User Guide states:
"ClearPass can profile devices using DHCP fingerprinting, a passive profiling method. When a device sends a DHCP Discover packet, ClearPass examines the packet’s attributes, including the order of options in DHCP Option 55 (Parameter Request List). The combination and order of these options are often unique to specific operating systems or device types. ClearPass matches these attributes against its DHCP fingerprint database to classify the device (e.g., identifying a device as a Windows 10 laptop or an Android phone)." (Page 247, DHCP Fingerprinting Section)
Additionally, the ClearPass Device Insight Data Sheet notes:
"DHCP fingerprinting allows ClearPass to passively collect device information without interfering with network traffic. By analyzing DHCP Option 55, ClearPass can accurately determine the device’s operating system and type, enabling precise policy enforcement." (Page 3)
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the settings on the company's MCs.

You have deployed about 100 new HPE Aruba Networking 335 APs. What is required for the APs to become managed?
Options:
Installing CA-signed certificates on the APs
Approving the APs as authorized APs on the AP whitelist
Installing self-signed certificates on the APs
Configuring a PAPI key that matches on the APs and MCs
Answer:
BExplanation:
The scenario involves an AOS-8 Mobility Controller (MC) with Control Plane Security (CPSec) enabled and auto certificate provisioning disabled. CPSec is a feature that secures the control plane communication between the MC and APs using certificates. When CPSec is enabled, APs must be authorized and trusted by the MC to become managed.
CPSec Enabled, Auto Cert Provisioning Disabled: When CPSec is enabled, APs must have a valid certificate to establish a secure control plane connection with the MC. If auto certificate provisioning is disabled (as shown in the exhibit), the MC does not automatically provision certificates to the APs. Instead, the APs must already have a factory-installed certificate (or a manually installed certificate), and the MC must trust the AP’s certificate by having the issuing CA in its trust list. Additionally, the AP must be on the MC’s AP whitelist to be authorized.
AP Whitelist: The AP whitelist is a list of authorized APs maintained on the MC (or Mobility Master, MM, if present). For an AP to become managed, its MAC address must be in the whitelist, especially when CPSec is enabled and auto provisioning is disabled. This ensures that only authorized APs can connect to the MC.
Option A, "Installing CA-signed certificates on the APs," is incorrect because HPE Aruba Networking APs, such as the 335 series, come with factory-installed certificates signed by Aruba’s CA. These certificates are sufficient for CPSec, provided the MC trusts the Aruba CA (which is typically preconfigured). Manually installing CA-signed certificates is not required unless the factory certificates are not used or trusted.
Option B, "Approving the APs as authorized APs on the AP whitelist," is correct. With CPSec enabled and auto cert provisioning disabled, the APs must be explicitly authorized by adding their MAC addresses to the AP whitelist on the MC. This step ensures that the MC accepts the AP’s certificate and allows it to become managed.
Option C, "Installing self-signed certificates on the APs," is incorrect because self-signed certificates are not typically used for CPSec. APs use factory-installed certificates, and the MC must trust the issuing CA. Self-signed certificates would require manual trust configuration on the MC, which is not a standard practice.
Option D, "Configuring a PAPI key that matches on the APs and MCs," is incorrect. PAPI (Protocol for AP Provisioning and Information) keys are used for securing communication between APs and the MC in non-CPSec environments or for specific configurations (e.g., when CPSec is disabled). When CPSec is enabled, certificate-based authentication replaces the need for a PAPI key.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide states:
"When Control Plane Security (CPSec) is enabled and auto certificate provisioning is disabled, APs must be authorized by adding their MAC addresses to the AP whitelist on the Mobility Controller (or Mobility Master). The AP uses its factory-installed certificate to establish a secure control plane connection with the MC. The MC must trust the CA that issued the AP’s certificate (e.g., Aruba’s CA), and the AP must be in the whitelist to become managed. To add an AP to the whitelist, navigate to Configuration > Access Points > AP Whitelist in the MC UI and add the AP’s MAC address." (Page 395, CPSec Configuration Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking CPSec Deployment Guide notes:
"If auto cert provisioning is disabled, the AP whitelist becomes mandatory for CPSec. Each AP must be explicitly approved by adding its MAC address to the whitelist, ensuring that only authorized APs can connect to the MC. The AP’s factory certificate is used for authentication, and no manual certificate installation is required on the AP." (Page 12, CPSec with Manual Provisioning Section)
What is an Authorized client, as defined by AOS Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIP)?
Options:
A client that is on the WIP whitelist
A client that has a certificate issued by a trusted Certification Authority (CA)
A client that is NOT on the WIP blacklist
A client that has successfully authenticated to an authorized AP and passed encrypted traffic
Answer:
DExplanation:
The AOS Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIP) in an AOS-8 architecture (Mobility Controllers or Mobility Master) is designed to detect and mitigate wireless threats, such as rogue APs and unauthorized clients. WIP classifies clients and APs based on their behavior and status in the network.
Authorized Client Definition: In the context of WIP, an "Authorized" client is one that has successfully authenticated to an authorized AP (an AP managed by the MC and part of the company’s network) and is actively passing encrypted traffic. This typically means the client has completed 802.1X authentication (e.g., in a WPA3-Enterprise network) or PSK authentication (e.g., in a WPA3-Personal network) and is communicating securely with the AP.
Option D, "A client that has successfully authenticated to an authorized AP and passed encrypted traffic," is correct. This matches the WIP definition of an Authorized client: the client must authenticate to an AP that is classified as "Authorized" (i.e., part of the company’s network) and must be passing encrypted traffic, indicating a secure connection (e.g., using WPA3 encryption).
Option A, "A client that is on the WIP whitelist," is incorrect. WIP does not use a client whitelist for classification. The AP whitelist is used to authorize APs, not clients. Client classification (e.g., Authorized, Interfering) is based on their authentication status and connection to authorized APs.
Option B, "A client that has a certificate issued by a trusted Certification Authority (CA)," is incorrect. While a certificate might be used for 802.1X authentication (e.g., EAP-TLS), WIP does not classify clients as Authorized based on their certificate status. The classification depends on successful authentication to an authorized AP and encrypted traffic.
Option C, "A client that is NOT on the WIP blacklist," is incorrect. WIP does use blacklisting (e.g., for clients that violate security policies), but being "not on the blacklist" does not make a client Authorized. A client must actively authenticate to an authorized AP and pass encrypted traffic to be classified as Authorized.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide states:
"In the Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) system, an ‘Authorized’ client is defined as a client that has successfully authenticated to an authorized AP and is passing encrypted traffic. An authorized AP is one that is managed by the Mobility Controller and part of the company’s network. For example, a client that completes 802.1X authentication to an authorized AP using WPA3-Enterprise and sends encrypted traffic is classified as Authorized." (Page 414, WIP Client Classification Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking Security Guide notes:
"WIP classifies clients as ‘Authorized’ if they have authenticated to an authorized AP and are passing encrypted traffic, indicating a secure connection. Clients that are not authenticated or are connected to rogue or neighbor APs are classified as ‘Interfering’ or other categories, depending on their behavior." (Page 78, WIP Classifications Section)
You have been instructed to look in the ArubaOS Security Dashboard's client list. Your goal is to find clients that belong to the company and have connected to devices that might belong to hackers.
Which client fits this description?
Options:
MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:70:ab; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: Rogue
MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6e:c5; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: Neighbor
MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6e:60; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: Authorized
MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6d:a4; Client Classification: Authorized; AP Classification: Rogue
Answer:
DExplanation:
The ArubaOS Security Dashboard, part of the AOS-8 architecture (Mobility Controllers or Mobility Master), provides visibility into wireless clients and access points (APs) through its Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) system. The goal is to identify clients that belong to the company (i.e., authorized clients) and have connected to devices that might belong to hackers (i.e., rogue APs).
Client Classification:
Authorized: A client that has successfully authenticated to an authorized AP and is recognized as part of the company’s network (e.g., an employee device).
Interfering: A client that is not authenticated to the company’s network and is considered external or potentially malicious.
AP Classification:
Authorized: An AP that is part of the company’s network and managed by the MC/MM.
Rogue: An AP that is not authorized and is suspected of being malicious (e.g., connected to the company’s wired network without permission).
Neighbor: An AP that is not part of the company’s network but is not connected to the wired network (e.g., a nearby AP from another organization).
The requirement is to find a client that is authorized (belongs to the company) and connected to a rogue AP (might belong to hackers).
Option A: MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:70:ab; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: RogueThis client is classified as "Interfering," meaning it does not belong to the company. Although it is connected to a rogue AP, it does not meet the requirement of being a company client.
Option B: MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6e:c5; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: NeighborThis client is "Interfering" (not a company client) and connected to a "Neighbor" AP, which is not considered a hacker’s device (it’s just a nearby AP).
Option C: MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6e:60; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: AuthorizedThis client is "Interfering" (not a company client) and connected to an "Authorized" AP, which is part of the company’s network, not a hacker’s device.
Option D: MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6d:a4; Client Classification: Authorized; AP Classification: RogueThis client is "Authorized," meaning it belongs to the company, and it is connected to a "Rogue" AP, which might belong to hackers. This matches the requirement perfectly.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide states:
"The Security Dashboard in ArubaOS provides a client list that includes the client classification and the AP classification for each client. A client classified as ‘Authorized’ has successfully authenticated to an authorized AP and is part of the company’s network. A ‘Rogue’ AP is an unauthorized AP that is suspected of being malicious, often because it is connected to the company’s wired network (e.g., detected via Eth-Wired-Mac-Table match). To identify potential security risks, look for authorized clients connected to rogue APs, as this may indicate that a company device has connected to a hacker’s AP." (Page 415, Security Dashboard Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking Security Guide notes:
"An ‘Authorized’ client is one that has authenticated to an AP managed by the controller, typically an employee or corporate device. A ‘Rogue’ AP is classified as such if it is not authorized and poses a potential threat, such as being connected to the corporate LAN. Identifying authorized clients connected to rogue APs is critical for detecting potential man-in-the-middle attacks." (Page 78, WIP Classifications Section)
You have an Aruba solution with multiple Mobility Controllers (MCs) and campus APs. You want to deploy a WPA3-Enterprise WLAN and authenticate users to Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) with EAP-TLS.
What is a guideline for ensuring a successful deployment?
Options:
Avoid enabling CNSA mode on the WLAN, which requires the internal MC RADIUS server.
