ASCP ASCP-MLT MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) Exam Practice Test
MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) Questions and Answers
The anticoagulant present in a light-blue stopper tube is:
A person classified as an ultrarapid metabolizer (UM) has a polymorphism that enhances the catabolic activity of the enzyme. This means that a UM would need more of the drug to achieve a 'normal' level since he/she is rapidly metabolizing the drug.
Chem
In therapeutic drug monitoring, a person who is classified as an ultrarapid metabolizer (UM) would need __________ of a drug metabolized by that enzyme.
The end of the initial phase of HH treatment is considered when the serum ferritin decreases to between 20 and 50 ng/mL.
What is a typical finding for determining the endpoint for the initial or iron-depletion phase of treatment for hereditary hemochromatosis (HH)?
Convert the following temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius
102 degrees F
In which disorder do neonates demonstrate the presence of Bart's hemoglobin that changes to beta chain tetramers in adults?
Which of the following legislation was developed to protect the privacy of all patient information in the health care?
The Westgard multi-rule 22S describes the scenario where two consecutive data points fall outside +2SD or -2SD. If this occurs, then the run must be rejected. This situation is most likely caused by a systematic error.
Which of the following describes the Westgard multi-rule 22S?
Waived tests are those considered to have an insignificant risk of erroneous results. Which of the following is NOT an example of a waived test?
Mode is defined as the number that occurs most frequently in a set of numbers.
The value that occurs most frequently in a set of results or values would be termed:
The part of the microscope that control the amount of light entering the specimen much like the iris of your eye controls light is called the iris _______________.
Anti-A, anti-P, anti-Leb, and anti-M all react best at 4o C as they are predominantly IgM antibodies. Other antibody group choices above include IgG antibodies such as anti-K, anti-s, anti-S, and anti-Fya, anti-Lub, etc. which react best at 37o C.
Which of the following groups of antibodies generally reacts most strongly at 4o C:
Gram positive organisms resist decolorization by ethyl alcohol. The large crystal violet-iodine complex is not able to penetrate the peptidoglycan layer, and is trapped within the cell in gram-positive organisms. Conversely, the outer membrane of gram-negative organisms is degraded and the thinner peptidoglycan layer of gram-negative cells is unable to retain the crystal violet-iodine complex and the color is lost.
What is the purpose of using ethyl alcohol or acetone in the gram stain procedure:
Cryoglobulin testing can be used to:
Delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions (DHTR) usually occur within which time period?
Hemolytic anemia, myelodysplasia, and liver disease may each fit this peripheral blood picture. Each of these conditions can display peripheral blood macrocytosis. It is easy to observe the overall larger size of the red blood cells in this image compared to the normal lymphocyte also present.
When macrocytes are present, they should be examined for their shape (round vs. oval), the hemoglobin content (central pallor), and whether or not there are any inclusions present in the cell.
Iron deficiency would not be the correct answer in this case, since this condition is associated with microcytosis instead.
The complete blood count was obtained from a patient recently admitted to the emergency room. The red blood cell indices obtained revealed an MCV of 115 femtoliters (fL) (normal range 80 - 90 fL). The patient met the criteria for a peripheral blood smear examination. A representative field is shown on the right.
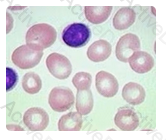
Which of the following conditions may be indicated by the results seen on this peripheral blood smear?
Normal pH of semen must be a value equal to or greater than which of the following?
The morphologic characteristic(s) associated with the Chediak-Higashi syndrome is (are):
Standard precautions should be followed:
Leptin signals the hypothalamus that there are changes in fat stores.
Resistin increases insulin resistance and enhances adhesion molecules present on endothelial cells.
IL-6 responds to tissue injury. IL-6 increases insulin resistance by inhibiting insulin receptor signal transduction in liver cells. It also increases other inflammatory cytokines, interleukin-1 (IL-1) and TNF-a, and stimulates the liver to produce C-reactive protein (CRP).
Adipose tissue and liver cells produce angiotensinogen, a precursor of angiotensin II. Besides increasing blood pressure, angiotensin II may stimulate adipose cell formation and thus increase adipose mass.
Which one of the following adipocyte products is an important messenger in metabolism, signaling the hypothalamus that there are changes in fat stores?
