CIMA E2 Project and Relationship Management Exam Practice Test
Project and Relationship Management Questions and Answers
What is the main use of the Thomas-Kilmann Conflict Mode Instrument?
The advantages of effective delegation include which THREE of the following?
Because of the severity of actions of the employer an employee takes the decision to resign. This could be classed as which of the following?
Drawbacks of the formal top-down approach to strategy include which THREE of the following?
Third party consultants, Member rotation, Confrontation, and Super-ordinate goals are examples of which of the following?
AW is a newly appointed manager of the accounts department in organisation S. Her appointment has been well received by members of the department who recognise AW as a skilled and well qualified accountant.
However, AW has been frustrated by progress in departmental team meetings which tend to be unruly, unproductive and disorganised. AW recognises a need to improve the effectiveness of the meetings.
Which THREE actions should AW take in order to have more effective meetings?
Based on the Tuckman model of team development, identify the stage when team relationships should start to harmonise and the team agrees on normal work patterns and the best way to tackle the work ahead of them. Job roles and relationships within the team are also agreed.
A, the Project Manager of Team Y, is frustrated at the lack of progress in the implementation of the new IT system. The team has the required skills and working conditions are good.
Which THREE of the following factors can A usefully manipulate to motivate the team to greater effort?
Which of the following statements relate to Handy's role culture?
Select ALL that apply.
In terms of Porter's Diamond model, a DEMAND condition as applied to the brewing industry in Germany would be which of the following?
X is a manufacturing company that has achieved long term success by understanding the structure of its industry, and where necessary changing its strategy in order to achieve improved performance by outperforming its competitors.
Success has depended on the company exploiting the underlying economic factors (such as economies of scale) better than its competitors and maintaining this over time, so achieving sustainable competitive advantage.
Researchers would call this an "outside-in" approach to strategy, with the company choosing a strategy that responds to the challenges and changes posed by the external environment.
Which type of strategy is X adopting?
Which of the following best describes the purpose of Michael Porter's Five Forces model?
Which of the following statements does NOT help characterise Quinn's notion of logical incrementalism?
Kumari is about to start her new roie in the secretarial function of a law firm.
Which of the following is likely to be key part of her job?
Which of the following are influential drivers of outsourcing?
Select ALL that apply.
China, Korea, Japan and Vietnam are high context cultures.
In business relationships in high context cultures, which THREE of the following are typical?
Four orthopaedic surgeons in a busy hospital department have very different work habits. Each has their own team of medical technicians who are used to the surgeons' personal preferences and are very comfortable with their routines; they basically do the same things every day. This way of working has gone on for several years.
When a new administration manager suggested that they train all of the technicians to work with all the surgeons this led to significant resistance from all of the parties involved. The technicians were concerned that they would no longer be able to perform their usual daily tasks.
On the basis of the scenario what would be the main cause of their resistance?
A company is currently at the stage of organising the data which is captured within the big data process. What will they need to do next in order to complete all stages?
Select ALL that apply.
The advantages of embedding the finance function within the business unit include which THREE of the following?
Which THREE of the following are benefits of having strong discipline and grievance procedures in place?
JJ is the project manager implementing a new software system in the customer services department of a large manufacturing organisation.
As part of the new ways of working, JJ is introducing changes to the working hours of the customer services team.
The customer services team is not happy with the changes and is complaining that it does not report to JJ, so why should it have to adapt its working hours.
This is an example of:
The role of competitor analysis, according to Wilson and Gilligan is threefold.
Which of the following does NOT apply?
Which of the following statements are not true based on Stalk, Evans and Schulman's principles of capability-based competition?
Select ALL that apply.
"The ability to exert influence and make someone act according to your own preferences" is the definition of which of the following?
