Cisco 300-220 Conducting Threat Hunting and Defending using Cisco Technologies for Cybersecurity 300-220 CBRTHD Exam Practice Test
Conducting Threat Hunting and Defending using Cisco Technologies for Cybersecurity 300-220 CBRTHD Questions and Answers
A SOC leadership team wants to demonstrate the business value of investing in Cisco-based threat hunting capabilities. Which outcome BEST demonstrates that value?
Refer to the exhibit.
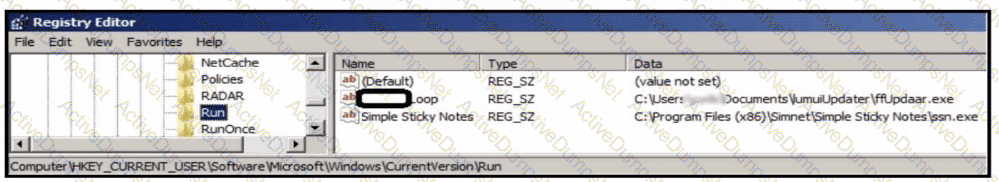
An analyst is evaluating artifacts and logs collected from recent breach. In the logs, ATP established persistency of malware by placing a path to the executable in a specific registry entry. What is the difference between the ATP's approach and using HKEY LOCAL MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run instead?
A threat hunter completes a structured hunt and confirms malicious lateral movement within the environment. Which action BEST ensures the hunt contributes to long-term defensive improvement?
Refer to the exhibit.
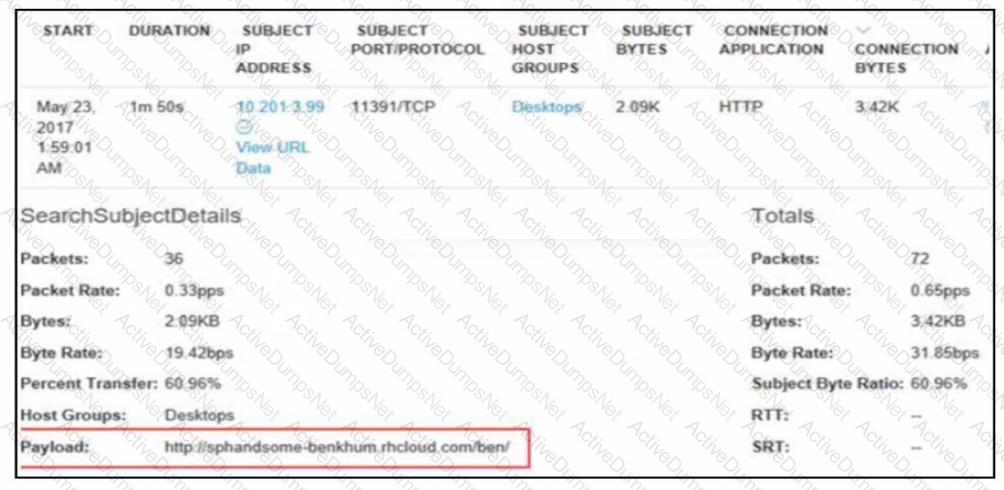
A security analyst receives an alert from Cisco Secure Network Analytics (formerly StealthWatch) with the C2 category. Which information aids the investigation?
A mature SOC notices that several incidents over the past year involved attackers abusing legitimate administrative tools rather than deploying custom malware. Leadership asks the threat hunting team to improve detection coverage in a way that increases attacker cost rather than relying on easily replaceable indicators. Which detection strategy best aligns with this objective?
A security architect is designing a threat model for a multi-tier cloud application that includes public APIs, backend microservices, and an identity provider. The goal is to identify how an attacker could chain multiple weaknesses together to achieve account takeover and data exfiltration. Which threat modeling technique is MOST appropriate?
A SOC team wants to detect lateral movement performed using legitimate administrative tools rather than malware. Which telemetry source provides the MOST reliable visibility for this hunting objective?
Refer to the exhibit.