The antiglobulin test may be omitted from the serological crossmatch if the patient's antibody screen is negative and there is no history of detection of unexpected antibodies.
Blood Bank
What must be true for the antiglobulin phase of the serologic crossmatch to be omitted (i.e., immediate spin crossmatch is done)? Please select all correct answers
True Statements:
Urine should be well mixed prior to dipping the reagent strip. Prolonged immersion may wash out test reagents.
False Statements:
Urine should be centrifuged prior to dipping the reagent strip. When visually reading the reagent strip, all results can be read immediately after dipping the strip in the urine specimen.
Which of the following statements are TRUE regarding the reagent strip test procedure? (Choose ALL of the correct answers)
Convert the following temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit
8 degrees C
Microcontainer collection order of draw differs from regular peripheral blood collection order of draw. When performing a capillary draw, the lavender top container is obtained first. This decreases the possibility of clots in the container which would invalidate the results of the complete blood count test.
After the lavender is drawn, other containers with anticoagulants would be collected, and containers without anticoagulants would be collected last.
A phlebotomist must perform a skin puncture to obtain capillary specimens for a complete blood count (CBC), a plasma-based chemistry test, and a serum-based immunology test. The microcollection containers that will be used are lavender top containing EDTA anticoagulant, green top containing heparin anticoagulant, and gold top containing no anticoagulant. Which microcollection container should be collected first?
Provide the equivalent measurement for 75 milligrams.
Question options:
Where can one find guidance on the minimum performance standards for clinical laboratories?
First, determine the number of WBC's from the hemocytometer as follows:
WBC count = (dilution ratio x # of cells counted x 10) / (# mm2 area counted)
Then: WBC count = (20 x 100 x 10) / (8) = 2500 WBC/mm3 (or 2500 WBC/uL or 2.5 x 103 WBC/uL)
Next, to find the WBC count per liter, multiply the WBC count/uL by the number of uL/L (there are 106 uL/L)
So: (2.5 x 103 WBC/uL) x (106 uL/L) = 2.5 x 109 WBC/L
Hematology
A 1:20 dilution is made for a manual WBC count. The four corner squares on both sides of a hemocytometer are counted. A TOTAL of 100 cells are counted in that area. What is the white blood cell count in terms of a liter (? x 10^9/L)?
The newest direction for laboratory testing procedures is
Platelets do not circulate in inactivated, spiny forms. The spiny, sticky form of the platelet is initiated once the platelets become activated in response to blood vessel damage.
Which of the following is not true in terms of platelet characteristics?
The FTA-ABS is used to confirm that a positive non-treponemal test like RPR is not the result of a biological false positive, which occur in about 1 to 10 percent of the population.
A positive RPR test and a negative FTA-ABS test is most likely the result of:
Which of the following organizations has developed standards to maintain the performance of the clinical laboratory at the highest standards for quality care?
Medical Technology is the profession concerned with performing laboratory analyses
The most likely causes of delayed hemolytic reactions are Kidd system antibodies. Both jka and jkb are often responsible for delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions.
Blood Bank
Delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions are usually caused by antibodies directed against what blood group system?
Heinz bodies occur as the result of denaturation and precipitation of hemoglobin, and are often attached to the red cell membrane. They require staining with crystal violet or methyl violet to be visible. They may be seen in thalassemia, with unstable hemoglobins, or during a hemolytic episode in G6PD deficiency.
Hematology
The intracellular precipitates seen in the RBCs in this illustration is termed:
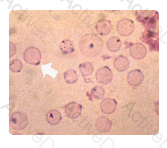
A positive RPR test and a negative FTA-ABS test is most likely the result of:
Although any one of the answers might be considered correct, a report of gram-positive cocci in chains provides sufficient information without going beyond what the observation might allow. In off-the record conversation with the physician, a technologist might divulge that the picture is consistent with Streptococcus; however, enterococci may have a similar Gram stain appearance, potentially leading to the wrong choice of empiric antibiotic agents.
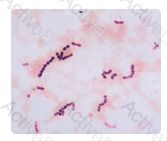
The image shows the Gram stain prepared from the positive blood culture. What is the MOST appropriate report?
