CIPS L4M5 Commercial Negotiation Exam Practice Test
Commercial Negotiation Questions and Answers
Any commercial negotiation process has only three stakeholders: procurement, budget holders, and users. Is this TRUE?
Which of the following are intangible values created by trust in business relationships? Select TWO that apply.
What letter R in the acronym SMART stands for?
In what circumstances is the bargaining power of suppliers likely to be high, in relation to buyer power? Select the THREE that apply:
Which of the following are stages of a win-win approach to negotiations?
Find out where the interests of both parties align
Design new options, where everyone gets more of what they need
Limit the resources to a fixed number
Insist that the agreement includes subjective regulatory standards
What are the potential sources of conflict between the buyer and supplier? Select TWO that apply.
Understanding supplier's mark-up and margin can provide procurement professional a comprehensive insight into supplier's net profits. Is this statement true?
As a buyer for a large stationery company you have been notified of an upcoming price increase from your provider for paper. When you check the contract you realise that it expired 30 days ago so you are no longer in contract. You realise the supplier can now charge what they like.
You call the supplier and attempt to negotiate over the phone but are unsuccessful. What would be the best thing to do?
Why is the use of power important for integrative commercial negotiations?
Moving negotiations forward when they get stuck on certain issues
Maximising the share of value gains for the negotiator's side
Coercion of the other party into a submissive agreement
Breaking through negotiation barriers related to attitude
A buyer continually states during negotiation that budget constraints limit their concessions. What tactic is being used?
Which of the following is a disadvantage of absorption costing method?
Power is used only in adversarial negotiation situations to secure a ‘win’ outcome against the other side. Is this statement correct?
A buyer is approaching a negotiation where the company is in a low-power negotiating position in relation to the supplier. How can the buyer improve leverage and power with the supplier?
Buyers should have the ability to analyse the costs of their purchases not only for determining their impact to their organisation’s cost but also for the purpose of reducing them during commercial negotiations to contribute to the profitability of their organisation. One way ofanalysing costs is to classify them into direct and indirect costs. Which ONE of the following is an explanation of ‘direct costs’?
Active listening in negotiation includes which of the following activities?
1. Hearing
2. Interpreting
3. Rapport
4. Influence
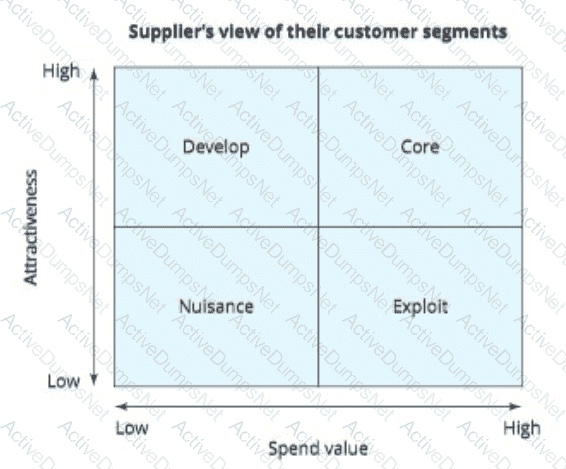
A senior buyer analyses the supply market and he realises that his organisation is treated as Exploit according to supplier's perspective model. What does he need to do?
Which characteristics are likely to feature in a partnership relationship in purchasing?
Close collaboration between supplier and buyer
Focus is on price and delivery only
Sharing of information
One-off commercial transactions
SBL provides contract bathroom furniture and fittings for a wide variety of domestic and commercial clients. To some suppliers, SBL spend claims a large portion of their revenue. But SBL is famous for imposing draconian obligations on these suppliers. Which of the following is most likely to be overarching objective of these suppliers to SBL?
An experienced procurement professional is developing strategies for forthcoming negotiations with her key supplier. To avoid negotiation deadlocks, she identifies the reasons why negotiations could fail. Which of the following are most likely to be reasons for negotiation failures? Select TWO that apply.
Which of the following are macroeconomic factors that may have influence to the commercial negotiation? Select TWO that apply
A public agency opens a tendering process for a road building project that lasts approximately 1 year. They post their requirements on public journal and receive some interests. After conducting due diligence process and selecting the lowest bidder, the project commences. However, the supplier complains that price of material increases because of a shortage of supply, then they demands an 5% uptick in contract value. The agency investigates the increment and sees that there is indeed a fluctuation in prices of supplier's input. They are likely to accept the proposal, but they are also concerned that supplier may demand more. To avoid making another concession with the supplier, which of the following should be a priority action of the agency?
