Cisco 352-011 Cisco Certified Design Expert Practical Exam Exam Practice Test
Cisco Certified Design Expert Practical Exam Questions and Answers
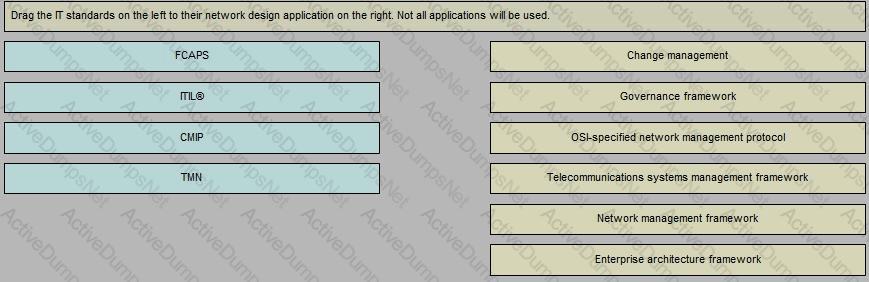
Which three options are important design functions of IPv6 first-hop security? (Choose three)
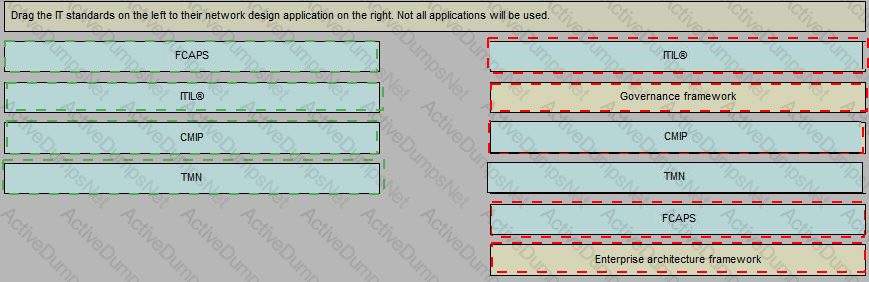
Refer to the exhibit.

This enterprise customer wants to stream one-way video from their head office to eight branch offices using multicast. Their current service provider provides a Layer 3VPN solution and manages the CE routers, but they do not currently multicast. Which solution quickly allows this multicast traffic to go through while allowing for future scalability?
When you design a network that uses IPsec, where can you reduce MTU to avoid network fragmentation?
Which two options describe the advantages of using DWDM over traditional optical networks? (Choose two)
ACME Agricultural requires that access to all network devices is granted based on identify validation, and an authentication server was installed for this purpose. Currently the network team uses a list of passwords based on regions to access the internal corporate network devices. Which protocol do you recommend to ensure identify validation from the authentication server to the corporate directory?
Refer to the exhibit.
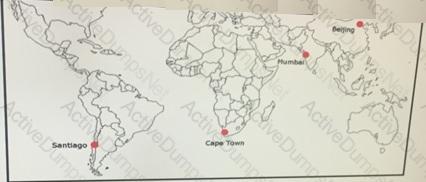
ACME Mining has four data centers in Santiago, Cape Town, Mumbai, and Beijing. They are full-mesh connected via a 400 Mb/s EVP-LAN. A 1-TB transfer occurs daily via FTP between the Santiago and Mumbai data centers. When testing, the data transfer took an ''unexpected and outrageous, with an average transfer rate of 47 KB/s. The team provided this information.
LAN bandwidth usage below 5% at both data centers during transfer.
WAN bandwidth usage was between 20-30% at both data centers during transfer.
The only QoS on WAN is KB/s strict priority configured for other types of traffic.
There is no QoS on LAN.
The ping RTT average between data centers is 378 milliseconds.
Which action improves the file transfer rate?
What is a design application of control plane policing?
Which feature or technology that affects the operations of IPsec should be taken into account when designing an IPsec network using Authentication header?
Refer to the exhibit,
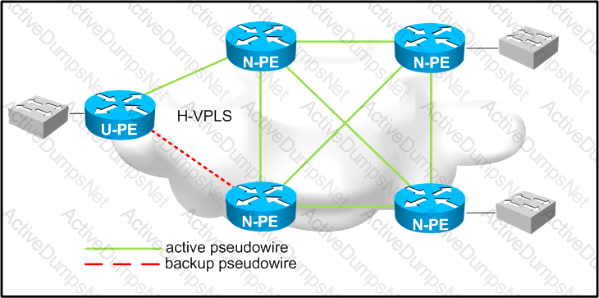
Which two design considerations should be implemented on the pseudowire between N-PE and U-PE routers for a loop-free hierarchical VPLS service? (Choose two)
Which mechanism should be added to a network design to identify unidirectional Spanning Tree Protocol failures through BPDU loss?
Which two are IoT sensor-specific constraints? (Choose two)
In a network with dynamic mutual redistribution between multiple OSPFv2 and EIGRP boundaries, which two mechanisms avoid suboptimal routing? (Choose two)
You are designing an optical network. Your goal is to ensure that your design contains the highest degree of resiliency. In which two ways should you leverage a wavelength-switched optical network solution in your network design? (Choose two.)
Which two conditions are required for successful route aggregation? (Choose two)
Refer to the exhibit.