The disc diffusion method for antibiotic susceptibility testing is the Kirby-Bauer method. The agar used for this procedure is Meuller-Hinton.
Which of the following media is commonly used when performing the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion?
In primary responses, the major class of antibody produced is IgM whereas in the secondary response, as mentioned in this question, it is IgG. IgG is present in the highest quantities compared to all other antibody classes and is the only antibody able to cross the placental barrier.
Which of the following antibody types is chiefly seen in the secondary immune response:
The recommended disinfectant for blood and body fluid contamination is:
Myoglobin release is strongly associated with muscle damage; therfore, it would most closely match a diagnosis of massive muscle trauma in this question.
Myoglobinuria is MOST likely to be noted in urine specimens from patients with which of the following disorders?
A combination of (nonselective) 5% sheep blood and (selective) MacConkey agars is sufficient for the recovery of the pathogenic microorganisms that are most commonly encountered in urinary tract infections (UTIs). MacConkey is the selective culture medium that is most commonly used to inhibit growth of gram-positive organisms (most UTIs are caused by gram-negative organisms).
Eosin methylene blue (EMB) is a selective agar that also inhibits the growth of gram-positive organisms. Therefore, using only a combination of MacConkey and EMB would prevent the detection of a gram-positive organism, if this were the cause of the infection.
Chocolate agar or other enriched media may be needed in addition to blood and MacConkey if a more fastidious organism is suspected.
Thayer-Martin would be used specifically for recovery of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Thayer-Martin (or Modified Thayer-Martin) inhibits other microorganisms and allows the selective recovery of both N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis.
Microbiology
Which culture agar combinations below will usually be sufficient for MOST routine urine culture investigations?
Neutrophils reside in the peripheral circulation for only 7-8 hours ( approx. 7.5 hours) before entering the tissues and body cavities. This process is called diapedesis.
Hematology
How long are healthy neutrophils expected to reside in the peripheral blood of an adult?
Microbiology
Matching: The detection of a distinct odor is often helpful in the presumptive identification of bacterial culture isolates. Match each of the odors listed with its corresponding bacterial species name.
1. Streptococcus anginosus (milleri)
2. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3. Eikenella corrodens
4. Alcaligenes faecalis
To make a 1 : 10 dilution, 270 µL of diluent should be added to 30 µL of sample, .
A spinal fluid that is slightly hazy is briefly examined microscopically. The technologist performing the count decides to make a 1:10 dilution using 30 µL of sample. What volume of diluent should be used?
The cell shown in this image is a myelocyte. Myelocytes typically have an eccentric nucleus with cytoplasm similar to a mature neutrophils with a slightly bluer tint due to the cell's immaturity.
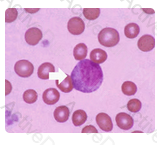
Myelocytes have both primary and secondary granules present in the cytoplasm. The nucleus is less mature and therefore has a loose chromatin clumping pattern.
Identify the cell in this illustration indicated by the arrow:
Gating sets up boundaries around a subset of data points to segregate those events for analysis.
Gating the proper cell population is crucial for flow cytometric analysis. The CD marker information presented on the histogram data is only representative of the cells inside the gate.
When analyzing the raw data of a sample on the flow cytometer, CD marker information on the histograms represents data inside the _____ population.
21 CFR 606.65 states, "Supplies and reagents shall be used in a manner consistent with instructions provided by the manufacturer."
The correct answer is A. The reagents must be used according to the manufacturer's instructions for use. If the instructions say one or two drops may be used and the facility procedures also allow one or two drops, then there is no problem with the staff members choosing to use two drops.
While equipment must be calibrated, it does not generally influence the number of drops used.
Staff members often ask co-workers and colleagues from other facilities how to perform tasks, but it is the manufacturer's instructions for the operation of equipment and the use of reagents that must be followed.
A laboratory employee who is performing an internal audit of routine ABO and Rh typing procedures notes that a technologist places two drops of Anti-D in a tube, centrifuges the tube for 20 seconds, and reads the reaction using a magnifying mirror. When questioned about the procedure, the technologist indicates that most staff use two drops of Anti-D reagent because the reactions are stronger with two drops. In addition to reviewing the facility procedure manual, what should be done to ensure regulatory compliance?