Ensure that clients trust the root CA for the MCs’ Server Certificates.
Educate users in selecting strong passwords with at least 8 characters.
Deploy certificates to clients, signed by a CA that CPPM trusts.
Answer:
DExplanation:
For WPA3-Enterprise with EAP-TLS, it's crucial that clients have a trusted certificate installed for the authentication process. EAP-TLS relies on a mutual exchange of certificates for authentication. Deploying client certificates signed by a CA that CPPM trusts ensures that the ClearPass Policy Manager can verify the authenticity of the client certificates during the TLS handshake process. Trust in the root CA is typically required for the server side of the authentication process, not the client side, which is covered by the client’s own certificate.
What is a use case for tunneling traffic between an Aruba switch and an AruDa Mobility Controller (MC)?
Options:
applying firewall policies and deep packet inspection to wired clients
enhancing the security of communications from the access layer to the core with data encryption
securing the network infrastructure control plane by creating a virtual out-of-band-management network
simplifying network infrastructure management by using the MC to push configurations to the switches
Answer:
CExplanation:
Tunneling traffic between an Aruba switch and an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC) allows for the centralized application of firewall policies and deep packet inspection to wired clients. By directing traffic through the MC, network administrators can implement a consistent set of security policies across both wired and wireless segments of the network, enhancing overall network security posture.
You are deploying a new wireless solution with an HPE Aruba Networking Mobility Master (MM), Mobility Controllers (MCs), and campus APs (CAPs). The solution will include a WLAN that uses Tunnel for the forwarding mode and WPA3-Enterprise for the security option.
You have decided to assign the WLAN to VLAN 301, a new VLAN. A pair of core routing switches will act as the default router for wireless user traffic.
Which links need to carry VLAN 301?
Options:
Only links on the path between APs and the core routing switches
Only links on the path between APs and the MC
All links in the campus LAN to ensure seamless roaming
Only links between MC ports and the core routing switches
Answer:
DExplanation:
In an HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 architecture with a Mobility Master (MM), Mobility Controllers (MCs), and campus APs (CAPs), the WLAN is configured to use Tunnel forwarding mode and WPA3-Enterprise security. In Tunnel mode, all user traffic from the APs is encapsulated in a GRE tunnel and sent to the MC, which then forwards the traffic to the appropriate VLAN. The WLAN is assigned to VLAN 301, and the core routing switches act as the default router for wireless user traffic.
Tunnel Forwarding Mode: In this mode, the AP does not directly place user traffic onto the wired network. Instead, the AP tunnels all user traffic to the MC over a GRE tunnel. The MC then decapsulates the traffic and places it onto the wired network in the specified VLAN (VLAN 301 in this case). This means the VLAN tagging for user traffic occurs at the MC, not at the AP.
VLAN 301 Assignment: Since the WLAN is assigned to VLAN 301, the MC will tag user traffic with VLAN 301 when forwarding it to the wired network. The core routing switches, acting as the default router, need to receive this traffic on VLAN 301 to route it appropriately.
Therefore, VLAN 301 needs to be carried on the links between the MC ports and the core routing switches, as this is where the MC forwards the user traffic after decapsulating it from the GRE tunnel.
Option A, "Only links on the path between APs and the core routing switches," is incorrect because, in Tunnel mode, the APs do not directly forward user traffic to the wired network. The traffic is tunneled to the MC, so the links between the APs and the core switches do not need to carry VLAN 301 for user traffic (though they may carry other VLANs for AP management).
Option B, "Only links on the path between APs and the MC," is incorrect for the same reason. The GRE tunnel between the AP and MC carries encapsulated user traffic, and VLAN 301 tagging occurs at the MC, not on the AP-to-MC link.
Option C, "All links in the campus LAN to ensure seamless roaming," is incorrect because VLAN 301 only needs to be present where the MC forwards user traffic to the wired network (i.e., between the MC and the core switches). Extending VLAN 301 to all links is unnecessary and could introduce security or scalability issues.
Option D, "Only links between MC ports and the core routing switches," is correct because the MC places user traffic onto VLAN 301 and forwards it to the core switches, which act as the default router.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide states:
"In Tunnel forwarding mode, the AP encapsulates all user traffic in a GRE tunnel and sends it to the Mobility Controller (MC). The MC decapsulates the traffic and forwards it to the wired network on the VLAN assigned to the WLAN. For example, if the WLAN is assigned to VLAN 301, the MC tags the user traffic with VLAN 301 and sends it out of its wired interface to the upstream switch. Therefore, the VLAN must be configured on the links between the MC and the upstream switch or router that acts as the default gateway for the VLAN." (Page 275, Tunnel Forwarding Mode Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking Wireless LAN Design Guide notes:
"When using Tunnel mode, the VLAN assigned to the WLAN must be carried on the wired links between the Mobility Controller and the default router for the VLAN. The links between the APs and the MC do not need to carry the user VLAN, as all traffic is tunneled to the MC, which handles VLAN tagging." (Page 52, VLAN Configuration Section)
You have been authorized to use containment to respond to rogue APs detected by ArubaOS Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP). What is a consideration for using tarpit containment versus traditional wireless containment?
Options:
Rather than function wirelessly, tarpit containment sends ARP frames over the wired network to poison rogue APs ARP tables and prevent them from transmitting on the wired network.
Rather than target all clients connected to rogue APs, tarpit containment targets only authorized clients that are connected to a rogue AP, reducing the chance of negative effects on neighbors.
Tarpit containment does not require an RF Protect license to function, while traditional wireless containment does.
Tarpit containment forms associations with clients to enable more effective containment with fewer disassociation frames than traditional wireless containment.
Answer:
DExplanation:
Tarpit containment is a method used in ArubaOS Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) to contain rogue APs. It differs from traditional wireless containment in several ways, particularly in how it interacts with clients and manages network resources.
Tarpit containment works by spoofing frames from an AP to confuse a client about its association. It forces the client to associate with a fake channel or BSSID, which is more efficient than rogue containment via repeated de-authorization requests. This method is designed to be less disruptive and more resource-efficient1.
Here’s why the other options are not correct:
Option A is incorrect because tarpit containment does not involve sending ARP frames over the wired network. It operates wirelessly by creating a fake channel or BSSID.
Option B is incorrect because tarpit containment does not selectively target authorized clients; it affects all clients connected to the rogue AP.
Option C is incorrect because tarpit containment does require an RF Protect license to function2.
Therefore, Option D is the correct answer. Tarpit containment is more effective at keeping clients off the network with fewer disassociation frames than traditional wireless containment. It achieves this by forming associations with clients, which leads to a more efficient use of airtime and reduces the chance of negative effects on legitimate network users12.
You are managing an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC). What is a reason for adding a "Log Settings" definition in the ArubaOS Diagnostics > System > Log Settings page?
Options:
Configuring the Syslog server settings for the server to which the MC forwards logs for a particular category and level
Configuring the MC to generate logs for a particular event category and level, but only for a specific user or AP.
Configuring a filter that you can apply to a defined Syslog server in order to filter events by subcategory
Configuring the log facility and log format that the MC will use for forwarding logs to all Syslog servers
Answer:
AExplanation:
The primary reason for adding a "Log Settings" definition in the ArubaOS Diagnostics > System > Log Settings page is to configure the Syslog server settings for the server to which the Mobility Controller (MC) forwards logs for a particular category and level. This setting enables the MC to send detailed logs to a Syslog server for centralized logging and monitoring, which is essential for troubleshooting, security analysis, and compliance with various policies.
What is one practice that can help you to maintain a digital chain or custody In your network?
Options:
Enable packet capturing on Instant AP or Moodily Controller (MC) datepath on an ongoing basis
Enable packet capturing on Instant AP or Mobility Controller (MC) control path on an ongoing basis.
Ensure that all network infrastructure devices receive a valid clock using authenticated NTP
Ensure that all network Infrastructure devices use RADIUS rather than TACACS+ to authenticate managers
Answer:
CExplanation:
To maintain a digital chain of custody in a network, a crucial practice is to ensure that all network infrastructure devices receive a valid clock using authenticated Network Time Protocol (NTP). Accurate and synchronized time stamps are essential for creating reliable and legally defensible logs. Authenticated NTP ensures that the time being set on devices is accurate and that the time source is verified, which is necessary for correlating logs from different devices and for forensic analysis.
What is a correct guideline for the management protocols that you should use on ArubaOS-Switches?
Options:
Disable Telnet and use TFTP instead.
Disable SSH and use https instead.
Disable Telnet and use SSH instead
Disable HTTPS and use SSH instead
Answer:
CExplanation:
In managing ArubaOS-Switches, the best practice is to disable less secure protocols such as Telnet and use more secure alternatives like SSH (Secure Shell). SSH provides encrypted connections between network devices, which is critical for maintaining the security and integrity of network communications. This guideline is aligned with general security best practices that prioritize the use of protocols with strong, built-in encryption mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access and ensure data privacy.
You have been instructed to look in an AOS Security Dashboard’s client list. Your goal is to find clients that belong to the company and have connected to devices that might belong to hackers.
Which client fits this description?
Options:
MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6d:a4; Client Classification: Authorized; AP Classification: Suspected Rogue
MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6e:c5; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: Neighbor
MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6e:60; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: Interfering
MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:70:ab; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: Suspected Rogue
Answer:
AExplanation:
The AOS Security Dashboard in an AOS-8 solution (Mobility Controllers or Mobility Master) provides a client list through its Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) system, showing the classification of clients and the APs they are connected to. The goal is to identify clients that belong to the company (Authorized clients) and have connected to devices that might belong to hackers (rogue or suspected rogue APs).
Client Classification:
Authorized: A client that has successfully authenticated to an authorized AP and is part of the company’s network (e.g., an employee device).
Interfering: A client that is not authenticated to the company’s network and is considered external or potentially malicious.
AP Classification:
Authorized: An AP that is part of the company’s network and managed by the MC.
Suspected Rogue: An AP that is not authorized and is suspected of being malicious, often because it exhibits suspicious behavior (e.g., a BSSID close to an authorized AP, indicating potential spoofing).
Neighbor: An AP that is not part of the company’s network but is not connected to the wired network (e.g., a nearby AP from another organization).
Interfering: An AP that is not part of the company’s network and may be causing interference, but is not necessarily malicious.
The requirement is to find a client that is Authorized (belongs to the company) and connected to a Suspected Rogue AP (might belong to hackers).