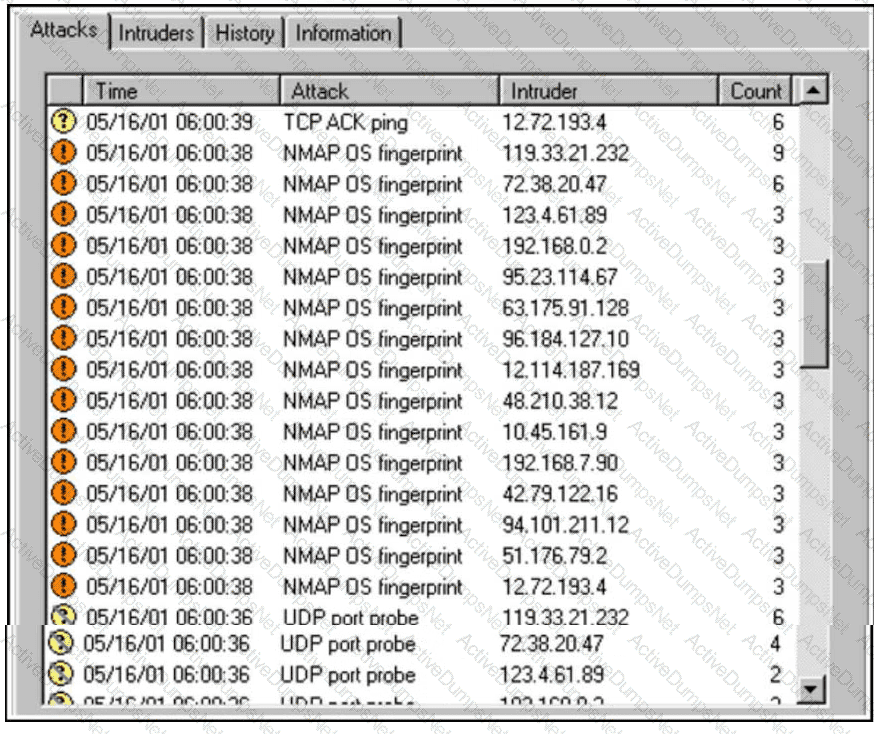
An increase in company traffic is observed by the SOC team. After they investigate the spike, it is concluded that the increase is due to ongoing scanning activity. Further analysis reveals that an adversary used Nmap for OS fingerprinting. Which type of indicators used by the adversary sits highest on the Pyramid of Pain?
Refer to the exhibit.
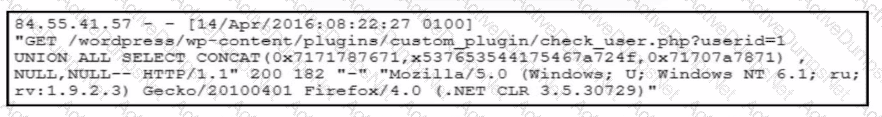
A forensic team must investigate how the company website was defaced. The team isolates the web server, clones the disk, and analyzes the logs. Which technique was used by the attacker initially to access the website?
Refer to the exhibit.

A company recently was breached and decided to improve their security posture going forward. A security assessment was ordered, specifically intended to test weak points exploited during the breach. A security analyst reviews server logs to identify activities related to the aforementioned security assessment. Which entry suggests a delivery method associated with authorized assessment?

Refer to the exhibit. A cybersecurity team receives an alert from its Intrusion Prevention System about multiple file changes to a file server. Before the changes were made, the team detected a successful remote sign-in from a user account to the server. Which type of threat occurred?
A SOC team using Cisco security technologies wants to distinguishIndicators of Attack (IOAs)fromIndicators of Compromise (IOCs)during threat hunting. Which scenario BEST represents an IOA rather than an IOC?
Which hunting technique is MOST effective for detecting stealthy data exfiltration over standard web protocols?
Refer to the exhibit.
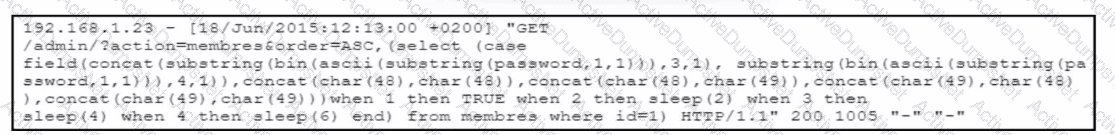
The cybersecurity team at a company detects an ongoing attack directed at the web server that hosts the company website. The team analyzes the logs of the web application firewall and discovers several HTTP requests encoded in Base64. The team decodes the payloads and retrieves the HTTP requests. What did the attackers use to exploit the server?
While investigating multiple incidents, analysts notice that attackers consistently use SMB for lateral movement and avoid PowerShell execution. Why is this observation valuable for attribution?
What is a limitation of automated dynamic malware analysis tools?
A threat hunter usesCisco Secure Endpointto investigate a suspected credential-harvesting attack that does not involve dropping files to disk. Which capability is MOST critical for detecting this activity?
The SOC team receives an alert about a user sign-in from an unusual country. After investigating the SIEM logs, the team confirms the user never signed in from that country. The incident is reported to the IT administrator who resets the user's password. Which threat hunting phase was initially used?
