Cisco 300-510 Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions Exam Practice Test
Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions Questions and Answers
Refer to the exhibit.

Customer traffic from the branch site to the hub is experiencing packet drops. The engineer verified that:
- Customer traffic from the hub is able to reach the branch site.
- The connection between PE1 and PE2 is working normally.
- Routers P1 and P2 are able to ping devices on the hub site.
Which action resolves the issue?
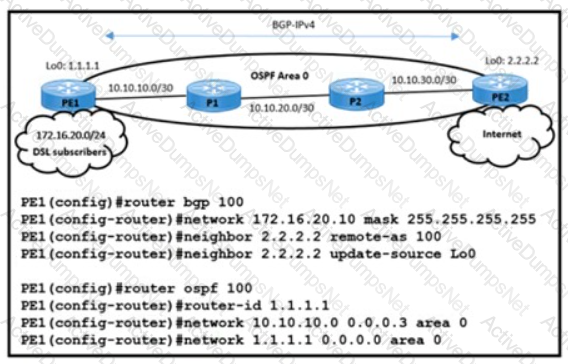
Refer to the exhibit The engineering team noticed route disruptions when DSL subscriber 172.16.20.10 goes offline. In this service provider environment:
The OSPF backbone area is configured to advertise loopback prefixes
The PE routers are running BGP-IPv4 address family in a BGP-free core topology.
The DSL subscriber IP subnet 172.16.20.10/32 is redistributed in BGP on PE1
Which configuration on PE1 resolves the issue?
Level 3 switch SW1 is part of an EIGRP enabled network located at the edge of an area. Cisco Express Forwarding and SSO are enabled on the router. A network engineer must minimize the downtime of data-transmit services in the network. HSRP group 2 has already been configured with standby preempt delay minimum 2 and standby timers 140. Which additional action must the engineer take on SW1 to suppress routing flaps for 2 minutes?
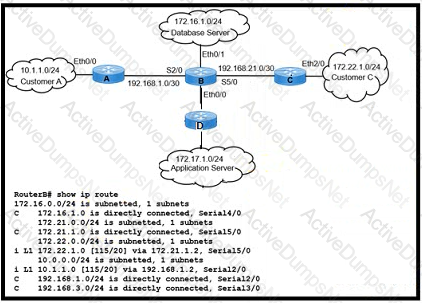
Refer to the exhibit. Customers A and C are experiencing packet drops when connecting to the application server While troubleshooting the problem the network engineer confirms that the IS-lS Level- 1/2 adjacency is up between routers A B C. and D and both customers can communicate with the database server without packet loss Which action must the engineer take to resolve the issue?
Refer to the exhibits.
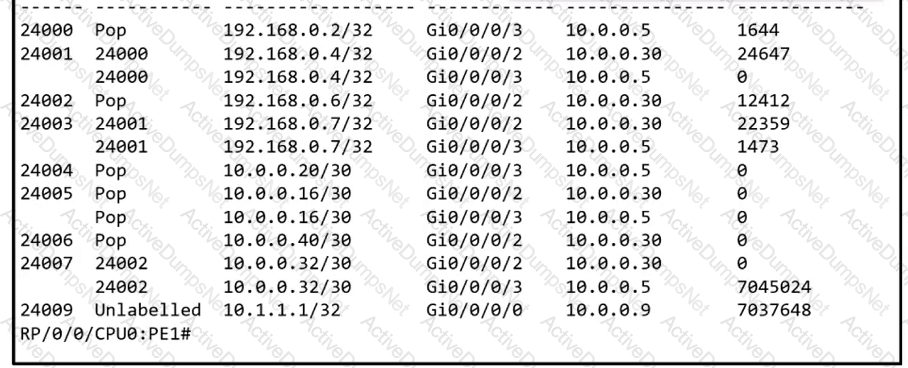
A network operator is troubleshooting packet loss seen from the R1 loopback interface to the R2 loopback interface over the core network. The operator is attempting to identify the next leg in the path from PE1. Which interface and label path should the operator investigate next?
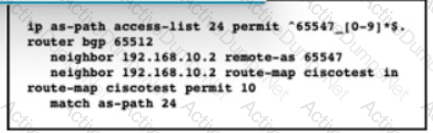
Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 is expected to receive routes that originate from AS 65547 only. However, R1 is receiving routes from AS 65547 and several other ASs that are directly attached to it. Which change to the AS path permit filter corrects the problem?
You have configured routing policies on a Cisco IOS XR device with routing policy language. Which two statements about the routing policies are true? (Choose two.)
An ISP has an MPLS VPN-based network with 12 PE routers. How many peerings are required between the 12 routers if the engineer has not configured route reflectors?

Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is troubleshooting an issue with traffic steering using the color-only automated steering mechanism. BGP is failing to automatically steer traffic into an SR policy with the given color of a route, regardless of the next hop. The layer 2 configuration is correct, and the physical connection between the devices is working normally. Whch additional command sequence must the engineer add to correct the issue?

What is the difference between basic IS-IS and OSPF packet types?
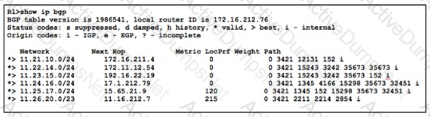
Refer to the exhibit. Company A established BGP sessions with several ISPs. A network engineer at the company must filter out all traffic except for routes that transit AS 152. The engineer configured the filtering policy “permit _152S_(_[0.9])” on R1, but after applying the configuration, the engineer notices that other routes are still visible. Which action resolves the issue?

Refer to the exhibit.
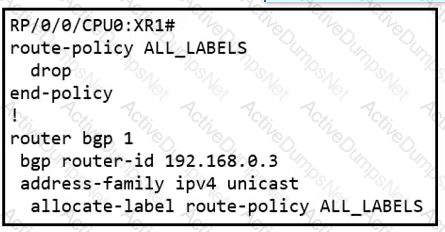
A network operator is working to deploy a Unified BGP design and allow it to be available only in selected markets and services in the future. The label allocation is not functioning as desired. Which action will fix the issue?
Refer to the exhibit.
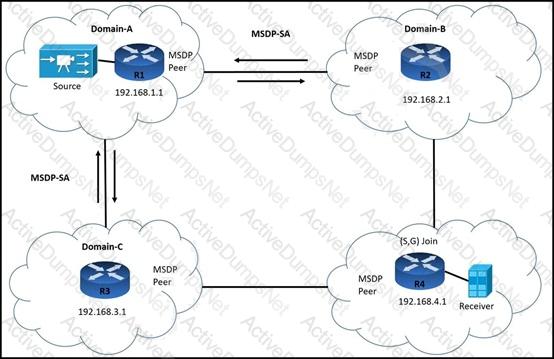
R3 is:
Which command must the engineer implement to resolve the issue?
A R3# ip msdp sa-filter in 192.168.3.1
B. R3# no ip msap sa-filter in 192.168.1.1
C R3# no ip msdp peer 192.168.1.1
D. R3# ip msdp sa-filter out 192.168.1.1
After an engineer configures BGP in R1, it starts receiving this message
*Jun 29 13:30:50.122: %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 192.168.10.1 Down User reset
Jun 29 13:30:52.341: %BGP-3-NOTIFICATION: sent to neighbor 192.168.10.1 2/6 (unacceptable hold time) 0 bytes
Which action makes the peering come back up again?
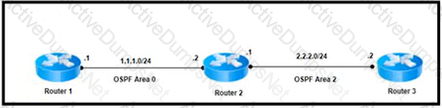
Refer to the exhibit A network engineer installed a new router (router 3) at the regional hub running MPLS services for scalability Router 3 is connected to the 10.44 4.0,'24. 10.44 5.024. 10 44.6.0/24. and 10 44 7 0/24 subnets The new router has been configured for OSPF area 2. and it is advertising the four connected networks. The engineer noticed that the same networks are listed as interarea summary routes, and they are being flooded into each area on the area borders Which action resolves the issue?
Refer to the exhibit.
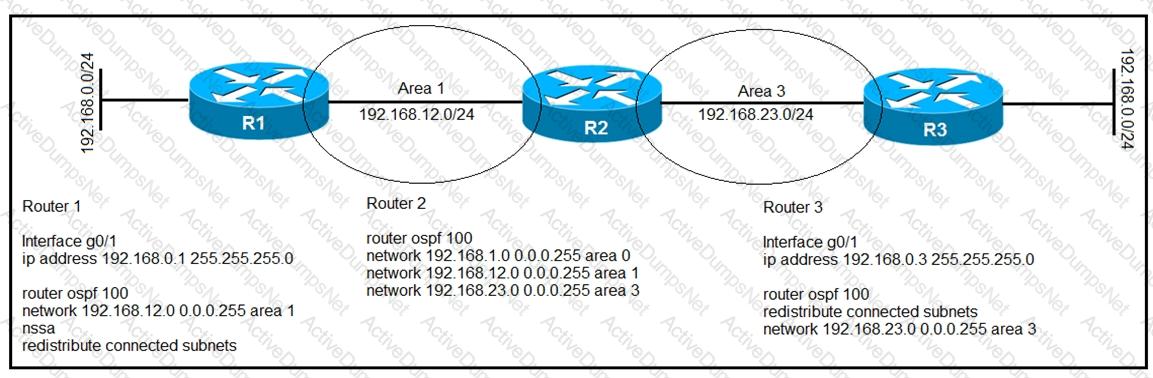
After troubleshooting an OSPF adjacency issue, routers 1, 2, and 3 have formed OSPF
neighbor relationships. Which statement about the configuration is true?
Refer to the exhibit.
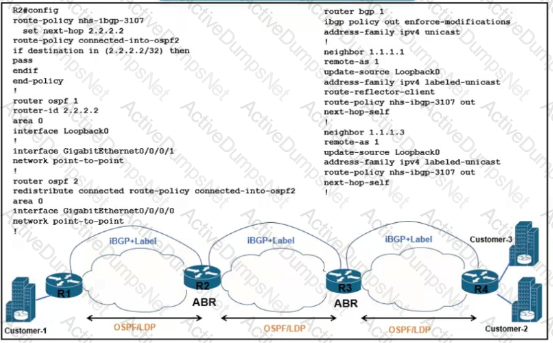
There is a connectivity issue between Customer-1 and Customer-2 File servers between the customers cannot send critical data R3 routes are missing from the routing table on the Customer-1 router All interlaces on Customer-1 are up Which configuration must be applied to router R2 to correct the problem?