Option A: MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6d:a4; Client Classification: Authorized; AP Classification: Suspected RogueThis client is classified as "Authorized," meaning it belongs to the company, and it is connected to a "Suspected Rogue" AP, which might belong to hackers. This matches the requirement perfectly.
Option B: MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6e:c5; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: NeighborThis client is "Interfering" (not a company client) and connected to a "Neighbor" AP, which is not considered a hacker’s device (it’s just a nearby AP).
Option C: MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:6e:60; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: InterferingThis client is "Interfering" (not a company client) and connected to an "Interfering" AP, which is not necessarily a hacker’s device (it may just be causing interference).
Option D: MAC address: d8:50:e6:f3:70:ab; Client Classification: Interfering; AP Classification: Suspected RogueThis client is "Interfering" (not a company client), although it is connected to a "Suspected Rogue" AP. It does not meet the requirement of being a company client.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide states:
"The Security Dashboard’s client list in ArubaOS shows the classification of each client and the AP it is connected to. An ‘Authorized’ client is one that has successfully authenticated to an authorized AP and is part of the company’s network. A ‘Suspected Rogue’ AP is an unauthorized AP that exhibits suspicious behavior, such as a BSSID close to an authorized AP, indicating potential spoofing by a hacker. To identify security risks, look for authorized clients connected to suspected rogue APs, as this may indicate a company device has connected to a malicious AP." (Page 415, Security Dashboard Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking Security Guide notes:
"WIP classifies clients as ‘Authorized’ if they have authenticated to an authorized AP managed by the controller. A ‘Suspected Rogue’ AP is a potential threat, as it may be attempting to mimic a legitimate AP to lure clients. Identifying authorized clients connected to suspected rogue APs is critical for detecting potential attacks, such as man-in-the-middle attempts by hackers." (Page 78, WIP Classifications Section)
What is social engineering?
Options:
Hackers use Artificial Intelligence (Al) to mimic a user’s online behavior so they can infiltrate a network and launch an attack.
Hackers use employees to circumvent network security and gather the information they need to launch an attack.
Hackers intercept traffic between two users, eavesdrop on their messages, and pretend to be one or both users.
Hackers spoof the source IP address in their communications so they appear to be a legitimate user.
Answer:
BExplanation:
Social engineering in the context of network security refers to the techniques used by hackers to manipulate individuals into breaking normal security procedures and best practices to gain unauthorized access to systems, networks, or physical locations, or for financial gain. Hackers use various forms of deception to trick employees into handing over confidential or personal information that can be used for fraudulent purposes. This definition encompasses phishing attacks, pretexting, baiting, and other manipulative techniques designed to exploit human psychology. Unlike other hacking methods that rely on technical means, social engineering targets the human element of security. References to social engineering, its methods, and defense strategies are commonly found in security training manuals, cybersecurity awareness programs, and authoritative resources like those from the SANS Institute or cybersecurity agencies.
How should admins deal with vulnerabilities that they find in their systems?
Options:
They should apply fixes, such as patches, to close the vulnerability before a hacker exploits it.
They should add the vulnerability to their Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE).
They should classify the vulnerability as malware. a DoS attack or a phishing attack.
They should notify the security team as soon as possible that the network has already been breached.
Answer:
AExplanation:
When vulnerabilities are identified in systems, it is crucial for administrators to act immediately to mitigate the risk of exploitation by attackers. The appropriate response involves applying fixes, such as software patches or configuration changes, to close the vulnerability. This proactive approach is necessary to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of the system resources and data. It's important to prioritize these actions based on the severity and exploitability of the vulnerability to ensure that the most critical issues are addressed first.
What is one difference between EAP-Tunneled Layer security (EAP-TLS) and Protected EAP (PEAP)?
Options:
EAP-TLS creates a TLS tunnel for transmitting user credentials, while PEAP authenticates the server and supplicant during a TLS handshake.
EAP-TLS requires the supplicant to authenticate with a certificate, hut PEAP allows the supplicant to use a username and password.
EAP-TLS begins with the establishment of a TLS tunnel, but PEAP does not use a TLS tunnel as part of Its process
EAP-TLS creates a TLS tunnel for transmitting user credentials securely while PEAP protects user credentials with TKIP encryption.
Answer:
BExplanation:
EAP-TLS and PEAP both provide secure authentication methods, but they differ in their requirements for client-side authentication. EAP-TLS requires both the client (supplicant) and the server to authenticate each other with certificates, thereby ensuring a very high level of security. On the other hand, PEAP requires a server-side certificate to create a secure tunnel and allows the client to authenticate using less stringent methods, such as a username and password, which are then protected by the tunnel. This makes PEAP more flexible in environments where client-side certificates are not feasible.
What is one of the roles of the network access server (NAS) in the AAA framework?
Options:
It negotiates with each user’s device to determine which EAP method is used for authentication.
It determines which resources authenticated users are allowed to access and monitors each user’s session.
It enforces access to network services and sends accounting information to the AAA server.
It authenticates legitimate users and uses policies to determine which resources each user is allowed to access.
Answer:
CExplanation:
The AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) framework is used in network security to manage user access. In this framework, the Network Access Server (NAS) plays a specific role. In an HPE Aruba Networking environment, the NAS is typically a device like a Mobility Controller (MC) or an AOS-CX switch that interacts with an AAA server (e.g., ClearPass Policy Manager, CPPM) to authenticate users.
NAS Role in AAA:
Authentication: The NAS acts as a client to the AAA server (e.g., via RADIUS), forwarding authentication requests from the user’s device to the server. It does not perform the authentication itself; the AAA server authenticates the user.
Authorization: After authentication, the NAS receives authorization attributes from the AAA server (e.g., a user role via Aruba-User-Role VSA) and enforces access policies (e.g., firewall rules, VLAN assignment) based on those attributes.
Accounting: The NAS sends accounting information (e.g., session start/stop, data usage) to the AAA server to track user activity.
Option A, "It negotiates with each user’s device to determine which EAP method is used for authentication," is incorrect. The NAS does not negotiate the EAP method with the user’s device. The EAP method (e.g., EAP-TLS, PEAP) is determined by the configuration on the NAS and the AAA server, and the client must support the configured method. The negotiation of EAP methods occurs between the client (supplicant) and the AAA server, with the NAS acting as a pass-through.
Option B, "It determines which resources authenticated users are allowed to access and monitors each user’s session," is incorrect. The NAS enforces access policies based on authorization attributes received from the AAA server, but it does not determine which resources users can access—that decision is made by the AAA server based on its policies. Monitoring sessions is part of accounting, but this option overstates the NAS’s role in determining access.
Option C, "It enforces access to network services and sends accounting information to the AAA server," is correct. The NAS enforces access by applying policies (e.g., firewall rules, VLANs) based on the authorization attributes received from the AAA server. It also sends accounting information (e.g., session start/stop, data usage) to the AAA server to track user activity, fulfilling its role in the accounting part of AAA.
Option D, "It authenticates legitimate users and uses policies to determine which resources each user is allowed to access," is incorrect. The NAS does not authenticate users; the AAA server performs authentication. The NAS also does not determine resource access; it enforces the policies provided by the AAA server.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide states:
"In the AAA framework, the Network Access Server (NAS), such as a Mobility Controller, acts as a client to the AAA server (e.g., a RADIUS server). The NAS forwards authentication requests from the user’s device to the AAA server, enforces access to network services based on the authorization attributes returned by the server (e.g., user role, VLAN), and sends accounting information, such as session start and stop records, to the AAA server for tracking." (Page 310, AAA Framework Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager 6.11 User Guide notes:
"The NAS in the AAA framework, such as an Aruba Mobility Controller, does not authenticate users itself; it forwards authentication requests to the AAA server (ClearPass). After authentication, the NAS enforces access policies based on the server’s response and sends accounting data to the AAA server to log user activity, such as session duration and data usage." (Page 280, NAS Role in AAA Section)
Refer to the exhibit.
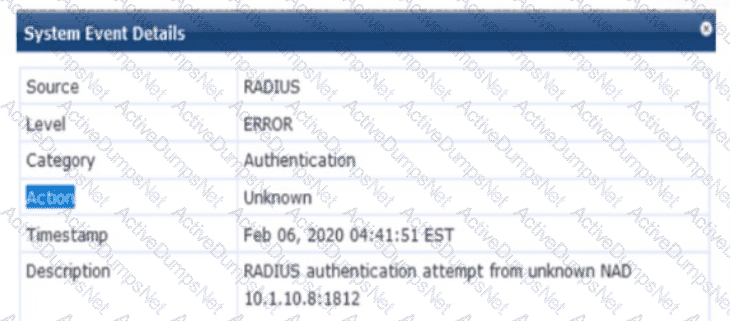
You are deploying a new HPE Aruba Networking Mobility Controller (MC), which is enforcing authentication to HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM). The authentication is not working correctly, and you find the error shown in the exhibit in the CPPM Event Viewer.
What should you check?
Options:
That the IP address that the MC is using to reach CPPM matches the one defined for the device on CPPM
That the MC has valid admin credentials configured on it for logging into the CPPM
That the MC has been added as a domain machine on the Active Directory domain with which CPPM is synchronized
That the shared secret configured for the CPPM authentication server matches the one defined for the device on CPPM
Answer:
AExplanation:
The exhibit shows an error in the CPPM Event Viewer: "RADIUS authentication attempt from unknown NAD 10.1.10.8:1812." This indicates that a new HPE Aruba Networking Mobility Controller (MC) is attempting to send RADIUS authentication requests to HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM), but CPPM does not recognize the MC as a Network Access Device (NAD), resulting in the authentication failure.
Unknown NAD Error: In CPPM, a NAD is a device (e.g., an MC, switch, or AP) that sends RADIUS requests to CPPM for authentication. Each NAD must be configured in CPPM with its IP address and a shared secret. The error "unknown NAD 10.1.10.8:1812" means that the IP address 10.1.10.8 (the source IP of the MC’s RADIUS request) is not listed as a NAD in CPPM’s configuration, so CPPM rejects the request.
Option A, "That the IP address that the MC is using to reach CPPM matches the one defined for the device on CPPM," is correct. You need to check that the MC’s IP address (10.1.10.8) is correctly configured as a NAD in CPPM. In CPPM, go to Configuration > Network > Devices, and verify that a NAD entry exists for 10.1.10.8. If the IP address does not match (e.g., due to NAT, a different interface, or a misconfiguration), CPPM will reject the request as coming from an unknown NAD.