Which of the following are hardball tactics in negotiations? Select TWO that apply.
During a negotiation, Jose Gomez, the salesperson for a strategic supplier, states that his sales director will not approve discounts against initial purchases. However, Jose offers a 5% discount against the aftercare package, which will provide the same monetary saving. Sally Pampas requires both the product and the aftercare package and has an objective to achieve a 5% discount off the purchase price. To achieve a win-win (integrative) negotiation, Sally should:
Which of the following is the most appropriate approach to investors or shareholders who have high level of influence but low interest in the running of business?
Which of the following is considered a weakness of a ‘dealer’ style negotiator?
When developing a negotiation approach, according to recognised theory (for example Mendelow), how should stakeholders with high interest but low power be managed?
A skilled negotiator will use a range of questioning techniques in a negotiation. If they wished to explore options with the other party without making any formal commitment, which type of question style would they use?
Commercial negotiations on price cover various aspects, including pricing arrangements. A buyer may negotiate a fixed-price agreement. Why is a fixed-price agreement advantageous to the buyer?
IHL has been supplying to XYZ Ltd for months. XYZ Ltd procurement manager Diana realises that the IHL's input prices are dropping and this is a good time to re-negotiate the price of the contract. She invites IHL representative to XYZ headquarter to make a bargain on the current price. At the opening stage of the negotiation, Diana requests a 10% reduction in price with an increase in volume purchased.
Is Diana's action appropriate in the opening phase?
Ranjit is a facilities category buyer for a hospital in the UK and is managing an overseas sourcing project for security guard clothing and personal protective equipment. Ranjit is aware that foreign exchange fluctuations can create risk for his organisation and would like to remove this risk. Ranjit has asked the international suppliers to quote in GBP sterling. Will Ranjit’s approach remove the fluctuation risk for the hospital?
Lina Rawlins is a senior buyer working for a medical equipment company. Lina is in charge of the company’s largest supplier account, Great Barrington Gas (GBG), a medical equipment supplier. Recently, GBG's performance has declined, leading to an increasing number of rejected items. Lina is aware of the seriousness of this and has asked GBG to attend an urgent meeting. In the meeting, Lina asked the GBG representative, “Can you tell me exactly what you are doing to ensure quality?" What type of question is Lina asking?
A skilled negotiator will use a range of questioning techniques in a negotiation. If they wished to explore options with the other party without making any formal commitment, which type of question style would they use?
Which of the following are most likely to help buyer become preferred customer in supplier's perspective? Select TWO that apply.
Stalemate is more likely to happen if both parties trade more variables in a commercial negotiation. Is this assumption true?
Which of the following are most likely to turn buying organisation into an unattractive customer in supplier's perspective? Select TWO that apply.
Sunita’s supplier states: “Meeting your needs is meeting my needs because we are in this together.” What type of negotiation is being undertaken?
Which of the following are examples of variable costs?
Building and site rent
Annual insurance premium
Raw materials expenditure
Delivery costs for materials
Colin Smith is preparing for a negotiation with a supplier that provides a chemical for grass fertiliser. Colin has been given an action to secure a commercial deal that achieves his organisation's objective of 'ethical and sustainable procurement.' As part of his negotiation plan, Colin is using the ‘must, intend, like (MIL)’ framework to prepare for the negotiation. Colin would categorise his organisation's objective within the negotiation plan as ...
A breakeven analysis uses which of the following aspects as part of the analysis?
In order to mitigate all risks involved in the negotiation process, the buyer only needs to undertake pre-negotiation research on the supply market and establish a BATNA. Is this a correct suggestion?
A supplier has offered international football tickets to the procurement manager while they are in the middle of a contract negotiation. What should the procurement manager do?
Which of the following are most likely to be the potential cultural differences that can make transactions with an international supplier more problematic that with local suppliers? Select TWO that apply.
Which of the following are microeconomic factors? Select THREE that apply.