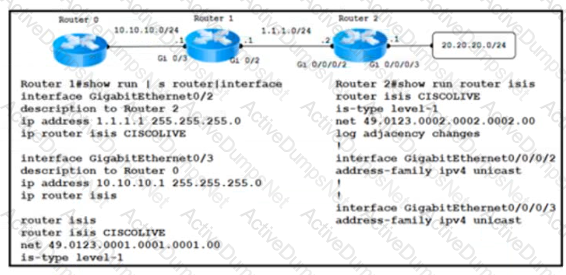
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is troubleshooting a network routing issue on this IS-IS network situated at the customer's regional hub. Router 2 that runs Cisco IOS XR Software cannot see the network 10.1.1.0/24 on router 1. The Layer 2 encapsulations are correct. The ARP connectivity for the Ethernet interface that runs IS-IS is working. Which action resolves the issue?
Refer to the exhibit.
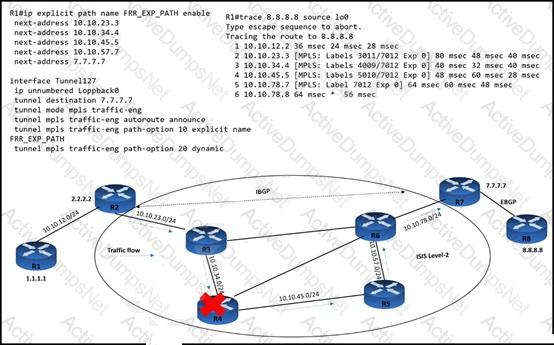
An MPLS core network has connectivity issues R4 has failed. It impacts traffic loss between R1 and R8. Customers report no access to their file servers, which delays their transformation work. Which quick action resolves the issue until R4 recovers?
Refer to the exhibit.