Option B, "That the MC has valid admin credentials configured on it for logging into the CPPM," is incorrect. Admin credentials on the MC are used for management access (e.g., SSH, web UI), not for RADIUS authentication. RADIUS communication between the MC and CPPM uses a shared secret, not admin credentials.
Option C, "That the MC has been added as a domain machine on the Active Directory domain with which CPPM is synchronized," is incorrect. Adding the MC as a domain machine in Active Directory (AD) is relevant only if the MC itself is authenticating users against AD (e.g., for machine authentication), but this is not required for the MC to act as a NAD sending RADIUS requests to CPPM.
Option D, "That the shared secret configured for the CPPM authentication server matches the one defined for the device on CPPM," is incorrect in this context. While a shared secret mismatch would cause authentication failures, it would not result in an "unknown NAD" error. The "unknown NAD" error occurs before the shared secret is checked, as CPPM does not recognize the IP address as a valid NAD.
The HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager 6.11 User Guide states:
"The error ‘RADIUS authentication attempt from unknown NAD
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide notes:
"When configuring a Mobility Controller to use ClearPass as a RADIUS server, ensure that the MC’s IP address is added as a NAD in ClearPass. If ClearPass logs an ‘unknown NAD’ error, verify that the IP address the MC uses to send RADIUS requests (e.g., the source IP of the request) matches the IP address configured in ClearPass under Configuration > Network > Devices." (Page 498, Configuring RADIUS Authentication Section)
You are checking the Security Dashboard in the Web Ul for your ArubaOS solution and see that Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) has discovered a rogue radio operating in ad hoc mode with open security. What correctly describes a threat that the radio could pose?
Options:
It could open a backdoor into the corporate LAN for unauthorized users.
It is running in a non-standard 802.11 mode and could effectively jam the wireless signal.
It is flooding the air with many wireless frames in a likely attempt at a DoS attack.
It could be attempting to conceal itself from detection by changing its BSSID and SSID frequently.
Answer:
AExplanation:
A rogue radio operating in ad hoc mode with open security can pose several threats to a network. Ad hoc networks allow direct device-to-device communication without centralized control. If such a radio is present within or near a corporate environment, it can potentially be used to create a peer-to-peer network that bypasses corporate security controls, effectively acting as a backdoor into the corporate network for unauthorized users or devices. This can lead to a breach of data security and unauthorized access to network resources.
A company has Aruba Mobility Controllers (MCs), Aruba campus APs, and ArubaOS-Switches. The company plans to use ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) to classify endpoints by type. This company is using only CPPM and no other ClearPass solutions.
The ClearPass admins tell you that they want to use HTTP User-Agent strings to help classify endpoints.
What should you do as a part of configuring the ArubaOS-Switches to support this requirement?
Options:
Create a device fingerprinting policy that includes HTTP, and apply the policy to edge ports.
Create remote mirrors that collect traffic on edge ports, and mirror it to CPPM's IP address.
Configure CPPM as the sFlow collector, and make sure that sFlow is enabled on edge ports.
Connect the switches to CPPM's span ports, and set up mirroring of HTTP traffic on the switches.
Answer:
CExplanation:
ArubaOS-Switches can use sFlow technology to sample network traffic and send the samples to a collector, such as ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM), for analysis. sFlow can be configured to capture various types of traffic, including HTTP, which typically contains User-Agent strings that can be used for device fingerprinting and classification.
To support the requirement for using HTTP User-Agent strings to classify endpoints, the switches would need to be configured to send sFlow samples containing HTTP traffic to CPPM. CPPM would then analyze these samples and use the User-Agent strings to classify the devices.
Therefore, the correct action to configure ArubaOS-Switches would involve:
Configuring CPPM as the sFlow collector on the switches.
Enabling sFlow on the edge ports that connect to endpoints.
This approach allows the network traffic to be analyzed by CPPM without requiring any additional mirroring or redirection of traffic, which would be resource-intensive and potentially disruptive to network performance.
A client has accessed an HTTPS server at myhost1.example.com using Chrome. The server sends a certificate that includes these properties:
Subject name: myhost.example.com
SAN: DNS: myhost.example.com; DNS: myhost1.example.com
Extended Key Usage (EKU): Server authentication
Issuer: MyCA_SigningThe server also sends an intermediate CA certificate for MyCA_Signing, which is signed by MyCA. The client’s Trusted CA Certificate list does not include the MyCA or MyCA_Signing certificates.Which factor or factors prevent the client from trusting the certificate?
Options:
The client does not have the correct trusted CA certificates.
The certificate lacks a valid SAN.
The certificate lacks the correct EKU.
The certificate lacks a valid SAN, and the client does not have the correct trusted CA certificates.
Answer:
AExplanation:
This question is identical to Question 17, with the same certificate properties and scenario. The client (Chrome browser) accesses an HTTPS server at myhost1.example.com, and the server presents a certificate with:
Subject name: myhost.example.com
SAN: DNS: myhost.example.com; DNS: myhost1.example.com
EKU: Server authentication
Issuer: MyCA_Signing (intermediate CA)
The intermediate CA certificate (MyCA_Signing) is signed by MyCA (root CA).
The client’s Trusted CA Certificate list does not include MyCA or MyCA_Signing.
The certificate validation process is the same as in Question 17:
Name Validation: The SAN includes "myhost1.example.com," which matches the server’s hostname, so this passes.
EKU Validation: The EKU is "Server authentication," which is correct for HTTPS, so this passes.
Chain of Trust Validation: The client attempts to build a chain from the server’s certificate to a trusted root CA:
Server certificate → MyCA_Signing → MyCA Since MyCA is not in the client’s Trusted CA Certificate list, the chain cannot be validated, and the client does not trust the certificate.
Option A, "The client does not have the correct trusted CA certificates," is correct. The absence of MyCA in the client’s trust store prevents the client from validating the certificate chain.
Option B, "The certificate lacks a valid SAN," is incorrect because the SAN includes "myhost1.example.com," which is valid.
Option C, "The certificate lacks the correct EKU," is incorrect because the EKU is correctly set to "Server authentication."
Option D, "The certificate lacks a valid SAN, and the client does not have the correct trusted CA certificates," is incorrect because the SAN is valid; the only issue is the missing trusted CA certificates.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-CX 10.12 Security Guide states:
"For a client to trust a server’s certificate during HTTPS communication, the client must validate the certificate chain to a trusted root CA in its trust store. If the root CA (e.g., MyCA) or intermediate CA (e.g., MyCA_Signing) is not in the client’s Trusted CA Certificate list, the chain of trust cannot be established, and the client will reject the certificate. The Subject Alternative Name (SAN) must include the server’s hostname, and the Extended Key Usage (EKU) must include ‘Server authentication’ for HTTPS." (Page 205, Certificate Validation Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking Security Fundamentals Guide notes:
"A common reason for certificate validation failure is the absence of the root CA certificate in the client’s trust store. For example, if a server’s certificate is issued by an intermediate CA (e.g., MyCA_Signing) that chains to a root CA (e.g., MyCA), the client must have the root CA certificate in its Trusted CA Certificate list to trust the chain." (Page 45, Certificate Trust Issues Section)
Which correctly describes a way to deploy certificates to end-user devices?
Options:
ClearPass Onboard can help to deploy certificates to end-user devices, whether or not they are members of a Windows domain
ClearPass Device Insight can automatically discover end-user devices and deploy the proper certificates to them
ClearPass OnGuard can help to deploy certificates to end-user devices, whether or not they are members of a Windows domain
in a Windows domain, domain group policy objects (GPOs) can automatically install computer, but not user certificates
Answer:
AExplanation:
ClearPass Onboard is part of the Aruba ClearPass suite and it provides a mechanism to deploy certificates to end-user devices, regardless of whether or not they are members of a Windows domain. ClearPass Onboard facilitates the configuration and provisioning of network settings and security, including the delivery and installation of certificates to ensure secure network access. This capability enables a bring-your-own-device (BYOD) environment where devices can be securely managed and provided with the necessary certificates for network authentication.
Which is an accurate description of a type of malware?
Options:
Worms are usually delivered in spear-phishing attacks and require users to open and run a file.
Rootkits can help hackers gain elevated access to a system and often actively conceal themselves from detection.
A Trojan is any type of malware that replicates itself and spreads to other systems automatically.
Malvertising can only infect a system if the user encounters the malware on an untrustworthy site.
Answer:
BExplanation:
Malware (malicious software) is a broad category of software designed to harm or exploit systems. HPE Aruba Networking documentation often discusses malware in the context of network security threats and mitigation strategies, such as those detected by the Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) system.
Option A, "Worms are usually delivered in spear-phishing attacks and require users to open and run a file," is incorrect. Worms are a type of malware that replicate and spread automatically across networks without user interaction (e.g., by exploiting vulnerabilities). They are not typically delivered via spear-phishing, which is more associated with Trojans or ransomware. Worms do not require users to open and run a file; that behavior is characteristic of Trojans.
Option B, "Rootkits can help hackers gain elevated access to a system and often actively conceal themselves from detection," is correct. A rootkit is a type of malware that provides hackers with privileged (elevated) access to a system, often by modifying the operating system or kernel. Rootkits are designed to hide their presence (e.g., by concealing processes, files, or network connections) to evade detection by antivirus software or system administrators, making them a stealthy and dangerous type of malware.
Option C, "A Trojan is any type of malware that replicates itself and spreads to other systems automatically," is incorrect. A Trojan is a type of malware that disguises itself as legitimate software to trick users into installing it. Unlike worms, Trojans do not replicate or spread automatically; they require user interaction (e.g., downloading and running a file) to infect a system.
Option D, "Malvertising can only infect a system if the user encounters the malware on an untrustworthy site," is incorrect. Malvertising (malicious advertising) involves embedding malware in online ads, which can appear on both trustworthy and untrustworthy sites. For example, a legitimate website might unknowingly serve a malicious ad that exploits a browser vulnerability to infect the user’s system, even without the user clicking the ad.
The HPE Aruba Networking Security Guide states:
"Rootkits are a type of malware that can help hackers gain elevated access to a system by modifying the operating system or kernel. They often actively conceal themselves from detection by hiding processes, files, or network connections, making them difficult to detect and remove. Rootkits are commonly used to maintain persistent access to a compromised system." (Page 22, Malware Types Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide notes:
"The Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) system can detect various types of malware. Rootkits, for example, are designed to provide hackers with elevated access and often conceal themselves to evade detection, allowing the hacker to maintain control over the infected system for extended periods." (Page 421, Malware Threats Section)
From which solution can ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) receive detailed information about client device type OS and status?