The intended response is Vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies. Each of these conditions lead to a megaloblastic production of the red blood cells in the bone marrow. Since vitamin B12 and folate are needed in order to produce a synchronous development of the nucleus with the cytoplasm in hematologic cells, oval-macrocytosis often occurs if these nutrients are not in adequate supply within the body. This can also affect neutrophils, allowing for the characteristic hypersegmented nucleus.
The photographic field contains several oval-macrocytes and a hypersegmented neutrophil with greater than 5 nuclear segments. Oval macrocytes are most commonly associated with pernicious anemia and malabsorption syndromes leading to vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiencies.
Clinical information relating to chronic infection, aplastic anemia, and other hematologic maligancies provide the context for the presence of the oval macrocyte.
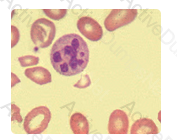
Macrocytic erythrocytes and hypersegmented neutrophils are not present in thalassemias or in Pelger-Huet anomaly (hyposegmented neutrophils).
Conditions suggested by the macrocytes and the neutrophil in the photograph to the right include which of the following?
The agency within Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) responsible for implementing CLIA'88 is:
Enterococcus spp. are bile esculin positive and grow in 6.5% NaCl. If they grow on the 6 µg/mL vancomycin screen agar as this isolate does, it is vancomycin resistant. If there is no growth on the 6 µg/mL vancomycin screen agar, the isolate is susceptible to vancomycin. Streptococcus Group D, not Enterococcus will not grow in the 6.5% NaCl and should not be tested for vancomycin resistance. Staphylococcus epidermidis is catalase positive.

The images below represent a gram-positive, catalase-negative, non-motile coccus inoculated to bile esculin agar, 6.5% NaCl broth and to 6 µg/mL of vancomycin in Mueller Hinton agar. It should be reported as:
White top tubes are used for blood cultures.
Question options:
A zone of inhibition is the area around an antibiotic-infused paper disk that does not show any bacterial growth. The antibiotic impregnated on the disk will diffuse into the agar in the area surrounding the disk. If the bacteria are sensitive to the antibiotic, they cannot grow near the disk. The size of the zone is proportional to how sensitive the organism is. If the organism is resistant to the antibiotic, it will grow very closely to the disk.
The size of the zone of suppressed growth on a sensitivity plate using sensitivity disks is referred to as the zone of:
An employer who fails to provide sufficient personal protective equipment (PPE) for employees may be fined by the:
Ferritin and hemosiderin are considered storage forms of iron.
Which substance(s) is/are considered iron storage compounds?
Which of the following CD markers is NOT present on a normal mature T cell?
The normal pH of blood is 7.40. In order for most metabolic processes to take place, the pH must remain within a narrow range close to this value. The range is usually defined in adults as 7.35-7.45. If blood pH falls below 7.35, the blood becomes too acidic (acidosis). If blood rises above 7.45, the blood is too alkaline (alkalosis).
As blood pH decreases, the kidneys will retain bicarbonate (HCO3-) from the glomerular filtrate; therefore, bicarbonate is increased. However, in this case, the increased HCO3- could not compensate for the markedly elevated pCO2 (the respiratory component) and the condition that results is uncompensated respiratory acidosis.
What condition is indicated by the following blood gas results: Bicarbonate = 32 mmol/L (Normal = 22 - 26 mmol/L); pCO2 = 65 mm Hg (Normal = 35 - 45 mmHg); pH = 7.28 (normal = 7.35 - 7.45)
Fatty casts contain refractile oval fat bodies or free fat droplets. They are derived from renal tubular cells, and may be seen in nephrotic syndrome.
Identify the urine sediment element:
A patient is admitted to the hospital with acute chest pain, but which of the following enzymes will be elevated FIRST if the patient had an MI?
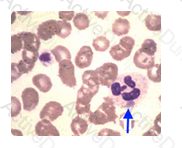
May-Hegglin anomaly is a rare autosomal dominant condition in which patients are at risk for bleeding and infections. It is characterized by the presence of large Dohle body like inclusions within neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes.
The WBC anomaly indicated by the arrow in this illustration is:
Listeria are non-capsulated, non-acid-fast, ß-hemolytic, gram-positive bacilli that have a characteristic tumbling motility. They are found primarily in the environment and in the human GI tract. Since L. monocytogenes multiplies intracellularly, control of listeriosis requires cell-mediated immunity; thus, immunocompromised patients (such as newborns) are at high risk.