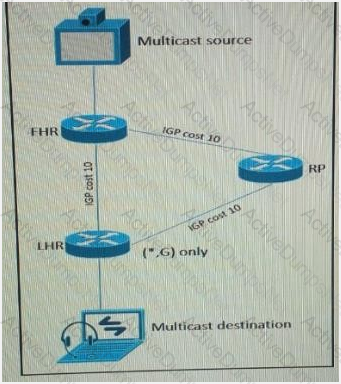 As part of a redesign project, you must predict multicast behavior. What is the resultant multicast traffic receiving on the shared tree( , G), if it is received on the LHR interface indicated?
As part of a redesign project, you must predict multicast behavior. What is the resultant multicast traffic receiving on the shared tree( , G), if it is received on the LHR interface indicated?
A data center provider has designed a network using these requirements
Two data center sites are connected to the public internet
Both data centers are connected to different Internet providers
Both data centers are also directly connected with a private connection for the internal traffic can also be at this direct connection The data center provider has only /19 public IP address block
Under normal conditions, Internet traffic should be routed directly to the data center where the services are located. When one Internet connections fails to complete traffic for both data centers should be routed by using the remaining Internet connection in which two ways can this routing be achieved? (Choose two)
ACME Corporation is deploying a new HR application that requires the network infrastructure to monitor and react to certain condition in the network.
Which feature should be used to meet this design requirement?
You are designing dual-homed active/active ISP connections from an enterprise customer for internet services, and you have recommended BGP between the customer and ISP. When three security mechanisms do you enable to secure the connection? (Choose three)
Which interconnectivity method offers the fastest convergence in the event of a unidirectional issue between three Layer 3 switches connected together with routed links in the same rack in a data center?
A large ISP is analysing which IGP meets these following requirements
Network must be resilient against unstable MTU in one side of newly released transmission pieces of equipment
Network must support MPLS traffic engineering solution for future use
Which IGP must be selected and why?
Which two SAN designs appropriate to support large-scale SAN environments? (Choose two)
Company ABC grew organically and now their single-area OSPF network has an unacceptably slow convergence time after a topology change. To address the slow convergence time, they want to introduce a multiarea OSPF design and implement address summarization at the area border routers, which option should be their main concern about this redesign?
As network designer, which option is your main concern with regards to virtualizing multiple network zones into a single hardware device?
Which option is a critical mechanism to optimize convergence speed when using MPLS FRR?
What is an effect of using ingress filtering to prevent spoofed addresses on a network design?
A network engineering team is in the process of designing a lab network for a customer demonstration. The design engineer wants to show that the resiliency of the MPLS traffic Engineering Fast Reroute solution has the same failover/failback times as a traditional SONET/SDH network (around 50MSEC). In order to address both link failure and node failure within the lab typology network, which type of the MPLS TE tunnels must be considered for this demonstration?
Which two statements about VXLAN are true? (Choose two)
Your client is considering acquiring a new IPv6 address block so that all Ethernet interfaces on the network receive addresses based on their burned-in hardware addresses, with support for 600 VLANs. Which action do you recommend?
What is an advantage of placing the IS-IS flooding domain boundary at the core Layer in a three-layer hierarchical network?
Refer to the exhibit.
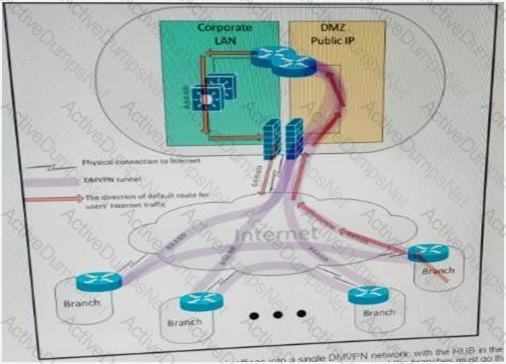
A customer interconnected hundreds of branch offices into a single DMVPN network, with the HUB in the main data center. Due to security policies, the customer requires that the default route for all Internet traffic from the users at the branches must go through the tunnel and the only connections that are allowed to and from the branch router over the local internet circuit are the DMVPN tunnels. Which two combined actions must you take on the branch router to address these security requirements and keep the solution scalable? (Choose two)
Which two conditions must be met for EIGRP to maintain an alternate loop-free path to a remote network? (Choose two)
Which option reduces jitter in a VoIP network?
Which two impacts of adding the Ip events dampening feature to a network design are true? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit.
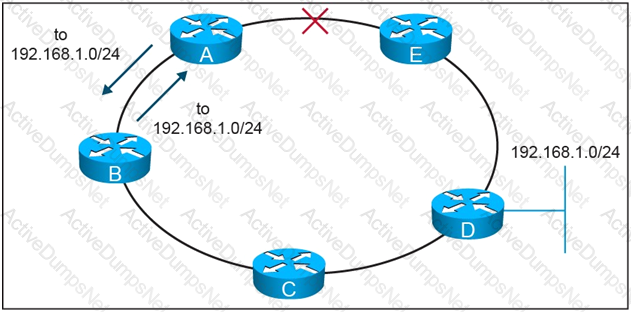
On this MPLS-based network ring, links have failed between router A and router E. These failures formed microloops while the network converged, when A forwarded traffic to B but B forwards it back to A. Which technology is the simplest solution to avoid microloops without enabling a new protocol in the network?
Which mechanism provides fast path failure detection?
Which two options are reasons for designing a large OSPF network with multiple areas connected to the backbone? (Choose two)