After configuring IS-IS on routers R1 and R2, an engineer notices that only the loopback interface at 2000:1::1 /96 is known to router R2. Which change must be made so that only Loopback2 is advertised from R1 to R2?
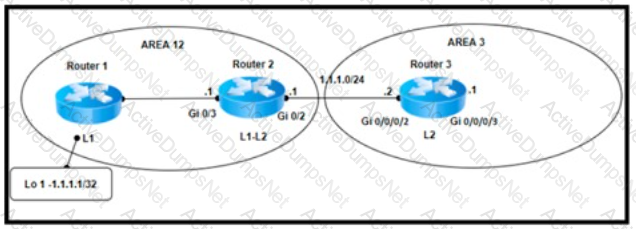
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer configured three new PE routers to expand the network. The new routers run in the IS-IS routing protocol and reside in the data center in the same exchange as the existing routers. However, the network is now experiencing suboptimal routing. The Layer 2 configuration and VLANs are configured correctly to provide segregation between networks, but the Level 1 routes are not being converted to Level 2 routes. Which action resolves the issue?
What is the purpose of a BGP confederation?
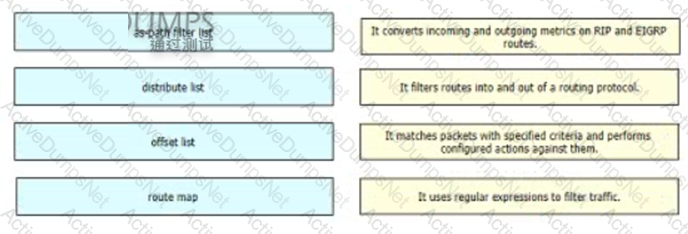
Drag and drop the route-manipulation methods from the left onto their features on the right
Refer to the exhibit.
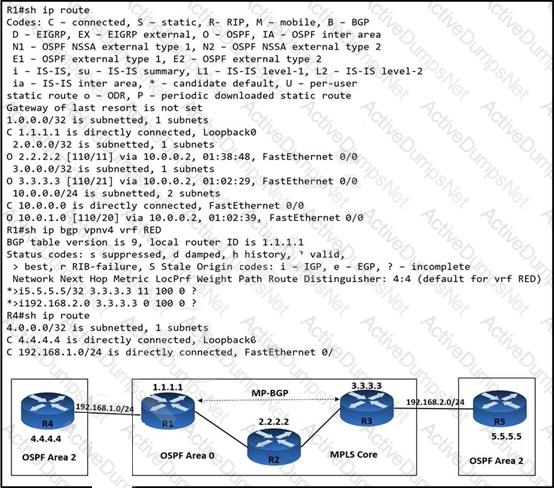
An engineer is troubleshooting connectivity issues on the MPLS core network. A customer connected through R4 cannot reach the OSPF domain on R5. While checking the routing table of R1, the engineer cannot see all the routes from R3 and R5. Which task must the engineer perform so that R4 is able to reach R5?
Which lag command is used within route-map to redistribute routes that match with routes tagged with the specified tag numbers?
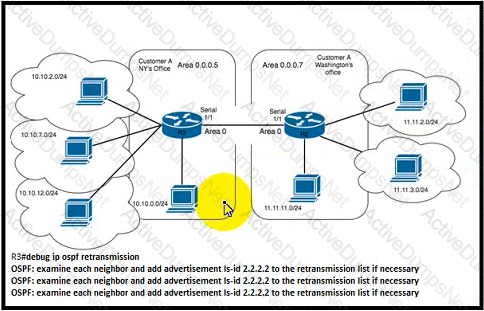
Refer to the exhibit. Customer A is a small media company with two offices connected by a 512 Kbps line. Their NY office is connected to several external partners by static routes on router R3. VoIP services use VoIP codec G729 Users reported poor voice quality and slow data transfer between the offices A network engineer configured ip tcp header-compression iphc-format on R2 and R3 routers Which additional action must the engineer take to fix the issue?
Which two conditions must be met before separate ISPs can provide interdomain multicast routing? (Choose
two.)
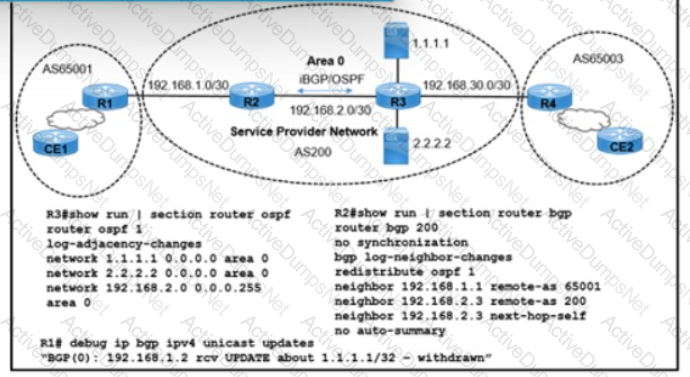
Refer to the exhibit. Users connected to an application on 1.1.1.1 via routers CE1 and CE2 are complaining of frequent disconnections. While troubleshooting the issue, a network engineer with an employee ID: 4333:96:916 determined that the application itself is working normally, but the link connected to the 1.1.1.1 application is flapping. The users on CE1 and CE2 are accessing applications on 2.2.2.2 without difficulty. Which action resolves the issue?
While configuring Cisco NSF awareness, a network engineer enters the bgp graceful-restart command after the BGP session is established in a router that runs IOS XE Software. Graceful restart capabilities are not exchanged. Which two actions should be taken? (Choose two.)
After changing the IP address on an IOS XR router, an engineer cannot ping the new address Which step did the engineer forget to complete?
What is the purpose of ACL type prefix set entries in RPL prefix sets?
Refer to the exhibit.