Options:
ClearPass Onboard
ClearPass Access Tracker
ClearPass OnGuard
ClearPass Guest
Answer:
CExplanation:
ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) can receive detailed information about client device type, OS, and status from ClearPass OnGuard. ClearPass OnGuard is part of the ClearPass suite and provides posture assessment and endpoint health checks. It gathers detailed information on the status and security posture of devices trying to connect to the network, such as whether antivirus software is up to date, which operating system is running, and other details that characterize the device's compliance with the network's security policies.
A user attempts to connect to an SSID configured on an AOS-8 mobility architecture with Mobility Controllers (MCs) and APs. The SSID enforces WPA3-Enterprise security and uses HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) as the authentication server. The WLAN has initial role, logon, and 802.1X default role, guest.
A user attempts to connect to the SSID, and CPPM sends an Access-Accept with an Aruba-User-Role VSA of "contractor," which exists on the MC.
What does the MC do?
Options:
Applies the rules in the logon role, then guest role, and the contractor role
Applies the rules in the contractor role
Applies the rules in the contractor role and the logon role
Applies the rules in the contractor role and guest role
Answer:
BExplanation:
In an AOS-8 mobility architecture, the Mobility Controller (MC) manages user roles and policies for wireless clients connecting to SSIDs. When a user connects to an SSID with WPA3-Enterprise security, the MC uses 802.1X authentication to validate the user against an authentication server, in this case, HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM). The SSID is configured with specific roles:
Initial role: Applied before authentication begins (not specified in the question, but typically used for pre-authentication access).
Logon role: Applied during the authentication process to allow access to authentication services (e.g., DNS, DHCP, or RADIUS traffic).
802.1X default role (guest): Applied if 802.1X authentication fails or if no specific role is assigned by the RADIUS server after successful authentication.
In this scenario, the user successfully authenticates, and CPPM sends an Access-Accept message with an Aruba-User-Role Vendor-Specific Attribute (VSA) set to "contractor." The "contractor" role exists on the MC, meaning it is a predefined role in the MC’s configuration.
When the MC receives the Aruba-User-Role VSA, it applies the specified role ("contractor") to the user session, overriding the default 802.1X role ("guest"). The MC does not combine the contractor role with other roles like logon or guest; it applies only the role specified by the RADIUS server (CPPM) in the Aruba-User-Role VSA. This is the standard behavior in AOS-8 for role assignment after successful authentication when a VSA specifies a role.
Option A, "Applies the rules in the logon role, then guest role, and the contractor role," is incorrect because the MC does not apply multiple roles in sequence. The logon role is used only during authentication, and the guest role (default 802.1X role) is overridden by the contractor role specified in the VSA.
Option C, "Applies the rules in the contractor role and the logon role," is incorrect because the logon role is no longer applied once authentication is complete; only the contractor role is applied.
Option D, "Applies the rules in the contractor role and guest role," is incorrect because the guest role (default 802.1X role) is not applied when a specific role is assigned via the Aruba-User-Role VSA.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide states:
"When a user authenticates successfully via 802.1X, the Mobility Controller applies the role specified in the Aruba-User-Role VSA returned by the RADIUS server in the Access-Accept message. If the role specified in the VSA exists on the controller, it is applied to the user session, overriding any default 802.1X role configured for the WLAN. The controller does not combine the VSA-specified role with other roles, such as the initial, logon, or default roles." (Page 305, Role Assignment Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager 6.11 User Guide notes:
"ClearPass can send the Aruba-User-Role VSA in a RADIUS Access-Accept message to assign a specific role to the user on Aruba Mobility Controllers. The role specified in the VSA takes precedence over any default roles configured on the WLAN, ensuring that the user is placed in the intended role." (Page 289, RADIUS Enforcement Section)
What are the roles of 802.1X authenticators and authentication servers?
Options:
The authenticator stores the user account database, while the server stores access policies.
The authenticator supports only EAP, while the authentication server supports only RADIUS.
The authenticator is a RADIUS client and the authentication server is a RADIUS server.
The authenticator makes access decisions and the server communicates them to the supplicant.
Answer:
CExplanation:
In the 802.1X network access control model, the roles of the authenticator and the authentication server are distinct yet complementary. The authenticator acts as a RADIUS client, which is a network device, like a switch or wireless access point, that directly interfaces with the client machine (supplicant). The authentication server, typically a RADIUS server, is responsible for verifying the credentials provided by the supplicant through the authenticator. This setup helps in separating the duties where the authenticator enforces authentication but does not decide on the validity of the credentials, which is the role of the authentication server.
You have deployed a new Aruba Mobility Controller (MC) and campus APs (CAPs). One of the WLANs enforces 802.IX authentication lo Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager {CPPM) When you test connecting the client to the WLAN. the test falls You check Aruba ClearPass Access Tracker and cannot find a record of the authentication attempt You ping from the MC to CPPM. and the ping is successful.
What is a good next step for troubleshooting?
Options:
Renew CPPM's RADIUS/EAP certificate
Reset the user credentials
Check CPPM Event viewer.
Check connectivity between CPPM and a backend directory server
Answer:
CExplanation:
When dealing with a failed 802.1X authentication attempt to a WLAN enforced by Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) where no record of the attempt is seen in ClearPass Access Tracker, a good next troubleshooting step is to check the CPPM Event Viewer. Since you are able to successfully ping from the Mobility Controller to CPPM, this indicates that there is network connectivity between these two devices. The lack of a record in Access Tracker suggests that the issue may not be with the RADIUS/EAP certificate or user credentials, but possibly with the ClearPass service itself or its reception of authentication requests. The Event Viewer can provide detailed logs that might reveal internal errors or misconfigurations within CPPM that could prevent it from processing authentication attempts properly.
Device A is contacting https://arubapedia.arubanetworks.com. The web server sends a certificate chain. What does the browser do as part of validating the web server certificate?
Options:
It makes sure that the key in the certificate matches the key that DeviceA uses for HTTPS.
It makes sure the certificate has a DNS SAN that matches arubapedia.arubanetworks.com
It makes sure that the public key in the certificate matches DeviceA's private HTTPS key.
It makes sure that the public key in the certificate matches a private key stored on DeviceA.
Answer:
BExplanation:
When a device like Device A contacts a secure website and receives a certificate chain from the server, the browser's primary task is to validate the web server's certificate to ensure it is trustworthy. Part of this validation includes checking that the certificate contains a DNS Subject Alternative Name (SAN) that matches the domain name of the website being accessed—in this case, arubapedia.arubanetworks.com. This ensures that the certificate was indeed issued to the entity operating the domain and helps prevent man-in-the-middle attacks where an invalid certificate could be presented by an attacker. The DNS SAN check is critical because it directly ties the digital certificate to the domain it secures, confirming the authenticity of the website to the user's browser.
A company is deploying AOS-CX switches to support 114 employees, which will tunnel client traffic to an HPE Aruba Networking Mobility Controller (MC) for the MC to apply firewall policies and deep packet inspection (DPI). This MC will be dedicated to receiving traffic from the AOS-CX switches.
What are the licensing requirements for the MC?
Options:
One PEF license per switch
One PEF license per switch, and one WCC license per switch
One AP license per switch
One AP license per switch, and one PEF license per switch
Answer:
AExplanation:
The scenario involves AOS-CX switches tunneling client traffic to an HPE Aruba Networking Mobility Controller (MC) in an AOS-8 architecture. The MC will apply firewall policies and perform deep packet inspection (DPI) on the tunneled traffic. The MC is dedicated to receiving traffic from the AOS-CX switches, and there are 114 employees (implying 114 potential clients). The question asks about the licensing requirements for the MC.
Tunneling from AOS-CX Switches to MC: In this setup, the AOS-CX switches act as Layer 2 devices, tunneling client traffic to the MC using a mechanism like GRE or VXLAN (though GRE is more common in AOS-8). The MC treats the tunneled traffic as if it were coming from wireless clients, applying firewall policies and DPI.
Licensing in AOS-8:
AP License (Access Point License): Required for each AP managed by the MC. Since the scenario involves AOS-CX switches tunneling traffic, not APs, AP licenses are not required.
PEF License (Policy Enforcement Firewall License): Required to enable the stateful firewall and DPI features on the MC. The PEF license is based on the number of devices (e.g., switches, APs) or users that the MC processes traffic for. In this case, the MC is processing traffic from AOS-CX switches, and the license is typically per switch (not per user or employee).
WCC License (Web Content Classification License): An optional license that enhances DPI by enabling URL-based filtering and web content classification. This is not mentioned as a requirement in the scenario.
Option A, "One PEF license per switch," is correct. Since the MC is dedicated to receiving traffic from the AOS-CX switches, and the MC will apply firewall policies and DPI, a PEF license is required. In AOS-8, when switches tunnel traffic to an MC, the PEF license is typically required per switch (not per user). With 114 employees, the number of switches is not specified, but the licensing model is per switch, so one PEF license per switch is needed.
Option B, "One PEF license per switch, and one WCC license per switch," is incorrect. While a PEF license is required, a WCC license is not mentioned as a requirement. WCC is for advanced web filtering, which is not specified in the scenario.
Option C, "One AP license per switch," is incorrect. AP licenses are for managing APs, not switches. Since the scenario involves switches tunneling traffic, not APs, AP licenses are not required.
Option D, "One AP license per switch, and one PEF license per switch," is incorrect for the same reason as Option C. AP licenses are not needed, but the PEF license per switch is correct.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide states:
"The Policy Enforcement Firewall (PEF) license is required on the Mobility Controller to enable stateful firewall policies and deep packet inspection (DPI). When AOS-CX switches tunnel client traffic to the MC for firewall processing, a PEF license is required for each switch. The license is based on the number of devices (e.g., switches) sending traffic to the MC, not the number of users. For example, if 10 switches tunnel traffic to the MC, 10 PEF licenses are required." (Page 375, Licensing Requirements Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking Licensing Guide notes:
"PEF licenses on the Mobility Controller are required for firewall and DPI features. In deployments where switches tunnel traffic to the MC, the PEF license is typically per switch. AP licenses are not required unless the MC is managing APs. The Web Content Classification (WCC) license is optional and only needed for advanced URL filtering, which is not required for basic DPI." (Page 15, PEF Licensing Section)
What is an example or phishing?