Leitax is a consumer electronics firm with headquarters in the US and with a global sales presence. The company maintains seven to nine models in its product portfolio, each of which has multiple SKUs. Product life ranges from fifteen to nine months and is getting shorter. The demand planning and master planning processes at the company were ill-defined. Data relevant to forecasting were usually inaccurate, incomplete, or unavailable and the lack of objectives and monitoring mechanisms for the demand planning process meant that process improvement could not be managed. Support for supply management was equally ill-defined, as master production schedules were sporadic and unreliable and suppliers had learned to mistrust them. Leitax's newly appointed Supply chain director, Jessica realises that the “buy-in” of different functional groups was critical to the improvement of demand planning. She invites relevant stakeholders to a meeting so that they can express their opinions openly. What tactic is Jessica using?
Which of the following are ways of developing rapport when undertaking a negotiation?
A negotiation process ends once the negotiating meeting has finished. Is this statement true?
During a negotiation, a procurement manager suggests that the two companies should split the difference which would benefit both the supplier and buyer. Which persuasion method is she using?
The bargaining power of buyers is likely to be high in relation to suppliers in which of the following situations?
Procurement gets involved in negotiating purchase requisitions only when there is a value analysis to ensure that only value-adding aspects are included. Is this statement true?
A buyer has lost trust in a supplier but wishes to repair the relationship. What is the appropriate first step?
Which of the following is a challenge when calculating absorption costing?
When is an adversarial style of negotiation appropriate?
Which of the following is the most appropriate pricing arrangement in contracts where major inputs are commodities?
There are no commitments in hypothetical questions. Is this statement true?
A procurement manager is considering accepting a fixed price agreement for 12 months with an IT supplier. What are the advantages of fixed price agreements? Select TWO that apply.
Which of the following is the area where two or more negotiating parties may find common ground?
XYZ Ltd is importing goods from overseas. They prefer to pay their supplier in their own currency. Which of the following is a true statement?
One difference between perfect competition and monopolistic competition is that...?
Different types of relationships impact negotiations. Which source of leverage would most support the buyer?
What are the potential sources of conflict between the buyer and supplier? Select TWO that apply.
Which of the following can be prepared before negotiation to achieve an agreement that benefits both parties?
Zone of potential agreement (ZOPA)
Attendee list
Walk-away point
Venue for the talks
An adversarial style of negotiation is appropriate when the buyer has greater bargaining power. In what other situation may the buyer adopt this style?
Which of the following are effective approaches when procurement professionals negotiate with monopoly suppliers?
1. Delaying payment with monopoly suppliers as long as possible to increase bargaining power
2. Setting up stronger BATNA
3. Engaging in the negotiation with a distributive approach
4. Eliminating requirements in the specification that prioritises monopoly suppliers
Which TWO strategies are recognised for achieving a win–lose outcome?
Making the other party lower its resistance point
Making the other party believe this settlement is the best it can achieve
Employing empathy to gain mutual understanding
Using compromise and creativity tactics
Which of the following tactics would be appropriate in an integrative negotiation?
An oil refinery plant imports much of its crude oil from overseas. A procurement manager in the refinery suggests that fixing the crude oil contract price for 36 months would be beneficial for the company. Would this be a right thing to do?
Where a negotiator uses numerical reasoning with facts as part of their negotiation approach, which of the following techniques will they be adopting?
A negotiation meeting commences with the supplier asking the buyer ‘How do you feel about the service you receive from us currently?’ The supplier then asks ‘What do you think about our latest products?’ followed by ‘How do we compare with other suppliers you use?’ The supplier is using which type of questions?
Which of the following are types of questions that are useful in opening and testing phases of a negotiation? Select the TWO that apply.
Which of the following constitutes a key element to developing high-trust supplier relationships?
When is the best time in procurement process in which procurement should get involved so that the cost-saving opportunities are the greatest?
Which of the following are most likely to be macro factors that may influence the balance of power in commercial negotiation? Select THREE that apply.
Community Meal Partners (CMP) is a not-for-profit company that delivers cooked meals to older residents in their homes. CMP uses a fleet of bespoke vans with onboard ovens. In planning the future procurement of the fleet, CMP has conducted a review of the microeconomics of the van supply market and found that the vans are supplied by a monopoly supplier due to patented technology. Which of the following strategies could CMP utilise to optimise its bargaining position with the van supplier?
Which of the following are most likely to be abilities of a person with high emotional intelligence? Select TWO that apply.
Under EU public procurement directives, which of the following are procedures in which there is no commercial negotiation allowed?
Macroeconomics can have an impact on commercial negotiations. Is this statement correct?
Where can we find the data on macroeconomics?
1. From trade journal
2. From supplier's marketing catalogue
3. From stock exchange market
4. From government's statistics
Which of the following are stages within the negotiation process?