Which task must you perform on interface g1/0/0 to complete the SSM implementation?
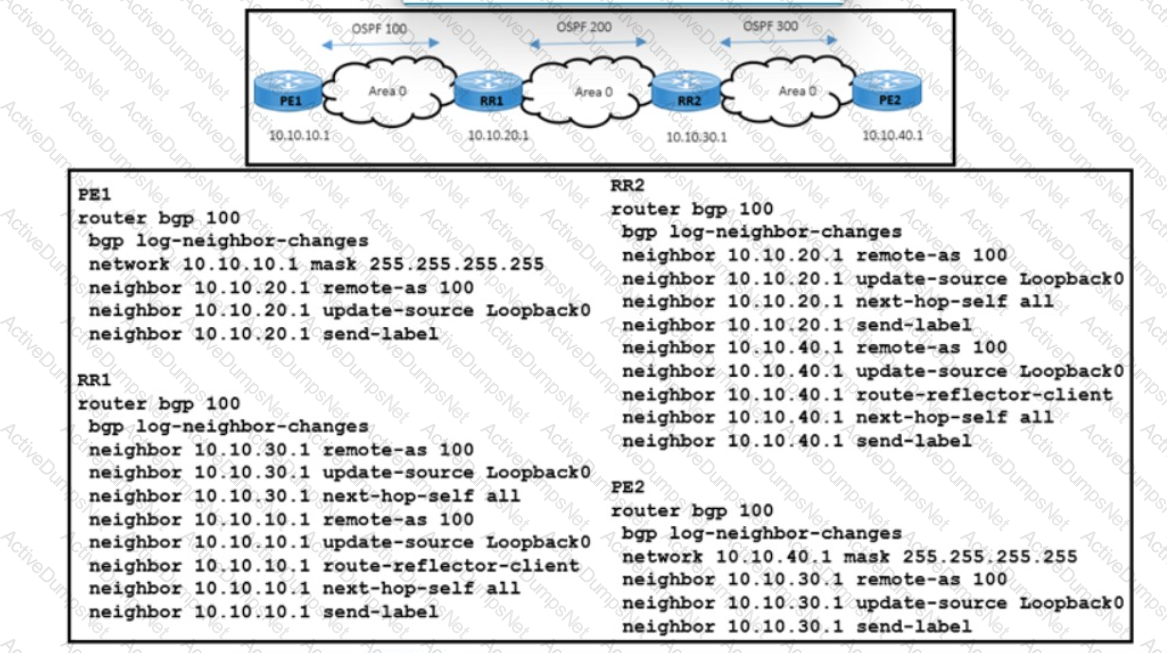
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is investigating a report of packet drops in an application running on a server connected to PE2 The engineer determined that:
- The OSPF adjacency in area 0 is up. and it is learning the loopback addresses of all routers in area 0.
- Traffic from users connected to PE1 to the application is also passing normally.
- Packets from PE2 back to PE1 are being dropped
Which action resolves the issue?

Refer io the exhibit.

While applying the configurations on two routers an engineer notices that OSPF adjacency Between them remains down Through the ping test the engineer confirmed that both me routers have Layer 3 reachability between them Which action should me engineer take to make the adjacencies to full?
What is the difference between RPL and route-maps?
Refer to the exhibit.
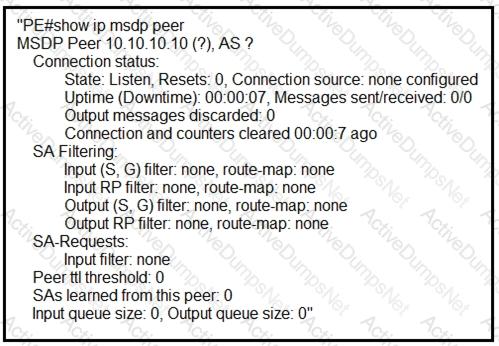
A service provider technician is working on a multicast issue for a customer. While
checking the multicast table, the technician notices that no flags are present for the (1.1.1.1, 239.1.1.1) entry, yet flags are present for the (1.1.1.1, 232.1.1.1) entry.
Which factor might explain this issue?
An engineer is troubleshooting slow performance issues on a customer’s network after the last multicast configuration change was applied on it While checking the running configuration on the router the engineer notices there are many ip igmp join-group commands applied on several interfaces of the router which caused the high CPU utilization usage. What action must the engineer take to solve this issue?
After you change the IP address on an IOS XR router, you cannot ping the new address.
Which step did you forget to complete?
Refer to the exhibit.