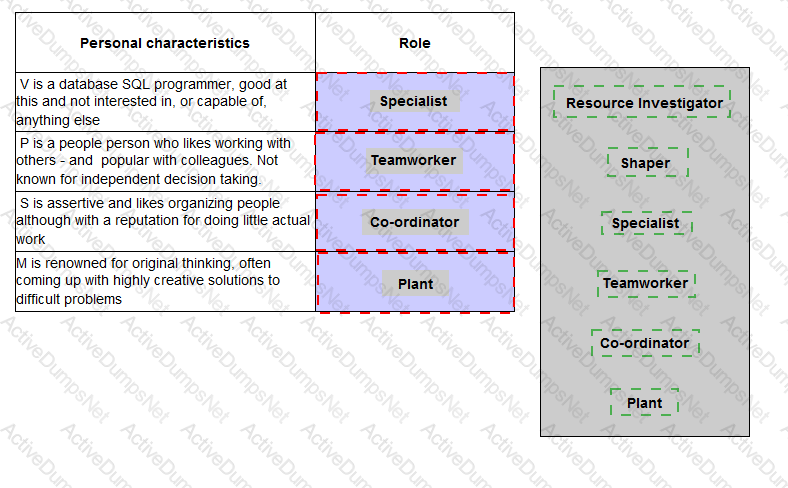
Meredith Belbin carried out some notable research which concluded that successful teams need a good balance of complementary roles and personalities. His work concluded with the definition of nine distinctive roles that people adopt when working together in a team.
Applying this research, place the correct designated Belbin role label against the relevant personal characteristics.
The Thomas-Kilmann model suggests five conflict handling strategies. Which THREE of the following are part of the model?
DD is in charge of a group of twelve people involved in complex work. The group work together amicably and DD's leadership is valued. DD is supported by KK, who often deals with the group on behalf of DD.
Recently KK resigned for family reasons, along with another member of the group who became despondent with change and DD has now recruited new members to the group.
DD has found the group dynamics have changed and various members complain about what they are expected to do.
Which of the following is the least appropriate approach that DD should adopt to ensure the group reverts back to its former cohesiveness?
The means by which competitive advantage might be gained differs, depending on whether a resource based approach or a positioning approach is adopted.
Which of the following options characterises the resource based approach?
Select ALL that apply:
A low cost airline is operating three flights a day between two industrial cities in neighbouring countries. The cities are 300 km apart and the terrain between the two countries is mostly flat grasslands. The two cities are also linked by motorways and a railway line.
At first the airline enjoyed first mover advantage and generated healthy profits for three years. But more recently, the airline is experiencing intense competitive pressures, reduced passenger numbers and lower returns. The airline directors are using Porter's Five Forces framework to analyse the nature and severity of the various competitive forces being experienced.
In the context of this model which of the following forces would be considered as a threat of a substitute product or service?
University Z is about to take on a major project of changing from traditional written examinations to computer-based objective test questons.
Y is the systems manager at the university and has been appointed as the Project Manager. The university is very traditional in its management structure, whereby functional specialists manage each department. However, for this project, Y considers that a matrix structure would be required. The Vice Chancellor is not convinced that a matrix structure would be appropriate.
There are a number of advantages of a matrix structure. Which of the following should Y use in his argument to convince the Vice Chancellor that a matrix structure is appropriate?
Select ALL that apply.
A business manufacturing running trainers is considering exporting to a fast growing Asian market. Using Porter's Five Forces, which of the following statements is most likely to be incorrect?
What event occurs between the second and third stages of Gido and Clement's Project Life Cycle?
X Company's Board of Directors uses its expertise to develop future strategies. The Board defines objectives that need to be achieved and then, through formal proactive planning and careful analysis, it selects the most appropriate means to achieve them.
Which method of strategy formulation is the Board using?
Z is an entrepreneur that has just bought a chain of 10 prestigious restaurants. Z has decided that there is an urgent need for cost savings and plans to install state-of-the-art computer systems to make each restaurant more efficient and less dependent on manual processes. This means that every employee must be trained to operate the new systems and there will be changes in roles and responsibilities.
Z has decided to use the biggest restaurant as a training centre, where the new systems will first be installed. Staff from the other restaurants will then train at the biggest restaurant for a week while new systems are installed at their own restaurant. Z has told the staff that no one will be dismissed because of the changes. The planned opening of a new restaurant will absorb any employees displaced due to the efficiency of the new systems.
Z is concerned about staff resistance. Which approach will be most effective in these circumstances?
Which type of culture, according to Charles Handy, is identified by an individual's tasks being clearly defined and their power coming from their position in the hierarchy?
Barney (1991) identified four criteria necessary for a resource to be classed as unique and thus give competitive advantage. One of these is that it shouldn't be substitutable and another is that it should be rare.
Which TWO of the options below make up the list of four?
What are the disadvantages of a divisional organisational structure? Select ALL that apply.
An organisation facing difficult business conditions as a result of strong competition is aware of the need to improve its performance in bringing new products to market.
The director is aware of conflicting problems the organisation faces in its approach to new product development between the marketing department and the research and development department.