Options:
An attacker sends TCP messages to many different ports to discover which ports are open.
An attacker checks a user’s password by using trying millions of potential passwords.
An attacker lures clients to connect to a software-based AP that is using a legitimate SSID.
An attacker sends emails posing as a service team member to get users to disclose their passwords.
Answer:
DExplanation:
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack where an attacker impersonates a trusted entity to deceive people into providing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card numbers. An example of phishing is when an attacker sends emails posing as a service team member or a legitimate organization with the intention of getting users to disclose their passwords or other confidential information. These emails often contain links to fake websites that look remarkably similar to legitimate ones, tricking users into entering their details.
Your Aruba Mobility Master-based solution has detected a rogue AP Among other information the ArubaOS Detected Radios page lists this Information for the AP
SSID = PubllcWiFI
BSSID = a8M27 12 34:56
Match method = Exact match
Match type = Eth-GW-wired-Mac-Table
The security team asks you to explain why this AP is classified as a rogue. What should you explain?
Options:
The AP Is connected to your LAN because It is transmitting wireless traffic with your network's default gateway's MAC address as a source MAC Because it does not belong to the company, it is a rogue
The ap has a BSSID mat matches authorized client MAC addresses. This indicates that the AP is spoofing the MAC address to gam unauthorized access to your company's wireless services, so It is a rogue
The AP has been detected as launching a DoS attack against your company's default gateway. This qualities it as a rogue which needs to be contained with wireless association frames immediately
The AP is spoofing a routers MAC address as its BSSID. This indicates mat, even though WIP cannot determine whether the AP is connected to your LAN. it is a rogue.
Answer:
AExplanation:
The AP is classified as a rogue because it is connected to your LAN and is transmitting wireless traffic with your network's default gateway's MAC address as a source MAC. In this scenario, the 'Match method = Exact match' and 'Match type = Eth-GW-wired-Mac-Table' indicates that the rogue AP has been detected by matching the Ethernet gateway's MAC address, which is on the wired network, implying that the rogue AP is connected to the corporate LAN. Since the AP does not belong to the company, its presence on the network is unauthorized and is thus classified as a rogue AP.
Two wireless clients, client 1 and client 2, are connected to an ArubaOS Mobility Controller. Subnet 10.1.10.10/24 is a network of servers on the other side of the ArubaOS firewall. The exhibit shows all three firewall rules that apply to these clients.
Which traffic is permitted?
Options:
an HTTPS request from client 1 to 10.1.10.10 and an HTTPS response from 10.1.10.10 to client 1
an HTTPS request from client 1 to 10.1.10.10 and an HTTPS request from 10.1.10.11 to client 1
an HTTPS request from 10.1.10.10 to client 1 and an HTTPS re-sponse from client 1 to 10.1.10.10
an HTTPS request from client 1 to client 2 and an HTTPS request from client 2 to client 1
Answer:
AExplanation:
Based on the exhibit showing the firewall rules, the following traffic is permitted:
Client 1 is allowed to send HTTPS traffic to any destination within the subnet 10.1.10.0/24 because there is a permit rule for the user to access svc-https to that subnet.
Responses to initiated connections are typically allowed by stateful firewalls; hence, an HTTPS response from 10.1.10.10 to client 1 is expected to be permitted even though it is not explicitly mentioned in the firewall rules (assuming the stateful nature of the firewall).
Which endpoint classification capabilities do Aruba network infrastructure devices have on their own without ClearPass solutions?
Options:
ArubaOS-CX switches can use a combination of active and passive methods to assign roles to clients.
ArubaOS devices (controllers and lAPs) can use DHCP fingerprints to assign roles to clients.
ArubaOS devices can use a combination of DHCP fingerprints, HTTP User-Agent strings, and Nmap to construct endpoint profiles.
ArubaOS-Switches can use DHCP fingerprints to construct detailed endpoint profiles.
Answer:
BExplanation:
Without the integration of Aruba ClearPass or other advanced network access control solutions, ArubaOS devices (controllers and Instant APs) are able to use DHCP fingerprinting to assign roles to clients. This method allows the devices to identify the type of client devices connecting to the network based on the DHCP requests they send. While this is a more basic form of endpoint classification compared to the capabilities provided by ClearPass, it still enables some level of access control based on device type. This functionality and its limitations are described in Aruba's product documentation for ArubaOS devices, highlighting the benefits of integrating a full-featured solution like ClearPass for more granular and powerful endpoint classification capabilities.
What is a difference between radius and TACACS+?
Options:
RADIUS combines the authentication and authorization process while TACACS+ separates them.
RADIUS uses TCP for Its connection protocol, while TACACS+ uses UDP tor its connection protocol.
RADIUS encrypts the complete packet, white TACACS+ only offers partial encryption.
RADIUS uses Attribute Value Pairs (AVPs) in its messages, while TACACS+ does not use them.
Answer:
AExplanation:
RADIUS and TACACS+ are both protocols used for networking authentication, but they handle the processes of authentication and authorization differently. RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) combines authentication and authorization into a single process, whereas TACACS+ (Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System Plus) separates these processes. This separation in TACACS+ allows more flexible policy enforcement and better control over commands a user can execute. This difference is well-documented in various network security resources, including Cisco's technical documentation and security protocol manuals.
A company has HPE Aruba Networking Mobility Controllers (MCs), HPE Aruba Networking campus APs, and AOS-CX switches. The company plans to use HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) to classify endpoints by type. The company is contemplating the use of ClearPass's TCP fingerprinting capabilities.
What is a consideration for using those capabilities?
Options:
You will need to mirror traffic to one of CPPM’s span ports from a device such as a core routing switch.
ClearPass admins will need to provide the credentials of an API admin account to configure on HPE Aruba Networking devices.
AOS-CX switches do not offer the support necessary for CPPM to use TCP fingerprinting on wired endpoints.
TCP fingerprinting of wireless endpoints requires a third-party Mobility Device Management (MDM) solution.
Answer:
AExplanation:
HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) uses TCP fingerprinting as a passive profiling method to classify endpoints by analyzing TCP packet headers (e.g., TTL, window size) to identify the operating system (e.g., Windows, Linux). The company in this scenario has Mobility Controllers (MCs), campus APs, and AOS-CX switches, and wants to use CPPM’s TCP fingerprinting capabilities for endpoint classification.
TCP Fingerprinting: This method requires CPPM to receive TCP traffic from endpoints. Since CPPM is not typically inline with network traffic, the traffic must be mirrored to CPPM for analysis. This is often done using a SPAN (Switched Port Analyzer) port or mirror port on a switch or controller.
Option A, "You will need to mirror traffic to one of CPPM’s span ports from a device such as a core routing switch," is correct. For CPPM to perform TCP fingerprinting, it needs to see the TCP traffic from endpoints. This is typically achieved by mirroring traffic from a core routing switch (or another device like an MC) to a SPAN port on the CPPM server. For example, on an AOS-CX switch, you can configure a mirror session with the command mirror session 1 destination interface
Option B, "ClearPass admins will need to provide the credentials of an API admin account to configure on HPE Aruba Networking devices," is incorrect. TCP fingerprinting does not require API credentials. It is a passive profiling method that analyzes mirrored traffic, and no API interaction is needed between CPPM and Aruba devices for this purpose.
Option C, "AOS-CX switches do not offer the support necessary for CPPM to use TCP fingerprinting on wired endpoints," is incorrect. AOS-CX switches support mirroring traffic to CPPM (e.g., using a mirror session), which enables CPPM to perform TCP fingerprinting on wired endpoints. The switch does not need to perform the fingerprinting itself; it only needs to send the traffic to CPPM.
Option D, "TCP fingerprinting of wireless endpoints requires a third-party Mobility Device Management (MDM) solution," is incorrect. TCP fingerprinting is a built-in capability of CPPM and does not require an MDM solution. For wireless endpoints, the MC can mirror client traffic to CPPM (e.g., using a datapath mirror), allowing CPPM to perform TCP fingerprinting.
The HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager 6.11 User Guide states:
"TCP fingerprinting requires ClearPass to receive TCP traffic from endpoints for analysis. A key consideration is that you must mirror traffic to one of ClearPass’s SPAN ports from a device such as a core routing switch or Mobility Controller. For example, on an AOS-CX switch, configure a mirror session with mirror session 1 destination interface
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide notes:
"For ClearPass to perform TCP fingerprinting on wireless endpoints, the Mobility Controller can mirror client traffic to ClearPass using a datapath mirror. For wired endpoints, an AOS-CX switch can mirror traffic to ClearPass’s SPAN port, enabling TCP fingerprinting without requiring additional support on the switch itself." (Page 351, Device Profiling with CPPM Section)
Refer to the exhibit.
How can you use the thumbprint?
Options:
Install this thumbprint on management stations to use as two-factor authentication along with manager usernames and passwords, this will ensure managers connect from valid stations
Copy the thumbprint to other Aruba switches to establish a consistent SSH Key for all switches this will enable managers to connect to the switches securely with less effort
When you first connect to the switch with SSH from a management station, make sure that the thumbprint matches to ensure that a man-in-t he-mid die (MITM) attack is not occurring
install this thumbprint on management stations the stations can then authenticate with the thumbprint instead of admins having to enter usernames and passwords.
Answer:
CExplanation:
The thumbprint (also known as a fingerprint) of a certificate or SSH key is a hash that uniquely represents the public key contained within. When you first connect to the switch with SSH from a management station, you should ensure that the thumbprint matches what you expect. This is a security measure to confirm the identity of the device you are connecting to and to ensure that a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack is not occurring. If the thumbprint matches the known good thumbprint of the switch, it is safe to proceed with the connection.
Your HPE Aruba Networking Mobility Master-based solution has detected a rogue AP. Among other information, the AOS Detected Radios page lists this information for the AP:
SSID = PublicWiFi
BSSID = a8:bd:27:12:34:56
Match method = Plus one
Match method = Eth-Wired-Mac-Table
The security team asks you to explain why this AP is classified as a rogue. What should you explain?
Options:
The AP has been detected using multiple MAC addresses. This indicates that the AP is spoofing its MAC address, which qualifies it as a suspected rogue.
The AP is probably connected to your LAN because it has a BSSID that is close to a MAC address that has been detected in your LAN. Because it does not belong to the company, it is a suspected rogue.
The AP is an AP that belongs to your solution. However, the AOS has detected that it is behaving suspiciously. It might have been compromised, so it is classified as a suspected rogue.