What is the effect of this configuration?
Which keyword is used with the match route-type command to redistribute the external BGP and IGP routes using route map?
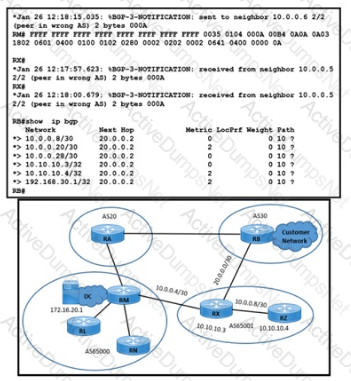
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer working for a private telecommunication company with an employee id: 4233:46:364 notices that the customer network going through AS30-AS65001-AS65000 is experiencing packet drops when it accesses an application at 172.16.20.1/32 In the DC cloud. The BGP link between AS20 and AS30 is inaccessible because of a fiber cut. Routers RL, RN, and RZ are configured with confederation identifier 10. Which action resolves this Issue?

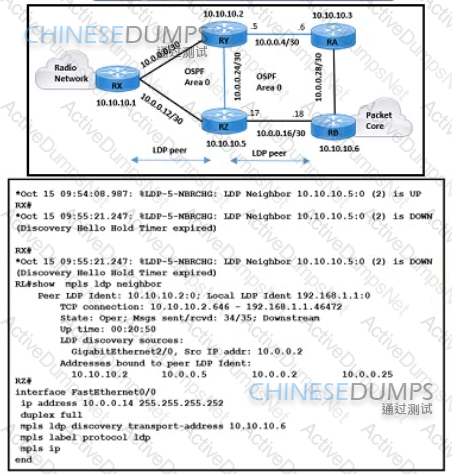
Refer to the exhibit MPLS traffic from the packet core that is connected to router RX (10 10 101) to the radio network that is connected to router RB (10 10 10 6) uses the longer route RB R2 RY RX RX and R2 are configured with a default value of LDP hello and hold intervals The team verified that OSPF neighborship in Area 0 is established between RX and R2 Which action must be taken to choose the shortest path and resolve the issue?
A)

B)

C)

D)

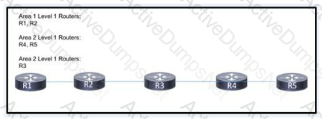
Refer to the exhibit. This network is deployed with all connected links configured to run IS-IS. The routing protocol is enacted globally on each router, and the network engineer expects full routing Information to be shared among all routers. R5 is receiving routes from R4 but is missing routes from R1. Which action corrects the issue so that all routes are shared among the routers?
An engineer is working to implement segment routing protocol on the customer's core network. Which step should the engineer take before the segment routing is enabled and is running with BGP?
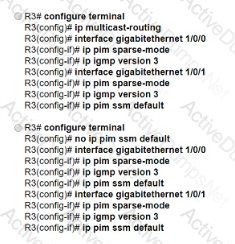
A network engineer recently deployed a wireless network for users at a new office to join video conferences wirelessly The existing network consists of routers that are configured for EIGRP and BGP. which are located at several data centers in different physical locations The engineer configured PIM-SSM within a single domain from a single source However, during the testing phase, the video conference failed to work for any of the users. The IPs are reachable and firewalls in the network are configured correctly to allow the traffic. Which action resolves the issue?
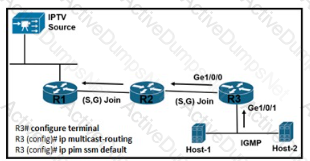
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is configuring router R3 to handle multicast streams, but Host-2 cannot send subscriptions messages to the IPTV source. Which configuration must the engineer apply to router R3 so it passes the IPTV stream to Host-2?