Planning and preparation
Arguing and persuasion
Accepting hospitality
Testing and proposing
The only procurement risk inherent in a distributive negotiation approach is the potential loss in the outcome. Is this statement TRUE?
According French and Raven's base model, which of the following are sources of personal power that can be used in commercial negotiation? Select THREE that apply.
Which of the following are the most typical characteristics of integrative approach to negotiation? Select TWO that apply.
Which of the following are sources of power in organisational relationships?
Coercive power
Intruded power
Referent power
Tactical power
How can having a best alternative to a negotiated agreement (BATNA) support the buyer in a negotiation? Select THREE options that apply.
A procurement manager is considering negotiating variable pricing for a contract duration of 12 months. Would this be the right thing to do?
Which of the following is most likely a consequence of falling interest rate?
Which factors give rise to conflict within the procurement negotiation context? Select THREE that apply.
Finding the middle ground between buyer and supplier by moving towards each other's position is a satisfactory way to complete contract negotiations and maintain ongoing relations for future negotiations. Is this statement correct?
A negotiation meeting between a buyer and supplier has taken several hours. Both parties believe the negotiation is starting to reach a close. Before the supplier takes steps to make their closing statements, they are most likely to be doing which of the following?
A procurement manager is preparing for a negotiation with an important supplier. He plans to withhold some crucial information so that his company gains the upper hand in the negotiation. Is this correct when considering using integrative approach to the negotiation?
A procurement manager withholds important information to strengthen negotiating power. Is this appropriate when using an integrative negotiation style?
In a commercial negotiation, a procurement professional believe that the larger the order quantity from buyer, the lower the supplier's average costs. Is this assumption true?
Which of the following is the process enabling the buyer to share with the supplier their purposes and needs to focus on some specific areas such as quality, cost, social and environmental standards, etc in the supplier's bids?
A skilled negotiator will use a range of questioning techniques in a negotiation. If they wished to explore options with the other party without making any formal commitment, which type of question style would they use?
Logibox Ltd is releasing a new range of stackable storage boxes. It has adopted a pricing strategy that aims to sell at a price the consumer is prepared to pay.
Which of the following is it using?
In preparation for holding negotiation meetings with existing suppliers, category manager Stephen would like to appraise the bargaining strength of his organisation. Which of the following are examples of buyer power? Select TWO that apply:
Which best describes features of the recovery phase in a business cycle? Select TWO.
Which of these personal power bases stems from the manager's position in the organisation and the authority that lies in that position?
A negotiation meeting commences with the supplier asking the buyer 'How do you feel about the service you receive from us currently?', followed by 'What do you think about our latest products?' and 'How do we compare with other suppliers you use?'
The supplier is using which type of questions?
Champion Toys (CT) is negotiating a large order of luxury toys with its supplier. CT has identified that lead times, order quantities, and delivery locations are tradeables that could be used in this negotiation. At which negotiation stage should CT introduce these tradeables?
Commercial negotiations on prices cover a range of aspects including pricing arrangements. A buyer may negotiate for a 'fixed price agreement'. Why is a fixed price agreement advantageous to the buyer?
Which of the following are features of a single-sourced type of relationship on the relationship spectrum?
Exclusivity granted in relation to a particular product
The supplier is an oligopoly market structure
The supplier is trusted and collaborative
Framework contracts are used to identify the supplier
Which of the following should be the final step of a negotiation process if both parties cannot reach an agreement?
Two firms negotiating a contract have an adversarial relationship. What type of negotiation would you expect?
Langham Industries is seeking to expand its operations globally. The CEO has asked the procurement department to engage in a macroeconomic analysis for its potential new supply chain to meet organisational objectives and outcomes. Which of the following would be a source of macroeconomic data?
The National Schools Purchasing Forum (NSPF) is a procurement organisation that purchases goods and services on behalf of schools on a national scale. NSPF is close to concluding negotiations in a meeting with Hygienics For All (HFA) for the supply of consumables to school washrooms. Both parties have reached an agreeable position, and NSPF feels it is important that they conclude the negotiation at this point. What type of questions should NSPF ask HFA to achieve this?
Which of the following is the true statement?
Which of the following are tools that help procurement visualise cost breakdowns of products and services purchased from supplier?