The AP has a BSSID that is close to your authorized APs’ BSSIDs. This indicates that the AP might be spoofing the corporate SSID and attempting to lure clients to it, making the AP a suspected rogue.
Answer:
BExplanation:
HPE Aruba Networking’s Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) system, part of the AOS-8 architecture (Mobility Master and Mobility Controllers), is designed to detect and classify rogue APs. The "AOS Detected Radios" page provides details about detected APs, including their SSID, BSSID, and match methods used to classify them.
In this case, the AP is classified as a rogue with the following match methods:
Plus one: This indicates that the BSSID of the detected AP is numerically close (e.g., differs by one in the last octet) to the MAC address of a known device in the network.
Eth-Wired-Mac-Table: This indicates that the AP’s MAC address (or a closely related MAC address) was found in the wired network’s MAC address table, suggesting that the AP is connected to the LAN.
These match methods suggest that the AP is likely connected to the company’s wired LAN (via the Eth-Wired-Mac-Table match) and has a BSSID that is close to a known device’s MAC address (Plus one match). Since this AP is not part of the company’s authorized AP list (it’s broadcasting "PublicWiFi," which may not be a corporate SSID), it is classified as a suspected rogue. This scenario is common when an unauthorized AP is plugged into the corporate LAN, posing a security risk.
Option A, "The AP has been detected using multiple MAC addresses," is incorrect because the match methods do not indicate multiple MAC addresses; they indicate a close match to a known MAC and a presence in the wired MAC table.
Option C, "The AP is an AP that belongs to your solution," is incorrect because the AP is classified as a rogue, meaning it is not part of the authorized APs in the solution.
Option D, "The AP has a BSSID that is close to your authorized APs’ BSSIDs," is partially correct in that the "Plus one" match indicates a close BSSID, but the key reason for the rogue classification is its connection to the LAN (Eth-Wired-Mac-Table), not just the BSSID similarity.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide states:
"The Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) system detects rogue APs by analyzing their BSSIDs, SSIDs, and connectivity to the wired network. The ‘Eth-Wired-Mac-Table’ match method indicates that the AP’s MAC address (or a closely related address) was found in the wired network’s MAC address table, suggesting that the AP is connected to the LAN. The ‘Plus one’ match method indicates that the AP’s BSSID is numerically close to a known MAC address in the network, which can indicate a potential rogue device attempting to mimic a legitimate device." (Page 412, Rogue AP Detection Section)
Additionally, the guide notes:
"A rogue AP is classified as ‘suspected rogue’ if it is detected on the wired network (e.g., via Eth-Wired-Mac-Table) and is not part of the authorized AP list. This often occurs when an unauthorized AP is connected to the corporate LAN." (Page 413, Rogue AP Classification Section)
Which attack is an example or social engineering?
Options:
An email Is used to impersonate a Dank and trick users into entering their bank login information on a fake website page.
A hacker eavesdrops on insecure communications, such as Remote Desktop Program (RDP). and discovers login credentials.
A user visits a website and downloads a file that contains a worm, which sell-replicates throughout the network.
An attack exploits an operating system vulnerability and locks out users until they pay the ransom.
Answer:
AExplanation:
An example of a social engineering attack is described in option A, where an email is used to impersonate a bank and deceive users into entering their bank login information on a counterfeit website. Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology rather than technical hacking techniques to gain access to systems, data, or personal information. These attacks often involve tricking people into breaking normal security procedures. The other options describe different types of technical attacks that do not primarily rely on manipulating individuals through deceptive personal interactions.
The monitoring admin has asked you to set up an AOS-CX switch to meet these criteria:
Send logs to a SIEM Syslog server at 10.4.13.15 at the standard TCP port (514)
Send a log for all events at the "warning" level or above; do not send logs with a lower level than "warning"The switch did not have any "logging" configuration on it. You then entered this command:AOS-CX(config)# logging 10.4.13.15 tcp vrf defaultWhat should you do to finish configuring to the requirements?
Options:
Specify the "warning" severity level for the logging server.
Add logging categories at the global level.
Ask for the Syslog password and configure it on the switch.
Configure logging as a debug destination.
Answer:
AExplanation:
The task is to configure an AOS-CX switch to send logs to a SIEM Syslog server at IP address 10.4.13.15 using TCP port 514, with logs for events at the "warning" severity level or above (i.e., warning, error, critical, alert, emergency). The initial command entered is:
AOS-CX(config)# logging 10.4.13.15 tcp vrf default
This command configures the switch to send logs to the Syslog server at 10.4.13.15 using TCP (port 514 is the default for TCP Syslog unless specified otherwise) and the default VRF. However, this command alone does not specify the severity level of the logs to be sent, which is a requirement of the task.
Severity Level Configuration: AOS-CX switches allow you to specify the severity level for logs sent to a Syslog server. The severity levels, in increasing order of severity, are: debug, informational, notice, warning, error, critical, alert, and emergency. The requirement is to send logs at the "warning" level or above, meaning warning, error, critical, alert, and emergency logs should be sent, but debug, informational, and notice logs should not.
Option A, "Specify the ‘warning’ severity level for the logging server," is correct. To meet the requirement, you need to add the severity level to the logging configuration for the specific Syslog server. The command to do this is:
AOS-CX(config)# logging 10.4.13.15 severity warning
This command ensures that only logs with a severity of warning or higher are sent to the Syslog server at 10.4.13.15. Since the initial command already specified TCP and the default VRF, this additional command completes the configuration.
Option B, "Add logging categories at the global level," is incorrect. Logging categories (e.g., system, security, network) are used to filter logs based on the type of event, not the severity level. The requirement is about severity ("warning" or above), not specific categories, so this step is not necessary to meet the stated criteria.
Option C, "Ask for the Syslog password and configure it on the switch," is incorrect. Syslog servers typically do not require a password for receiving logs, and AOS-CX switches do not have a configuration option to specify a Syslog password. Authentication or encryption for Syslog (e.g., using TLS) is not mentioned in the requirements.
Option D, "Configure logging as a debug destination," is incorrect. Configuring a debug destination (e.g., using the debug command) is used to send debug-level logs to a destination (e.g., console, buffer, or Syslog), but the requirement is to send logs at the "warning" level or above, not debug-level logs. Additionally, the logging command already specifies the Syslog server as the destination.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-CX 10.12 System Management Guide states:
"To configure a Syslog server on an AOS-CX switch, use the logging
Additionally, the guide notes:
"Severity levels for logging on AOS-CX switches are, in increasing order: debug, informational, notice, warning, error, critical, alert, emergency. Specifying a severity level of ‘warning’ ensures that only logs at that level or higher are sent to the configured destination." (Page 90, Logging Severity Levels Section)
What is a benefit of Protected Management Frames (PMF). sometimes called Management Frame Protection (MFP)?
Options:
PMF helps to protect APs and MCs from unauthorized management access by hackers.
PMF ensures trial traffic between APs and Mobility Controllers (MCs) is encrypted.
PMF prevents hackers from capturing the traffic between APs and Mobility Controllers.
PMF protects clients from DoS attacks based on forged de-authentication frames
Answer:
DExplanation:
Protected Management Frames (PMF), also known as Management Frame Protection (MFP), is designed to protect clients from denial-of-service (DoS) attacks that involve forged de-authentication and disassociation frames. These attacks can disconnect legitimate clients from the network. PMF provides a way to authenticate these management frames, ensuring that they are not forged, thus enhancing the security of the wireless network.
What distinguishes a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack from a traditional Denial of Service (DoS) attack?
Options:
A DDoS attack originates from external devices, while a DoS attack originates from internal devices.
A DoS attack targets one server; a DDoS attack targets all the clients that use a server.
A DDoS attack targets multiple devices, while a DoS is designed to incapacitate only one device.
A DDoS attack is launched from multiple devices, while a DoS attack is launched from a single device.
Answer:
DExplanation:
Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are both designed to disrupt the availability of a network, service, or device by overwhelming it with traffic or requests. HPE Aruba Networking documentation, particularly in the context of Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) and network security, often discusses these attacks to help administrators mitigate them.
DoS Attack: A DoS attack is launched from a single source (e.g., one device or IP address) and aims to overwhelm a target (e.g., a server, network, or device) with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users. For example, a DoS attack might flood a server with SYN packets to exhaust its resources.
DDoS Attack: A DDoS attack is a more sophisticated version of a DoS attack, where the attack is launched from multiple sources (e.g., a botnet of compromised devices). These sources work together to overwhelm the target, making the attack harder to mitigate because the traffic comes from many different IP addresses.
Option A, "A DDoS attack originates from external devices, while a DoS attack originates from internal devices," is incorrect. Both DoS and DDoS attacks can originate from external or internal devices. The distinction is not about the location of the devices but the number of sources involved.
Option B, "A DoS attack targets one server; a DDoS attack targets all the clients that use a server," is incorrect. Both DoS and DDoS attacks typically target a single entity (e.g., a server, network, or device) to disrupt its availability. They do not target "all the clients that use a server."
Option C, "A DDoS attack targets multiple devices, while a DoS is designed to incapacitate only one device," is incorrect. Both DoS and DDoS attacks usually target a single device or service to overwhelm it. The difference lies in the source of the attack, not the number of targets.
Option D, "A DDoS attack is launched from multiple devices, while a DoS attack is launched from a single device," is correct. This is the primary distinction between the two: a DDoS attack involves multiple sources (e.g., a botnet), while a DoS attack originates from a single source.
The HPE Aruba Networking Security Guide states:
"A Denial of Service (DoS) attack is launched from a single device to overwhelm a target, such as a server or network, making it unavailable to legitimate users. A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, in contrast, is launched from multiple devices, often a botnet of compromised systems, to flood the target with traffic from many sources, making it harder to mitigate." (Page 20, DoS and DDoS Attacks Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide notes:
"The Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) system can detect DoS and DDoS attacks. A DoS attack originates from a single source, while a DDoS attack involves multiple sources working together to overwhelm the target, such as a server or network infrastructure." (Page 423, WIP Threat Detection Section)
You are configuring ArubaOS-CX switches to tunnel client traffic to an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC). What should you do to enhance security for control channel communications between the switches and the MC?
Options:
Create one UBT zone for control traffic and a second UBT zone for clients.
Configure a long, random PAPI security key that matches on the switches and the MC.
install certificates on the switches, and make sure that CPsec is enabled on the MC
Make sure that the UBT client vlan is assigned to the interface on which the switches reach the MC and only that interface.