Which term best describes this type of conflict?
According to Belbin the success of a group can depend significantly upon the balance of individual skills and personality types within the group. A well balanced group should contain eight main character types.
Which THREE of the following are character types as identified by Belbin?
KK manufactures mobile phones and it possesses an inimitable resource in the mobile phone market in which it currently competes.
Which of the following best describes this type of resource?
Setting a mission is the first stage of the rational approach to strategy setting. According to David, which THREE of the following are useful areas to include in an organisation's mission statement?
The type of culture typified in an organisation where there is a clear hierarchical structure, formalised rules for decision making and clearly defined jobs is called a
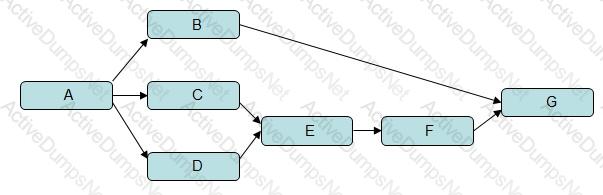
Examine the network diagram shown and identify ALL of the statements below that are true.
There are several techniques that can be used when planning a project. Which of the following best describes a Work Breakdown Structure?
A Company is undertaking a project for the first time and has given the Finance Manager the task of managing the project. He has been advised to use PERT, as it will help him with his Critical Path Analysis (CPA).
What information will the calculation using PERT provide the Finance Manager with to use in his CPA?
The task of C the project manager and his management team is to implement a new examination system. The success of the project depends on the expertise, skill and commitment of both C's project team and that of examiners contracted to produce examination material in a radically new format.
Which of the following leadership styles should C adopt in order to gain maximum commitment from both his project team and from the examiners contracted to produce the new examination material?
James argues that performance appraisal has its roots in three substantiated psychological principles, meaning that people work / learn / achieve more when they are given the opportunities.
Which of the following does NOT apply?
Japanese team working based on the Japanese production model, and widely copied around the world, possesses which THREE of the following characteristics?
An auto company A, has formed a joint venture with another auto company B to incorporate engines produced by company B into its own automobiles.
Which of Ansoff's strategic directions would best describe this strategic move?
Verbal and non-verbal communications often take place at the same time. Which of the following best describes the complementary nature of non-verbal communication?
Many analysts and researchers have written about understanding resistance in order to bring about successful and enduring changes in an organisation.
One writer wrote that "An issue is held in balance by the interaction of two opposing sets of forces - those seeking to promote change (driving forces) and those attempting to maintain the status quo (restraining forces)".
Select this writer.
A company, which is heavily reliant on its IT systems, experiences a critical problem affecting its just-in-time processes. The manager recognises an immediate need to change and upgrade systems, which he knows will meet resistance by some long serving staff.
Which of the following would be the most appropriate method for dealing with the resistance at this time?
Which of the following statements are not true about Gantt Charts, Resource Histograms and Work Breakdown Structures?
Select ALL that apply.
FR Company is undertaking analysis of its competitors. One part of its analysis will investigate its supplier whose products satisfy the same customer needs, but are technically quite different. Which of the following levels of competitors does this relate to?
Stimulating conflict can provide benefits for the organisation. Select ALL of the following that apply.
Which of the following is CIMA's definition of strategy?
A company displaying creativity in its workforce, and an ability to react to the dynamic environment in which it operates, is most likely to avoid which of the approaches to strategy formulation listed below?
P is a chartered management accountant working for a large project engineering company. P's functional superior is the Chief Management Accountant.
However for about two thirds of the time available, P is seconded to work with various project teams on a concurrent basis under a matrix organisation structure. This has turned out to be a demanding job role for P, with a number of disadvantages.
Select ALL the disadvantages that apply.
A Company achieves its competitive advantage by adopting a positioning view to strategy setting.
Which TWO of the technical models below are most suited to this approach?
The ability to negotiate is an important management skill. Which approach to negotiation is less likely to result in future further conflict?
While initiating a project to relocate to a larger site, a company looked at how the project proposal fits with the current set up of the business. The premises are only 20 miles away and it is feasible that the current staff would travel to the new factory to work.
As part of the feasibility considerations, this represents which type of feasibility?
Porter's Value Chain model is divided into two main categories. From the choices below identify the TWO categories:
Various methods of communication are available, including face to face, by telephone or online.
Which THREE of the following interactions are best conducted face to face?