1. Spend candlesticks
2. Spend tree
3. Aggregate expenditure model
4. Spend waterfall
A procurement expert has been asked to ensure they consider emotional intelligence in their negotiation strategy. They have agreed to this and have started planning their approach. Which of the following describes emotional intelligence?
A buyer is approaching a negotiation where the company is in a low-power negotiating position in relation to the supplier. How can the buyer improve leverage and power with the supplier?
Consolidate the expenditure from across the organisation to increase the size and value of the requirement
Understand the supplier's costs and margins prior to the negotiation to demonstrate that you know what it costs to produce the product
Take a distributive approach to the negotiation and refuse to make concessions
Limit communication and information sharing with the supplier so as not to give anything away
After studying Thomas-Kilmann conflict resolution model and considering different approaches carefully, the procurement team of XYZ Ltd. decides to adopt an avoiding approach to the upcoming negotiation with one of their suppliers. Which of the following will be the objective of XYZ procurement team in this negotiation?
Where a market consists of a large producer with high power, it is known as …
A supplier’s mark-up on all products is 25%. Supplier's profit margin is...?
In which of the following scenarios could you adopt a distributive-based negotiation approach?
Sally is negotiating with an oversea supplier on the price and payment period. Her company and the supplying organisation are equal in bargaining power. The supplier says that they are investing in new facilities and machinery so the payment period should not be longer than 30 days. Sally knows that her company often pays the suppliers after 45 days from the delivery, but at the moment the company has positive cash flow and it is able to pay immediately. Which of the following should be Sally's concession plan?
In a negotiation for a new contract, the supplier suggests the buyer to shorten payment period from 45 days to 15 days because they are investing in new facilities to expand the supply capacity. The buyer replies that she can only sign off the deal if the payment period is 30 days ormore since it often takes at least 30 days for her company to collect the payment from customers. A permission from senior management is required for this suggestion. In order to ensure that supplier understands the matter, she reiterates it throughout the meeting. Which tactics is she using?
1. Outrageous initial demand
2. Salami slicing
3. Lack of authority
4. Broken record
Mike is a junior buyer who has been working for a manufacturing organisation for two years, specializing in purchasing research. Over this time, he has built good relationships within his team and with other departments. Which of the following sources of power is Mike most likely to possess?
Which of the following is an example of non-verbal communication?
A procurement team has discussed, in advance of a negotiation, what they will do if there is no agreement with the current supplier. They have decided that they will perform the services themselves in-house on a trial basis if no deal is made. Which of the following describes what they have prepared here?

 Chart, table Description automatically generated
Chart, table Description automatically generated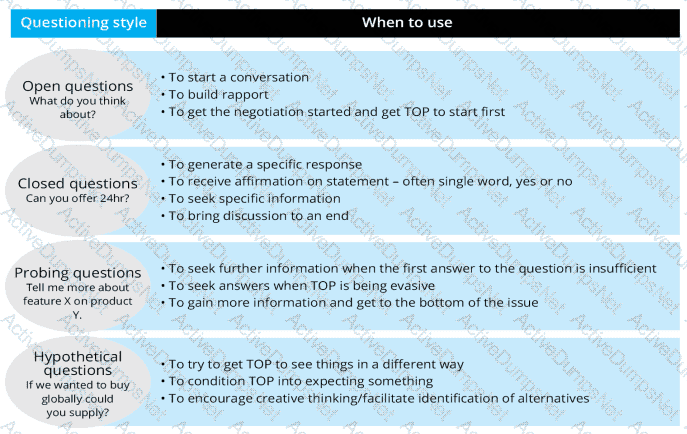 Text Description automatically generated
Text Description automatically generated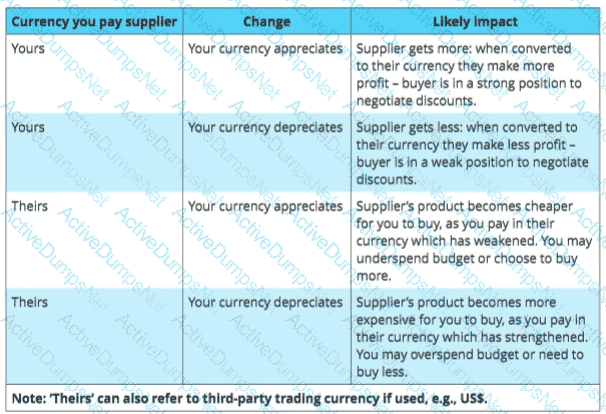 Table Description automatically generated
Table Description automatically generated