Which lag command is used within route-map to redistribute routes that match with routes tagged with the specified tag numbers?
For which reason do you deploy BGP confederations within a BGP transit backbone?
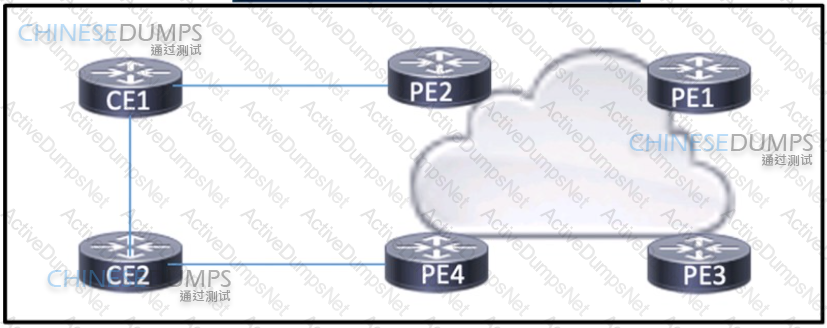
Refer to the exhibit. Company X is multihomed to a service provider. With the default settings, the link between PE2 and CE1 is the primary link, but company X has asked for the link between PE4 and CE2 to operate as the primary instead. A network engineer used a route map with local-preference to manipulate the routes from PE2 to CE1 to be less desirable and applied the route map on PE2 outbound to CE1. However, the path from PE2 to CE1 is still preferred. Which action must the engineer take so that the desired path is chosen?
What is the role of a segment routing mapping server?
What can be used to determine a path from the head-end to a tail-end router when implementing SR-TE with a head-end, with little information on the network topology?
What is a requirement of PIM-SM?
Refer to the exhibit.
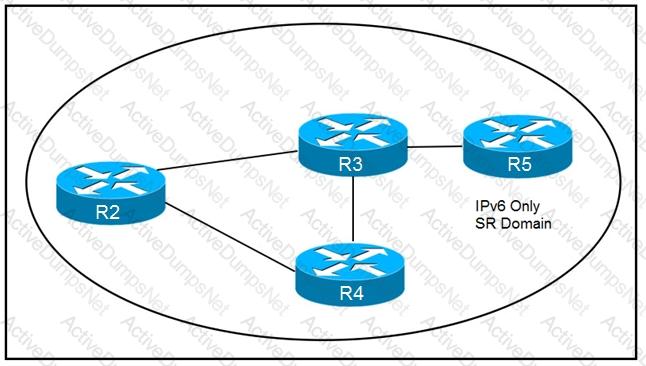
How are packets directed through the data plane when SRv6 is implemented?
Refer to the exhibit.
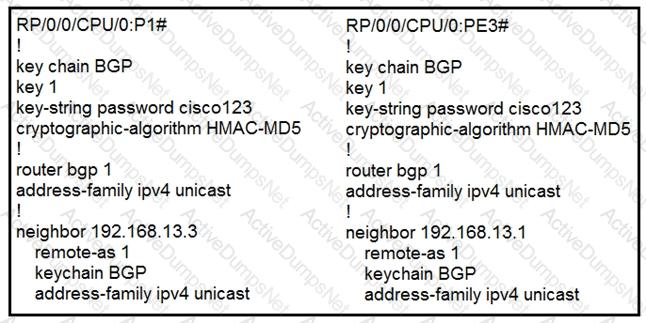
P1 and PE3 Cisco IOS XR routers are directly connected and have this configuration
applied. The BGP session is not coming up. Assume that there is no IP reachability problem and both routers
can open tcp port 179 to each other. Which action fixes the issue?
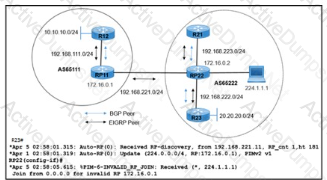
Refer to the exhibit. R21 is a multicast source sending multicast traffic 224.1.1.1 to R23, with RP22 serving as the rendezvous point inside AS65222. A network engineer noticed that when R21 goes down, R12 in AS65111 starts to send the same multicast group 224.1.1.1 through RP11. Which action resolves the issue ?
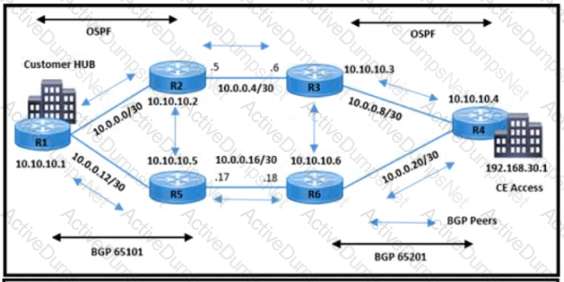
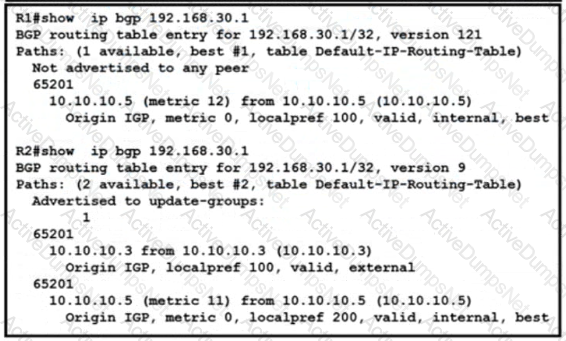
Refer to the exhibit. The service provider operations team was alerted that hub site traffic from BGP AS 65101 to AS 65201 uses a non-primary path via the R5-R6 link. IBGP peering between R1 and R2 is up. and no fiber failure has been reported on the R2-R3 link The team determined that the traffic flow between 10.10.10.1 and 192.168.30.1 is not considering the R1-R2-R3-R4 path. Which action resolves this issue?
Refer to the exhibit
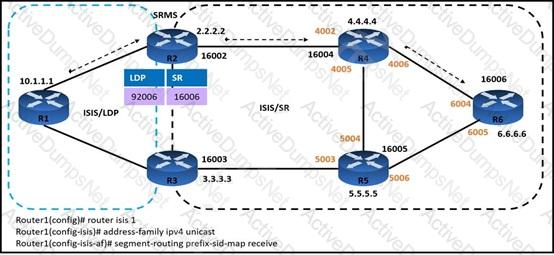
An engineer is configuring service traffic from router R1 to R6 as shown. Which additional configuration must the engineer implement so that the LDP and SR domains will participate and interwork with each other?
Which two statements about mapping multicast IP addresses to MAC addresses are true? (Choose two.)
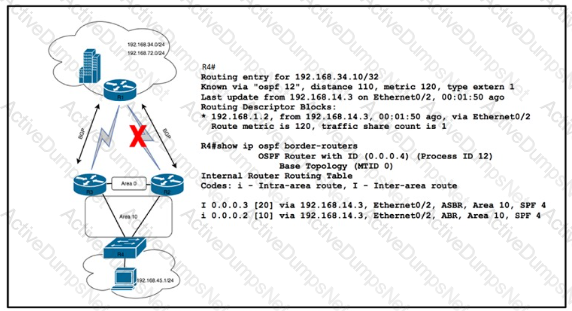
Refer to the exhibit. After a recent network implementation project, customer A is performing stress testing to verify network redundancy at the branch office connected to R4. When the link from R2 is shut öown as shown, the SLA tracking object fails and the cost of the link between R2 and R4 increases to 100. However, a traceroute operation from a PC in the Branch office shows that traffic to HQ is still routed via R2. Which solution corrects the problem and optimizes traffic flow via R3 without creating operational overhead?
Refer to the exhibit.