Answer:
BExplanation:
When configuring ArubaOS-CX switches to tunnel client traffic to an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC), securing the control channel communications is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and ensure data integrity. Option B is the correct answer as it involves configuring a long, random PAPI security key that matches on both the switches and the MC. The PAPI (Policy Access Point Interface) protocol is used for secure communication between Aruba devices, and employing a robust, randomized security key significantly enhances the security of the control channel. This setup prevents potential interception or manipulation of the control traffic between the devices.
You have an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC). for which you are already using Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) to authenticate access to the Web Ul with usernames and passwords You now want to enable managers to use certificates to log in to the Web Ul CPPM will continue to act as the external server to check the names in managers' certificates and tell the MC the managers' correct rote
in addition to enabling certificate authentication. what is a step that you should complete on the MC?
Options:
Verify that the MC has the correct certificates, and add RadSec to the RADIUS server configuration for CPPM
install all of the managers' certificates on the MC as OCSP Responder certificates
Verify that the MC trusts CPPM's HTTPS certificate by uploading a trusted CA certificate Also, configure a CPPM username and password on the MC
Create a local admin account mat uses certificates in the account, specify the correct trusted CA certificate and external authentication
Answer:
CExplanation:
To enable managers to use certificates to log into the Web UI of an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC), where Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) acts as the external server for authentication, it is essential to ensure that the MC trusts the HTTPS certificate used by CPPM. This involves uploading a trusted CA certificate to the MC that matches the one used by CPPM. Additionally, configuring a username and password for CPPM on the MC might be necessary to secure and facilitate communication between the MC and CPPM. This setup ensures that certificate-based authentication is securely validated, maintaining secure access control for the Web UI.
You have detected a Rogue AP using the Security Dashboard Which two actions should you take in responding to this event? (Select two)
Options:
There is no need to locale the AP If you manually contain It.
This is a serious security event, so you should always contain the AP immediately regardless of your company's specific policies.
You should receive permission before containing an AP. as this action could have legal Implications.
For forensic purposes, you should copy out logs with relevant information, such as the time mat the AP was detected and the AP's MAC address.
There is no need to locate the AP If the Aruba solution is properly configured to automatically contain it.
Answer:
C, DExplanation:
When responding to the detection of a Rogue AP, it's important to consider legal implications and to gather forensic evidence:
You should receive permission before containing an AP (Option C), as containing it could disrupt service and may have legal implications, especially if the AP is on a network that the organization does not own.
For forensic purposes, it is essential to document the event by copying out logs with relevant information, such as the time the AP was detected and the AP's MAC address (Option D). This information could be crucial if legal action is taken or if a detailed analysis of the security breach is required.
Automatically containing an AP without consideration for the context (Options A and E) can be problematic, as it might inadvertently interfere with neighboring networks and cause legal issues. Immediate containment without consideration of company policy (Option B) could also violate established incident response procedures.
You have an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC) that is locked in a closet. What is another step that Aruba recommends to protect the MC from unauthorized access?
Options:
Use local authentication rather than external authentication to authenticate admins.
Change the password recovery password.
Set the local admin password to a long random value that is unknown or locked up securely.
Disable local authentication of administrators entirely.
Answer:
BExplanation:
Protecting an Aruba Mobility Controller from unauthorized access involves several layers of security. One recommendation is to change the password recovery password, which is a special type of password used to recover access to the device in the event the admin password is lost. Changing this to something complex and unique adds an additional layer of security in the event the physical security of the device is compromised.
A client has accessed an HTTPS server at myhost1.example.com using Chrome. The server sends a certificate that includes these properties:
Subject name: myhost.example.com
SAN: DNS: myhost.example.com; DNS: myhost1.example.com
Extended Key Usage (EKU): Server authentication
Issuer: MyCA_SigningThe server also sends an intermediate CA certificate for MyCA_Signing, which is signed by MyCA. The client’s Trusted CA Certificate list does not include the MyCA or MyCA_Signing certificates.Which factor or factors prevent the client from trusting the certificate?
Options:
The client does not have the correct trusted CA certificates.
The certificate lacks a valid SAN.
The certificate lacks the correct EKU.
The certificate lacks a valid SAN, and the client does not have the correct trusted CA certificates.
Answer:
AExplanation:
When a client (e.g., a Chrome browser) accesses an HTTPS server, the server presents a certificate to establish a secure connection. The client must validate the certificate to trust the server. The certificate in this scenario has the following properties:
Subject name: myhost.example.com
SAN (Subject Alternative Name): DNS: myhost.example.com; DNS: myhost1.example.com
Extended Key Usage (EKU): Server authentication
Issuer: MyCA_Signing (an intermediate CA)
The server also sends an intermediate CA certificate for MyCA_Signing, signed by MyCA (the root CA).
The client’s Trusted CA Certificate list does not include MyCA or MyCA_Signing.
Certificate Validation Process:
Name Validation: The client checks if the server’s hostname (myhost1.example.com) matches the Subject name or a SAN in the certificate. Here, the SAN includes "myhost1.example.com," so the name validation passes.
EKU Validation: The client verifies that the certificate’s EKU includes "Server authentication," which is required for HTTPS. The EKU is correctly set to "Server authentication," so this validation passes.
Chain of Trust Validation: The client builds a certificate chain from the server’s certificate to a trusted root CA in its Trusted CA Certificate list. The chain is:
Server certificate (issued by MyCA_Signing)
Intermediate CA certificate (MyCA_Signing, issued by MyCA)
Root CA certificate (MyCA, which should be in the client’s trust store) The client’s Trusted CA Certificate list does not include MyCA or MyCA_Signing, meaning the client cannot build a chain to a trusted root CA. This causes the validation to fail.
Option A, "The client does not have the correct trusted CA certificates," is correct. The client’s trust store must include the root CA (MyCA) to trust the certificate chain. Since MyCA is not in the client’s Trusted CA Certificate list, the client cannot validate the chain, and the certificate is not trusted.
Option B, "The certificate lacks a valid SAN," is incorrect. The SAN includes "myhost1.example.com," which matches the server’s hostname, so the SAN is valid.
Option C, "The certificate lacks the correct EKU," is incorrect. The EKU is set to "Server authentication," which is appropriate for HTTPS.
Option D, "The certificate lacks a valid SAN, and the client does not have the correct trusted CA certificates," is incorrect because the SAN is valid, as explained above. The only issue is the missing trusted CA certificates.
The HPE Aruba Networking AOS-CX 10.12 Security Guide states:
"For a client to trust a server’s certificate during HTTPS communication, the client must validate the certificate chain to a trusted root CA in its trust store. If the root CA (e.g., MyCA) or intermediate CA (e.g., MyCA_Signing) is not in the client’s Trusted CA Certificate list, the chain of trust cannot be established, and the client will reject the certificate. The Subject Alternative Name (SAN) must include the server’s hostname, and the Extended Key Usage (EKU) must include ‘Server authentication’ for HTTPS." (Page 205, Certificate Validation Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking Security Fundamentals Guide notes:
"A common reason for certificate validation failure is the absence of the root CA certificate in the client’s trust store. For example, if a server’s certificate is issued by an intermediate CA (e.g., MyCA_Signing) that chains to a root CA (e.g., MyCA), the client must have the root CA certificate in its Trusted CA Certificate list to trust the chain." (Page 45, Certificate Trust Issues Section)
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the current network topology.
You are deploying a new wireless solution with an Aruba Mobility Master (MM). Aruba Mobility Controllers (MCs). and campus APs (CAPs). The solution will Include a WLAN that uses Tunnel for the forwarding mode and Implements WPA3-Enterprise security
What is a guideline for setting up the vlan for wireless devices connected to the WLAN?
Options:
Assign the WLAN to a single new VLAN which is dedicated to wireless users
Use wireless user roles to assign the devices to different VLANs in the 100-150 range
Assign the WLAN to a named VLAN which specified 100-150 as the range of IDs.
Use wireless user roles to assign the devices to a range of new vlan IDs.
Answer:
BExplanation:
When setting up VLANs for a wireless solution with an Aruba Mobility Master (MM), Aruba Mobility Controllers (MCs), and campus APs (CAPs), it is recommended to use wireless user roles to assign devices to different VLANs. This allows for greater flexibility and control over network resources and policies applied to different user groups. Wireless user roles can dynamically assign devices to the appropriate VLAN based on a variety of criteria such as user identity, device type, location, and the resources they need to access. This approach aligns with the ArubaOS features that leverage user roles for network access control, as detailed in Aruba's configuration and administration guides.
What are some functions of an AruDaOS user role?
Options:
The role determines which authentication methods the user must pass to gain network access
The role determines which firewall policies and bandwidth contract apply to the clients traffic
The role determines which wireless networks (SSiDs) a user is permitted to access
The role determines which control plane ACL rules apply to the client's traffic
Answer:
BExplanation:
An ArubaOS user role determines the firewall policies and bandwidth contracts that apply to the client’s traffic. When a user is authenticated, they are assigned a role, and this role has associated policies that govern network access rights, Quality of Service (QoS), Layer 2 forwarding, Layer 3 routing behaviors, and bandwidth contracts for users or devices.
What is an Authorized client as defined by ArubaOS Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIP)?
Options:
a client that has a certificate issued by a trusted Certification Authority (CA)
a client that is not on the WIP blacklist
a client that has successfully authenticated to an authorized AP and passed encrypted traffic
a client that is on the WIP whitelist.
Answer:
CExplanation:
In the context of ArubaOS Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIP), an authorized client is defined as a client that has successfully authenticated to an authorized Access Point (AP) and has passed encrypted traffic. This ensures that only clients which have been verified and authenticated according to the network's security policies are allowed to access network resources. Authentication typically involves credentials that are validated by a server, confirming the client's right to access the network securely.
Unlock HPE6-A78 Features
- HPE6-A78 All Real Exam Questions
- HPE6-A78 Exam easy to use and print PDF format
- Download Free HPE6-A78 Demo (Try before Buy)
- Free Frequent Updates
- 100% Passing Guarantee by Activedumpsnet
Questions & Answers PDF Demo
- HPE6-A78 All Real Exam Questions
- HPE6-A78 Exam easy to use and print PDF format
- Download Free HPE6-A78 Demo (Try before Buy)
- Free Frequent Updates
- 100% Passing Guarantee by Activedumpsnet
