ARDMS AE-Adult-Echocardiography AE Adult Echocardiography Examination Exam Practice Test
Total 137 questions
AE Adult Echocardiography Examination Questions and Answers
Which is an abnormal response to a stress echocardiogram?
What is the incidental finding seen by color Doppler in this four-chamber view of a patient with left atrial enlargement?
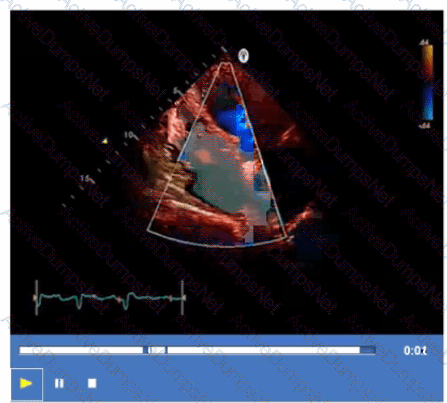
Which adjustment will improve the frame rate?
In patients with interrupted aortic arch, which structure allows Wood to flow into the descending aorta?
Which of the following does the pulmonary capillary wedge pressure estimate?
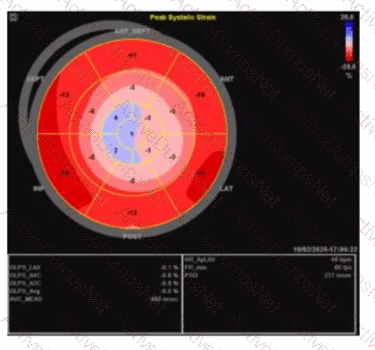
Which pathology is consistent with the left ventricular strain pattern shown in this image?
Which view is best used to evaluate a bicuspid aortic valve?
Which finding is associated with coarctation of the aorta?
Which type of valvular lesion most commonly requires further evaluation with a non-imaging transducer?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle does the left ventricular filling pressure equalize with left atrial pressure?
Which finding is most consistent with this M-mode image?
Which of the following occurs during the strain phase of the Valsalva maneuver?
A continuous flow murmur is most likely due to which abnormality?
Which of the following are key features of an unrepaired tetralogy of Fallot?
Which finding is associated with partial anomalous venous return?
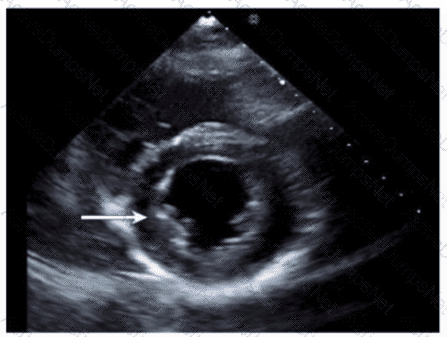
Which wall is indicated by the arrow on this image?
What potential source of error is the greatest when calculating the aortic valve area by the continuity equation?
What is the direction of the mitral regurgitant jet in this video clip?
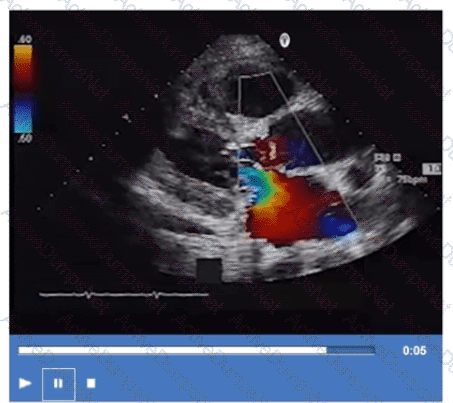
Which next step is appropriate after obtaining the Doppler signal in this image?
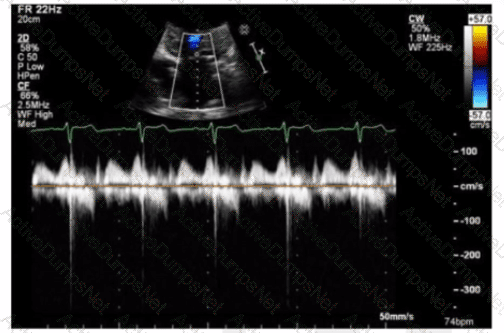
Which finding does peak mitral valve regurgitant Doppler velocity reflect?
Which congenital abnormality is most consistent with the findings in this video?
Which procedure is most appropriate for evaluation of an atrial septal defect in the presence of an atrial septal aneurysm?
What is the route of ventricular depolarization?
Which method is appropriate for measuring the left atrial diameter in parasternal long axis?
Which patient body positioning and respiration technique is optimal for obtaining the subcostal view?
How must the sonographer angle the transducer from the apical four-chamber view in order to visualize the aortic valve in the apical five-chamber view?
Which finding is shown in this image?
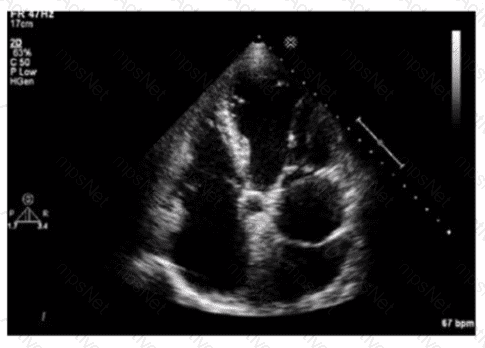
Which condition is most likely suggested by an apically sparing "cherry on top" left ventricular strain pattern?
Which view is best for assessing atrial situs in the presence of congenital heart disease?
Which view best demonstrates a wall thickening abnormality of the apical lateral segment?
Which maneuver aids in uncovering potential diastolic dysfunction while performing pulsed wave Doppler of the mitral valve?
Which adjustment is most likely to improve image quality from the suprasternal long axis window?
A patient with a ventricular septal defect, an atrial septal defect, and a cleft mitral valve is likely to have which abnormality?
A "dropout" or loss of echoes from structures posterior to a calcified mitral annulus results in which artifact?
Which of the following measurements is required for calculating the Qp/Qs ratio?
What is a normal response to dobutamine stress testing?
What minimum number of poorly-visualized contiguous left ventricular (i_V) regional wall segments indicate the use of contrast agents for LV endocardial border definition?
Which diagnosis is most likely confirmed by echocardiography in a 65-year-old female presenting with new onset chest pain associated with ST segment elevation on the electrocardiogram and angiographically normal coronary artenes?
Identify the right pulmonary artery.
Using your mouse, place the cursor on the appropriate region of the image and then left click the mouse button to indicate your selection.

Which mitral regurgitation jet direction is most consistent with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy?
Which type of defect can be seen in this video clip?

Which anatomic structure is represented by the arrow on this image?
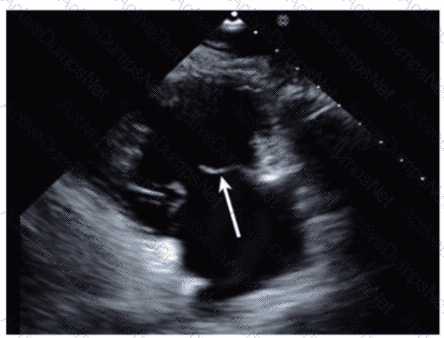
Total 137 questions