Customer traffic from the branch site to the hub is experiencing packet drops. The engineer verified that:
- Customer traffic from the hub is able to reach the branch site.
- The connection between PE1 and PE2 is working normally.
- Routers P1 and P2 are able to ping devices on the hub site.
Which action resolves the issue?
How does SRv6 function on the control plane?
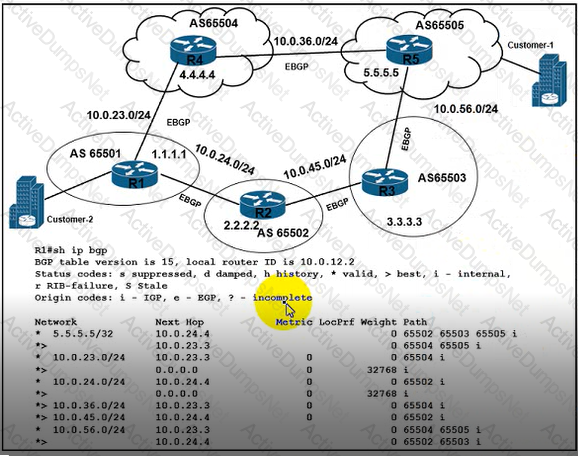
Refer to the exhibit There is a BGP traffic path issue between Customer-1 and Customer-2 Users from Customer-2 have reported file transfer issues High utilization on the path between both customers causes many packet drops. Which configuration resolves the issue?

What is the difference between RPL and route map actions?
Refer to the exhibits.
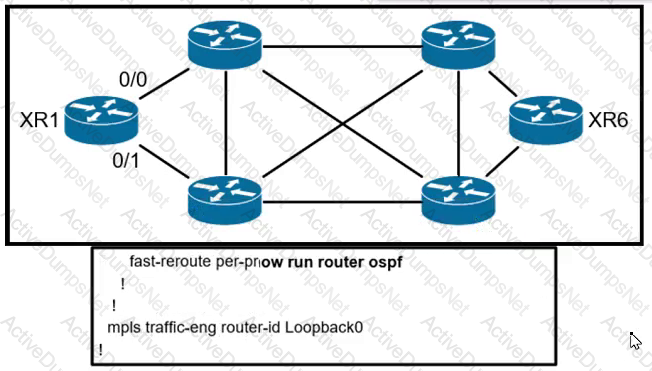
All links inside the network are configured at a default cost of one inside the fully converged OSPF domain. Given the configuration from XR1, which interface does traffic from XR1 that is destined to the loopback interface of XR6 select for the exiting interface?