Which bacterial species is a common agent of neonatal bacteremia?
Healthcare workers that worked closely with patient specimens were at an increased risk of contracting which viral infection before a vaccine was developed?
First, the RBC indices must be calculated. The MCV ((Hct/RBC) x 10) = 71 fL. Since the reference range for the MCV is 80-100 fL, this anemia would be classified as microcytic. The MCH ((Hgb/RBC) x 10) = 19.3 pg. Since the reference range for the MCH is 27-33 pg, this would be considered hypochromic. Finally, the MCHC ((Hgb/Hct) X 100) = 27%. Since the normal range for the MCHC is 33%-36%, this would indicate hypochromia which correlates with the MCH findings. The correct answer is therefore microcytic, hypochromic anemia.
A patient is admitted to the emergency room with lethargy and pallor. The CBC results are as follows:
RBC = 4.1 x 1012/L
Hemoglobin = 7.9 g/cL
Hematocrit = 29%
How would you classify this anemia?
In DIC, or disseminated intravascular coagulation, the prothrombin time is increased due to the consumption of the coagulation factors due to the tiny clots forming throughout the vasculature. This is also the reason that the fibrinogen levels and platelet levels are decreased. Finally FDP, or fibrin degredation products, are increased due to the formation and subsequent dissolving of many tiny clots in the vasculature. The FDPs are the pieces of fibrin that are left after the fibrinolytic processes take place.
Which of the following laboratory results would be seen in a patient with acute Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)?
Chemistry
Estrogen and progesterone markers are most commonly used to provide prognostic information about:
Molarity x Molecular Weight x Volume = Grams
Molecular Weight (aka Formula Weight) =
2(1) + 32 + 4(16) = 98
So, 4 x 98 x 0.2L = 78.4g
What weight of H2SO4 is contained in 200 ml of a 4 molar H2SO4 solution? (Atomic weight: H= 1; S = 32; 0 = 16)
hs-CRP is a more sensitive version of the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, a test that has been used for many years to assess inflammation in settings such as lupus, transplantation, infection, etc.
Which of the following cardiovascular risk markers is a more sensitive version of a test that is used to assess inflammation?
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a structured study that determines the underlying causes of adverse events. RCA focuses on systems, processes, and common causes that were involved in the adverse event. It then determines ways to prevent recurrence by identifying potential improvements in systems and processes that should decrease the likelihood of repeating the event.
Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) is used to evaluate a process prior to its implementation. Its purpose is to identify ways in which a process might possibly fail with the goal being to eliminate or reduce the likelihood of such a failure.
Monitoring quality indicators is important in the maintenance of quality health care. Quality indicators should be identified to prevent medical errors from occurring or to prevent the recurrence of a quality issue. However, it is not the method that is used to evaluate an adverse event after it has occurred.
A medical record audit may be a part of a root cause analysis.
A medical event occurs that results in serious injury to a patient. All systems, processes, and common causes that were involved in the adverse event should be evaluated. A method that can be implemented to effectively study the underlying causes is known as:
In order to perform a venipuncture on a newly admitted hospital patient, a phlebotomist needs to
Which immune elements are involved in a POSITIVE TB skin test?
What has happened in a titer, if tubes #5-7 show a stronger reaction than tubes #1-4?
The characteristic that distinguishes vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis from other Enterococcus species is their lack of motility.
Enterococci are all catalase-negative. Growth on bile esculin agar and in 6.5% salt broth are two characteristics that have commonly been used to identify Enterococcus to the genus level. A positive esculin in combination with a positive PYR reaction is another approach to presumptive identification.
Which one of these characteristics distinguishes vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis from other Enterococcus species?
If all newborns were tested, many positive DATs due to ABO incompatibility would be detected that are of no clinical significance.
Although many laboratories test infants born to group O Rh positive females due to the higher risk of ABO HDFN when the mother is group O, testing such infants is optional provided there is appropriate monitoring and follow-up for hyperbilirubinemia.
Blood Bank
Not performing direct antiglobulin tests (DATs) on newborns born to group O Rh positive mothers is acceptable good practice, providing there is appropriate surveillance and follow-up to detect hyperbilirubinemia.
Which of the following is NOT part of the stand or framework of the microscope?
Though automated extraction machines have many benefits over manual methods the costs are high and generally require a high throughput of samples in order to justify the costs.
Automated extraction has many benefits over the traditional manual methods. The most important benefit is that the nucleic acid isolated is constantly consistent. There is a reduced amount of manipulation with dramatically decreases the chance of cross contamination. Also, automated extraction machines are considered moderate complexity and can be performed by a wider variety of laboratory professionals.
All of the following are considered benefits of automated isolation and extraction equipment EXCEPT:
The most important purpose of a requisition form is:
Question options:
During primary hypothyroidism, where a defect in the thryoid gland is producing low levels of T3 and T4, the TSH level is increased. TSH is released in elevated quantities in an attempt to stimulate the thryoid to produce more T3 and T4 as part of a feedback mechanism.
Serum TSH levels five-times the upper limit of normal in the presence of a low T4 and low T3 uptake could mean which of the following:
Interferon gamma serves various purposes in immunologic response, including the promotion of natural killer cell activity as well as decreased viral replication by using enzymes to decrease protein replication, both viral or host, inside of the cell.
The lymphokine most important for increased natural killer cell activity and decreased viral replication in cells is:
The laboratory is under the direction of a:
There are many causes of CSF lymphocytosis. Lymphocytosis is seen in viral, fungal, and tuberculous infections, although a predominance of neutrophils may be present in the early stages of these infections. Lumbar puncture to obtain CSF samples is often contraindicated in those with a suspected brain abscess.
CSF lymphocytosis is associated with all of the following except:
The correct answer for this question is 1300 mg/dL. The laboratorian performed a 1:4 dilution by adding 0.25 mL (or 250 microliters) of patient sample to 750 microliters of diluent. This creates a total volume of 1000 microliters. So, the patient sample is 250 microliters of the 1000 microliter mixed sample, or a ratio of 1:4. Therefore, the result given by the chemistry analyzer must be multiplied by a dilution factor of 4. 325 mg/dL x 4 = 1300 mg/dL.
After experiencing extreme fatigue and polyuria, a patient's basic metabolic panel is analyzed in the laboratory. The result of the glucose is too high for the instrument to read. The laboratorian performs a dilution using 0.25 mL of patient sample to 750 microliters of diluent. The result now reads 325 mg/dL. How should the techologist report this patient's glucose result?
Parathyroid hormone regulates serum calcium by acting on bone, kidney, and intestines while regulating phosphate by stimulating the intestines and the kidneys, enhancing absorption and reabsorption respectively.
Chem
The parathyroid hormone is important in the regulation of:
What amount of absorbent material must be included between the primary receptacle and secondary packaging for either a category A or category B liquid specimen?
Small, dense LDL is most likely to interact with arterial walls, leading to deposition of cholesterol, and initiating or worsening atherosclerosis. Small, dense LDL is associated with more than a three-fold increase in the risk of coronary heart disease.
Large, buoyant LDL is less atherogenic than small, dense LDL.
The LDL phenotype A is normal. It is the so called 'B' pattern that is associated with increased risk.
Which of the following is most likely to interact with arterial walls, leading to deposition of cholesterol, and initiating or worsening atherosclerosis?
Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins, or TSI's, are IgG antibodies that can bind to thyrotropin (TSH) receptors on the thyroid gland. TSIs mimic the action of TSH, causing excess secretion of thyroxine and triiodothyronine. The TSI level is abnormally high in persons with hyperthyroidism due to Graves' disease.
Which of the following is an autoantibody that binds to TSH receptor sites on thyroid cell membranes preventing thyroid-stimulating hormone binding?
Which of the following is most likely to interact with arterial walls, leading to deposition of cholesterol, and initiating or worsening atherosclerosis?
Entamoeba gingivalis resembles Entamoeba histolytica both in size and in nuclear characteristics. Entamoeba gingivalis may contain numerous cytoplasmic inclusions such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and bacteria.
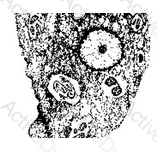
I reside in the mouth where I measure approximately 17 micro meters.
